Gas consumption in the EU has been reduced by about 20% since the beginning of Russia’s war on Ukraine. This is a considerable accomplishment and has been sustained for 2 years now. The major element in this has been the reduction of gas consumption in industry, but also households have successfully managed to reduce heating of rooms and water with gas.
Diversification of provision with sizable increases in the provision by the U.S.A is another element in the beginning of a trajectory of gas reduction in Europe. Germany as a major consumer of this type of energy supply is also making strides in shifting consumption. This is my short summary of the report by IEEFA.org in 2024-1. All electric devices like heat pumps could speed up the gas reduction further according to the policy recommendation by IEEFA in 2024-2 reducing costs of living and CO2 emissions further.
Data from Eurostat allow to compare monthly data across Member States. The overall trend is a market decrease with differential patterns of refilling supply capacities. Big countries in the EU made and continue to make a real difference compared to previous years (see table below). 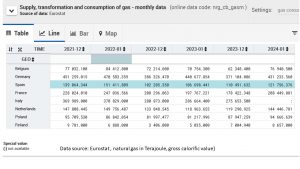 The comparison of December and January figures across years reflect the months with high sensitivity of the public for heat and cold. Further reductions of gas consumption is feasible due to the mild winter months of 23/24 which allow to reduce heating costs for many households and offices. Good news for the planet and hopefully a move in the right direction to shift away from heating with gas.
The comparison of December and January figures across years reflect the months with high sensitivity of the public for heat and cold. Further reductions of gas consumption is feasible due to the mild winter months of 23/24 which allow to reduce heating costs for many households and offices. Good news for the planet and hopefully a move in the right direction to shift away from heating with gas. 
Processed food
We eat a lot of pre-processed food. Our busy work schedules allow us to take only short breaks for meals in order to get more work done while in office or at work in general. The intensification of work has reached the next level and we move from pre-processed food to ultra-processed foods (UPFs). In medical journals and nutrition recommendations the warnings to not eat too much ultra-processed foods are abundant. The signs of obesity in societies reach higher levels from year to year. Especially younger people seem to be at higher risks to consume a lot of ultra-processed foods. Freisling et al. highlight the “risk of multimorbidity of cancer and cardiometabolic diseases” due to UPFs. The discussion between scientists is a lot on which UPFs are most harmful (beyond animal origin or and artificially sweetened beverages) and/or whether it is the combination of UPFs that additionally increases the danger of UPFs. Preventing the “too much of each” is probably the safest recommendation. Being able to read the nutrition information on the labels is already a difficult task. Just making the information abundant and very small print discourages most efforts to compare across products. Learning about basic human needs like food has never been more difficult. Combined with “shrinkflation” we have a hard time to make informed choices of what to buy and eat. There are many hurdles to overcome for a healthy meal.
