The digital drafting of blog posts facilitates the publishing of volumes based on a selection of entries. Pdf-files, or EPUB formats are quite common. The choice of a flipbook is more suitable for larger screens of tablets or notebooks. It also serves as a rapid stock taking of entries and missing topics to cover a broader field. In some fields AI is not yet popular, for example in agentic home applications, whereas in other fields text, translation or image production AI has grown into a threat to professional fields. Even computer languages are a major field of application with substantial negative employment effects.
Hence, enjoy the latest comments on AI towards the end of my latest Flipbook.
Just click here.

ChatGPT provides a summary of my AI-reader as follows:
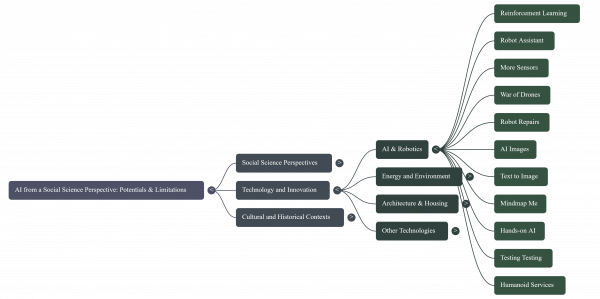
From the uploaded text AI from a Social Science Perspective (Dr. Klaus Schoemann), social science concerns with AI focus on potentials and limitations of how AI interacts with society:
- Labour and employment: AI impacts jobs, but adjustment processes are slow. For example, there’s a shortage of engineers and care workers, while robots are still limited to simple assistant tasks. This raises concerns about who benefits and who is left behind.
- Bias and fairness: The book highlights issues of biased results in research and decision-making. When AI systems rely on incomplete or selective samples, results can be misleading — a challenge also familiar to social scientists.
- Democracy and accountability: Journalists and scientists are framed as part of a “checks and balances” system. AI adds complexity here, as the fast spread of information without accountability can weaken democratic processes.
- Human–machine relations: Topics like intimacy, housing, and memory are re-thought in the context of AI and digitalization, raising questions about privacy, social norms, and cultural heritage.
- War and security: AI-driven technologies like drones change the nature of warfare, raising ethical and political questions.
On his blog, Schoemann also stresses the energy and resource costs of large AI models and how reinforcement learning offers a more efficient alternative. He warns that AI should be understood not just technically, but as part of an “all-electric society” where social sciences help assess risks, inequalities, and long-term consequences.
👉 In short: AI raises social science concerns about equity, bias, democracy, labour, cultural shifts, and global risks.