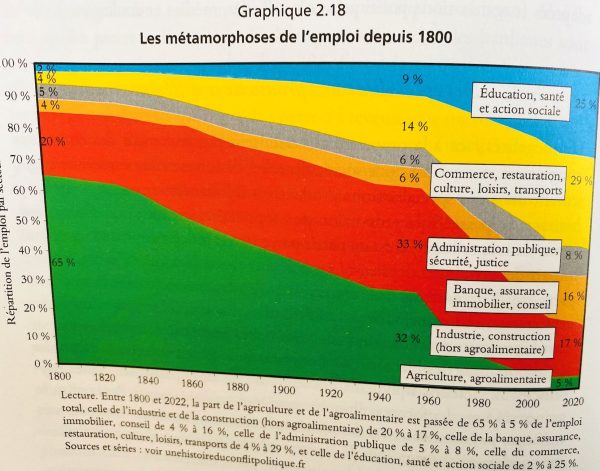
Urban Planning has to deal with the medium and long term time horizon. This is a challenge in a world of short term preferences of financial markets and creditors. The Paris Olympic Games of 2024 demonstrate in an impressive fashion that a balance between these different time horizons can be achieved. The whole of France debates 1 year after the opening of the olympic games what has remained of the investment and the exceptional achievements for the country and its population. The newspaper “Le Figaro” of 2025-7-26 p.12 has published an interview with Tony Estanguet, one of the main organizers concerning the subject. The best of the Paris games 2024 for him was “to see the whole country work together”. The united spirit to make these Paris games a success remains a special experience in an often very divided society. In 2025-7 the “vasque” has survived in “Les Tuilleries” after some debate once the games were over. Therefore, a bit of the Olympic spirit can still be experienced in the center of Paris where the games have become a part of French history.