Wage indexation
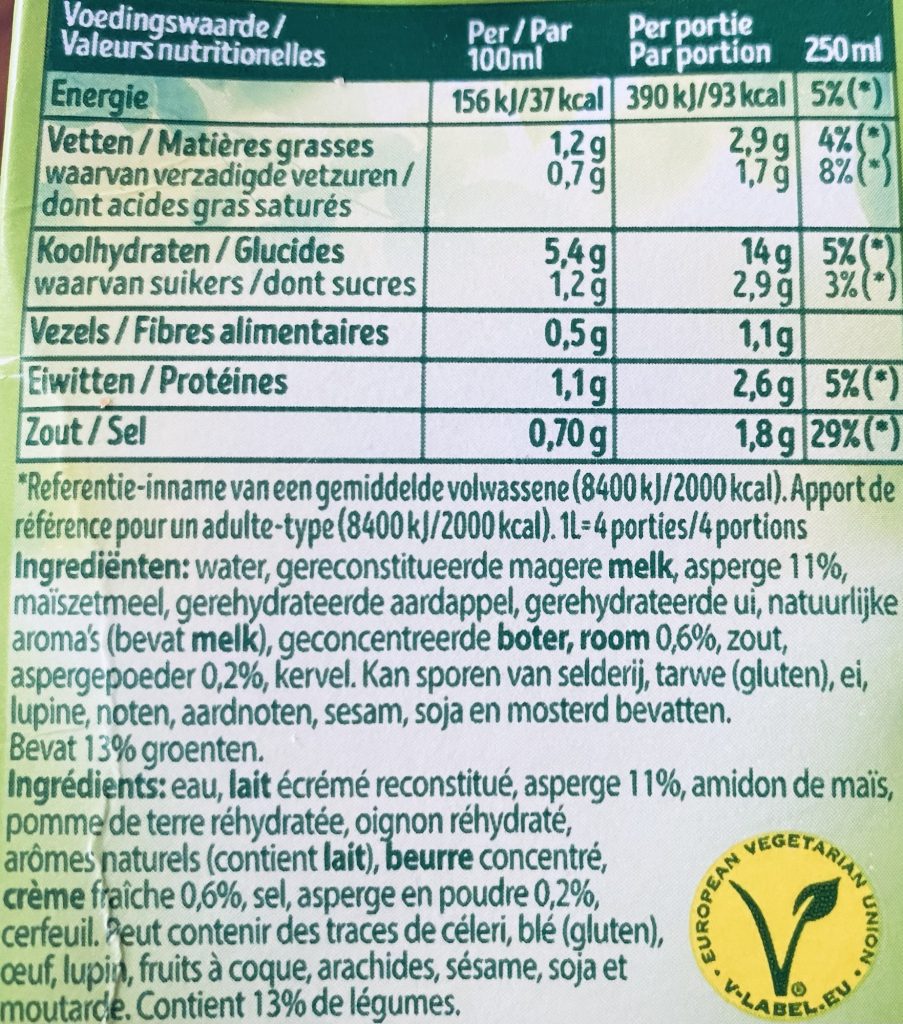
Currently inflation increases rapidly in many countries. Yes, Argentine. The Euro-zone and EEA have mastered the peak of inflation due to shifting away from Russian dependency and cheap prices for energy and dealt with carry-on effects related to high energy inputs. The annual rate of inflation calculated for January 2024 has returned in the Euro-area to 2.8 % close to the European Central Bank target of 2% (compare figure below). Inflation puts wages under pressure, because household with little savings have a very hard time to cope with sudden price increases. For society as a whole, inflation raises many questions of differential impact of inflation on different parts of society. Savings become devalued, but debt might become easier to be repaid in so-called real terms.
Wage earners suffer in terms of lower purchasing power unless in subsequent wage negotiations pay rises can be achieved. This then depends of negotiation power of groups or sectors of the economy. Trade unions have to enter into tough negotiations and conflicts to even regain the same status quo previously achieved in wage negotiations. A series of conflicts and economic readjustments by more or less powerful sectors or representation comes into play.
All this is happening in a year of a series of national and regional elections as well as the European Parliament election in June. Political turbulance and the rise of extremists might be a result of a lack of taking into account the needs of lower wage groups who are likely to feel the full blast of the high inflation previously still today. Wage indexation as in Belgium, which fixes wages to the rise in inflation previously takes out most of the explosive power of a sudden rise in inflation at the risk of an upward wage-price spiral. The recent inflation figures for Belgium, however, show that this is not the case. An overshooting has been followed by an undershooting of the Euro-zone inflation. The political disturbance and risk of redistribution to more powerful groups in society can be limited through general wage indexation or indexation of for example just minimum wages.
