Ballistic missiles have been studied as part of physics for centuries. The basic mechanics in gravitational fields like on earth are well known. Longer reach intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM) have been built by several countries for defensive or offensive purposes. China had demonstrated to master the science and technology of rockets since its latest launch of a ICBM in 1980. In 2024-9 China has demonstrated again, it is still capable to launch such missiles with long distance range (Japan Times 2024-9-25). This is both a technological task, but much more a geopolitical issue as a reminder to be taken seriously on the international political arena currently. Technological capabilities and capacities have regained geopolitical strategic importance as attempts to shift the global balance of power, which is undergoing multiple challenges or even changes. Flagging technological options is not only important to demonstrate own military strength, but to present a country as a potential strategic partner of global reach. Window dressing using weapons is much more oriented towards other countries (buyers of weapons mainly) than of relevance for Chinese society. Strategic alliances seek strategic partners. China is likely to receive more attention in the 21st century than before.
(Image: extrait de Gustave Courbet: La vague, 1870, Berlin SPK)
Instability
In political science the stability- instability paradox is much discussed (paper with game-theoretic analyses). The reliance on nuclear weapons, supposed to enhance stability in the world order, is rather driving the instability making conventional wars even more likely. Michael Beckley argues that containment of China’s expansionary policies is needed to avoid even more disastrous confrontations (Foreign Affairs, 2023 Nr.5).
Different from the German cold war doctrine “Wandel durch Annäherung” Beckley argues that commerce has not brought US and China closer together, but it is actually driving them further apart. After decades of trade imbalances with China the economic power of China can be felt as overwhelming. But there are multiple risks to its economic model and strategic interests to secure raw materials from across the world. Aging of China is another economic and social fallacy difficult to overcome with short-term measures.
We are about to witness another couple, triangular or more relationship to establish as “enduring rivals”. This may last for centuries rather than decades, although the French- German couple has managed quite successfully to turn such rivalry into an “entente” relationship of importance to the whole European continent. The shift in emphasis of US foreign policy is going to be significant. Containment with Russia has worked, so why should it not work with China as well. The likely answer is demographics again. The size of the internal market of China is sufficiently large to continue a splendid isolation after heavy one-sides trading is over. State control of the internet and social scoring of the population is also a powerful tool to suppress the formation of free will and independent opinions. After all, instability in external relations might even be used to ensure internal stability. Such strategies are common to all political systems. The stability- instability paradox is staying with us and this is rather stable even if the discussion changes continents. (Image: Comical battlefield Map 1854, by Berendsohn shown at Waterloo, Museum 2018) 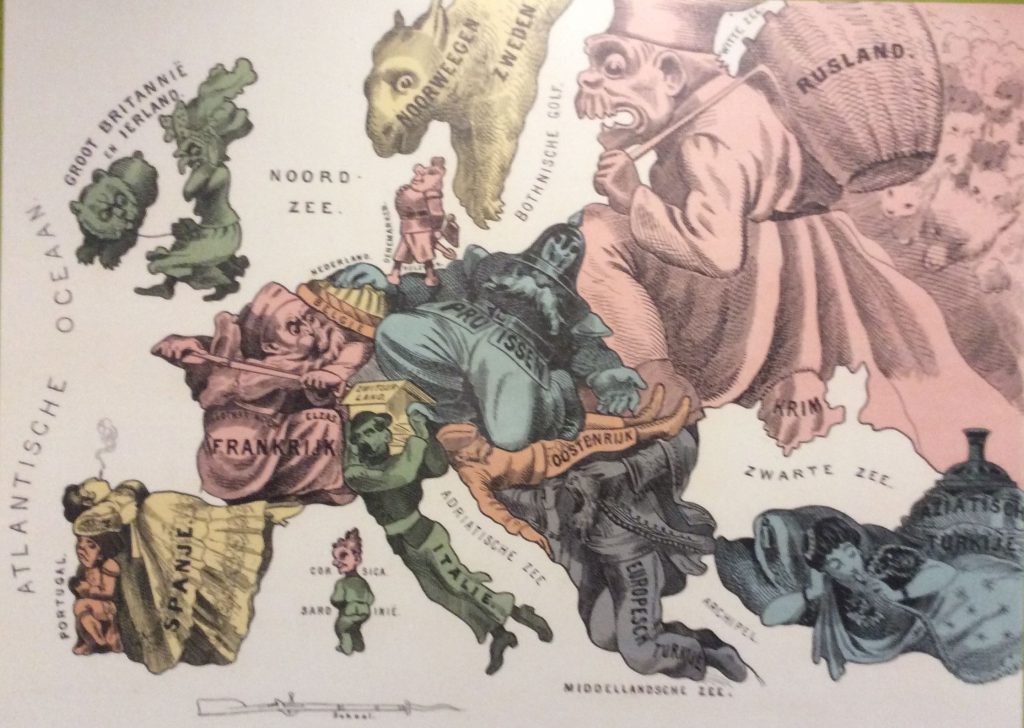
China altert
Zurückgehend auf die frühere strikte 1 Kind Politik erhöht sich der finanzielle Wohlstand der Chinesen alleine dadurch, dass das gleiche BIP auf weniger Köpfe verteilt werden muss. Eine Generation später ergibt sich aber durch das rasche Altern der Bevölkerung eventuell ein hohe finanzielle Last für weniger Beschäftigte bei gleichzeitig mehr älteren Menschen. Die Beschäftigungsquoten der älteren Menschen waren niedrig im Vergleich zu Europa, das bedeutet ein gestresstes System zur Finanzierung der Renten und, wie eine neue Studie (Lancet Public Health 2022) zeigt, für die Pflege der Älteren. Bis 2030 werden laut der Studie bis zu 14 Millionen Menschen zusätzlich Pflege benötigen. Das betrifft überwiegend Frauen und Personen im ländlichen Raum. Das ist bei uns auch so, denn Zugang zu ärztlicher Hilfe, Krankenhäusern und Unterstützung im täglichen Leben ist aufwendiger bei größeren Entfernungen und Fachkräftemangel. Das Ausmaß der Pflegebedürftigkeit hängt stark von dem gesunden Altern ab. Dies ist wiederum vielfach bedingt durch Bildungsniveaus und Lernfähigkeit und -wille im Alter bezüglich der eigenen Gesundheit. Bewegung ist der Schlüssel zu mehr Gesundheit. Damit lässt sich die Pflegebedürftigkeit lang hinauszögern. Also raus, auch wenn es frisch ist. Open access Lancet paper (hier) 