The Russian caused spike in inflation has been successfully mastered in the EU. The political economy of redistribution through inflation will remain an important element unless wage indexation is used in more countries to escape populists’ and extremists’ voices.  (Image Eurostat data and ESTATEC app)
(Image Eurostat data and ESTATEC app)
Greedflation
The teaching of economics and socioeconomic policies has to deal with the topics around inflation and economic inequality for centuries. Greedflation has become a newly coined term for the rise of inflation due to greedy firms who use a window of opportunity to achieve extra profit margins or windfall profits. At a time of perceived price rises in many sectors, sectors that have no cost increases might still try to push prices higher simply because almost everybody else does so. Higher profits then show up in the reporting season of enterprises quoted at the stock exchange and the increase in inequality between wage earners and shareholders will rise. Greedflation is a summary term for it. The ECB European Central Bank has mentioned this and Reuters has reported on it as well end of June 2023. Since then a wait and see strategy has been adopted. Now in February 2024 we witness the wider spread of extraordinary profits of big firms not only in the fossil energy sector but also bog banks. The economies and societies suffer huge losses and a massive redistribution of capital. Subsidies introduced to lower the shock of the coronavirus crisis and the Russian aggression are unpopular to be scaled back. Employees and their trade unions have a hard time negotiating adequate wage increases whereas most companies use the momentum of seemingly general price rises to push profit margins. The translation of this mechanism to the political economy risks to jeopardize the support for capitalism and market forces in general. Another wave of increasing inequality endangers the survival of democratic societies. Countries with only a short experience of the functioning of market economies are at a particular risk. Germany’s decline into dictatorship in the 1930s after the severe economic crisis should be remembered as a major threat. Greedflation is a very serious and very real threat which we have to address with economic and social policies rather than waiting until the European elections have passed. Time to act, the thinking has been done. Evidence accumulates to make the political case.

Skill loss
There is a sense of skill loss in watching the trends to increase comfort. We all use washing machines and maybe dishwashers. Households can save a lot of time by using those machines. Some porcelain and clothes should not be left to the machines. The need to organize traditional washing routines is almost forgotten after 1-2 generations. The same holds for many technical skills. Bicycle and car repairs or small repairs of electrical appliances are delegated to specialized repair shops. Not using or having learned these skills puts you in a form of dependency and at the risk to pay a price for specializing on other skills. Find out and focus on what you are best at. This has been the mantra of economic theory since Adam Smith. The potential value of satisfaction with an own production rather than a bought product is frequently acknowledged for baking cakes yourself rather than simply buying one in a shop. The same rationale holds for many other skills. Autonomy of own production with possibility to improve or repair are forgotten values. The have become a luxury item or a necessity for persons lacking financial spending power to buy products from others. Many skills will be lost rapidly because products have become so cheap to replace or order for home delivery. Industrial production is desperately searching for skilled persons but losing skills is pervasive at the same time. Public schools and academic curricula will not be able to stand the tide of pervasive skill loss.

Postmodernism
The grand narratives of the modern world, like modernism itself, are under serious criticism. Deconstruction of the modern way of thinking has become philosophical mainstream. Economics as a science is in the middle of the behavioural shift and changing or at least complementing its narratives. Sociology has embraced postmodern thinking in theoretical as well as empirical forms (Mirchandani, 2005). The empirical measurement focuses a lot on the groups and people who hold postmodern beliefs and values. The discussion in the social and literary sciences continue. In the arts reading on modernism and postmodernism is a must in order to understand much of contemporary art or art from the 19th and 20th century.
Bookstores in art galleries that cover long spells of history can make surprising links between historical periods of art. Books of postmodernism appear next to books on romanticism. A lot of the ideation of postmodernism rejoins romantic depiction about nature, re-naturalizing or the emotional connotations of wildlife, isolated places and stillness.
On the other hand, we are confronted with the brutal world of war, drugs and crime. Classical warfare and strategies are back in Europe with tanks and rockets killing like in previous wars. The Russian empire of a specific version of modernism strikes back as if it were to stop the postmodern turn of the 21st century. Neo-fascism tries to build on the losers of the transitions to the socio-ecological economy and society. There are manifold backlashes of modernism, but the postmodern world is under continuous construction, most of in our mindsets. 
AI or I
Generative AI receives a lot of attention. One of the main issues is, to study how AI interacts with humans. The hiring decision by managers or an AI algorithm is an interesting application. According to Marie-Pierre Dargnies et al. (2022) the preference for human decisions remains strong despite reasonably unbiased performance of an algorithm. The main issue is with the transparency of the algorithmic decision-making. As a worker or as a hiring manager the preferences continue to sit with the person rather than the AI. It is a worrying outcome, however, that if the rule of gender equality is removed from the algorithm both workers and managers tend to prefer the algorithmic outcome. I interpret this as a latent preference of study participants for gender bias, which could lead them to expect a more favoured outcome in case the AI makes the decision. Knowing what decision-making rules have gone into the hiring algorithm has an impact on all persons involved.
A new managerial competence is to be able to assess tasks carefully, whether you should perform the task yourself or delegate to AI. In this sense the old question: to do the task yourself or to delegate has simply been enlarged by an additional delegation option. The decision-tree goes from (1) To delegate or not to delegate, and (2) if I want/need to delegate, should I delegate to AI or somebody in person (not allowed to use AI).
I opted to use AI for image creation rather than to take a photo myself or by one from a professional photographer. (Image creation: NEUROFLASH AI – Image-Flash 2024-1-26) 
AI and We
Research is beginning to provide empirical evidence and experimental modelling results on the widespread use of generative AI. First results by Doshi and Hauser point at the individual benefits of using artificial intelligence but the widespread use of it is likely to narrow the scope of novel content. This research is particularly interesting because it deals with the micro level to macro level aggregation effects. It is fine for me to use AI. If it becomes a mass phenomenon, we expect in sum a negative outcome for society as a whole.
The example at hand deals with the capability to innovate or to come up with novel content. As more and more texts or newspapers are published with extensive use of genAI, the real element of creation will remain the domain of humans for quite some time.
In my opinion this is due to the difficulties for algorithms to differentiate between the positive and too risky negative aspects of innovative solutions. A query for AI might ask to come up with an innovative solution for auto-mobility of short distances. A human being might propose walking due to the additional health effects the AI might propose helicopter lifts. The not so stupid machine would need a lot of additional information about circumstances to generate useful solutions. Therefore it is not surprising that sometimes public transport apps propose to walk short distances rather than waiting for “delayed or unreliable services“ they provide themselves. Personal circumstances like mobility with children, other dependents or luggage are usually beyond the scope of the information base of the algorithms.
On the other hand, if the AI knows that 50.000 persons after an event want to take public transport at the same time the indication to walk or wait solves an aggregation problem of individual preferences to adapt to available capacities. Lots of issues to solve for AI and us or better yet, us and AI.
(Image creation: AI using Microsoft Dall-E Image creator: Prompt: a person with notebook in profile and in front of 5 other persons in Office with windows 26.1.2024, 8:24 PM) 
Shrinkflation
Shrinkflation is a hybrid term that combines “to shrink” with “inflation”. The trick is to keep prices at the same level for a product, but to reduce the weight or amount sold at a constant price. The intention of producers is to indirectly increase prices without touching at price tickets on products. As consumer you are likely to remember the price tag of a product, but much less the unit costs. However, the unit price is the basis for fair comparisons. In supermarkets there is an obligation to print also unit prices (€/kg or €/L) next to price labels. Comparisons allow information irrespective of package size. In shrinkflation the higher unit costs of a product will drive the official measure of inflation (Destatis, 2024). In Germany inflation for food had the top inflation rate in 2023, surpassing even price rises for energy.
On the one hand, shrinkflation is cheating on consumers to sell them less for the same price. On the other hand, oversized products that solicit higher consumption are part of the health and environmental problems we face. The obesity pandemic is part of the XXL consumption hype the food industry and supermarkets have created. In this respect, more expensive food (Eurostat info) potentially may trigger the rethinking of consumption and nutrition. “Eating better instead of less” has always been more expensive.
Besides the profit-maximising logic of shrinkflation, there is at least a small hope that behavioural changes might be triggered to consume less, to use less detergent in washing, less sugar drinks, smaller size pizza and so on. Shrinking our food intake is part of the solution for many problems. In the end cutting out most convenience food will save you a lot of money. As a side effect of such behavioural changes, eventually prices are likely to come down some time later again. 
Flotow CH
Noch 20 Jahre nach seinem Tod wurde Friedrich von Flotow recht prominent aufgeführt. Im Stadt- und Aktien- Theater der Stadt St. Gallen stand seine Oper “Martha” an einem Mittwoch 26.4.1905 auf dem Programm (Anfang 8 Uhr präzis), gefolgt von Mozarts Zauberflöte 2 Tage später. Was für eine Konkurrenz. Das Plakat zur Aufführung ist in der Digitalen Bibliothek der Kunstbibliothek in Berlin anzusehen (Link).
Die Geschichte des Theaters in St. Gallen ist aus ökonomischen, gesellschaftlichen und architektonischen Gründen interessant. Das Tagblatt berichtete in 2007 über den Abriss der historischen Städte und den sehr verspäteten Neubau einer moderneren, größeren und wirtschaftlicheren Spielstätte. Damals zu Beginn des 20. Jahrhunderts schon standen populäre Werke wie die Martha und die Zauberflöte auf dem Spielplan. Die Aktionäre des Stadt- und Aktien- Theaters der Stadt St. Gallen haben wohl schon immer etwas mehr auf das Geld geschaut, auch wenn es um Kunst geht. Mehr Zuschauende und Zuhörende ist demokratisch und nebenbei gut für’s Geschäft. Der Abriss war beklagenswerter Weise im Jahr 1971. Ein Neubau an anderem Ort startete bereits 1968. Dieser Bau musste ebenfalls nach 40 Jahren Spielzeit grundsaniert oder abgerissen werden. Heute findet sich darin ein lebhaftes Programm mit Musicals als ausgezeichnetem Schwerpunkt und beispielsweise des Theaterstücks „Gott“ von Ferdinand von Schirach . Die Stadt und die Aktionäre sind wohl aus der finanziellen Verantwortung, aber das Kanton St.Gallen und der Lotteriefond sind eingesprungen.  Bildquelle und Großansicht Kunstbibliothek SPK Berlin.
Bildquelle und Großansicht Kunstbibliothek SPK Berlin.
Stock taking
From time to time it is necessary to take stock of production and to review the material that has accumulated. As I have been working in archives, official book depositories and libraries for years, it comes almost naturally to deal with questions of how to keep track of all that content. Digital solutions are excellent devices in this regard. I do not have to deal with digitalisation, a huge issue for all historic archives and many recent small museums as well. I have to deal with backups at regular instances. To be sure, each engineer will assure you, better make a backup of your backup … . Yes, I do this as well. Now the ultimate backup of digital work is ? Got it, a printed copy of your digital work. The best advice I received on this comes from a computer magazine “ct” gadget mug with imprint advocating “No backup, no mercy“. To facilitate my printed archive I start with monthly collections of blog entries (Link to pdf-file December 2023 ->Brainstorming 23-12). The simple conversion yields 63 pages, a printer friendly version 56. Hence the expected yearly volume (60*12) will be somewhere near 720 pages. That is for the archive only or in case my eyes do no longer support online reading on screens for too long.
Digital archives have, of course, many other advantages. It is possible to reassemble my collection of entries by subject through a more thorough editing. Specific edited volumes will surface from this, which I have in my mind but only careful long-term followers of the entries might see already. Political economy and sociology are obvious candidates. Public health, labour, the world of arts and music could constitute other edited volumes. Lots of branches grow out of the trunk of content. 
Ethics of posterity
We have not inherited the earth from our ancestors; we are borrowing it from our descendants. (native American saying). Adeline Johns-Putra (2019) states this early in her book on “Climate change and the novel.” Her concern is how to think and write about the ethics of posterity. Approaches of ethics in the sense of parental care (for the planet) or motherhood environmentalism do not suffice in view of overpopulation of our planet. Shifting our identity away from toxic production and consumption is advocated in many novels. Science and science fiction offer many dystopian examples.
De Shalit (1995) wrote early on why posterity matters. It is not the standard of living of contemporaries that matters but we should consider ourselves as a part of a transgenerational community. The time horizon of our decisions matters. In pursuing arguments by John Rawls who re-established a contractionalist perspective on justice, we have to include future generations into our contractual obligations. Following this approach we might arrive at Brundtland’s perspective on the ethics of posterity which is called sufficientarianism in opposition to simple utilitarianism. In sufficientarianism we owe future generations a just and decent living or at least the possibility to have similar starting conditions. Shifting beyond the apocalyptic view of environmental disasters Adeline Johns-Putra (2019) brings to the forefront that we have to substantially lengthen our time horizon both for consequences of climate change and for dealing with it, albeit the fact that most destructive practices operate much faster than the re-establishing of greater biodiversity.
P.S.:Thanks to the curators of the Lese Lounge Staatsbibliothek Berlin for ease of access to the literature.
(Image: Natur & Kultur in “Extreme tension: Art between Politics and Society” Collection of the Nationalgalerie 1945-2000“. 2024-1) 
Air quality EU
On some days of the year there is a cumulative effect of bad influences on air quality in Europe. Cold winter temperatures increase emissions from heating. Outdated heating with coal, still important in Eastern Europe, causes high amounts of extra particles in the atmosphere. In January 2024 a train conductor strike in Germany irrespective of the good reasons for it, makes people take their cars. Road blockades by opponents to reducing diesel subsidies to agri-business add to the pollution situation on a specific day. Overall the population suffers and breathes additional amounts of cancerous particles. Particles settle as dust on crop producing soil, of which we all feed ourselves. This is a vicious circle, which we need to break in the interest of all of us, particularly for the more fragile people and children. The latter start to crowd the medical doctors with sometimes lacking the delivery of crucial medicines for this target group. Where do we go from here? Compromises are key, security of supply chain and allowing, not too much, time for transition periods.
Renewables
Renewable energy has reached for the 1sr time a share of more than 50% in Spain and Germany in 2023. This is an astonishing milestone in the energy transition of both countries. For Spain a report from Red Energy Espanola attributes the Spanish success story to the expansion of mainly wind energy (Link). The increase of renewable energy in Germany is due to a more rapid expansion of solar energy (Link). In any case a continued expansion of both forms of renewables allows to reduce the share of fossil fuel even more rapidly than previously estimated. Good news for the planet particularly to phase out energy from coal due to its highly polluting side effect. Countries with faster trajectories shall serve as examples that it is feasible to manage the energy transition also for large countries. Political instability might be a price worth paying considering the positive effects for future generations. Managing the transition in a just way which means to assist poorer households, ensures the respect of social policy targets at the same time. With this in mind the energy transition can be perceived by all as an opportunity rather than a threat to their welfare and wellbeing.

Museum Orga
The cathedrals of modernity are under permanent scrutiny. The discussion in Germany was sparked by a recommendation of the scientific advisory council to the federal government (Wissenschaftsrat) to separate the Prussian heritage museums and institutions (SPK) in Berlin into separate entities that have higher autonomy to shape their individual profiles. Too much hierarchy blocks innovation and openness to new approaches that might not fit an overriding instance of decision making. The arts and sciences as well as their libraries need substantial degrees of freedom to flourish in their specific cultural and societal environment. The same discussion is currently occupying Paris and France, since overall the visitors after the Covid-19 crises have not yet come back to the same levels. Digitalization has opened up new opportunities and potentials to reach new audiences. This needed new resources even at a time of budget constraints. Museums have started to take their social functions more seriously besides their role to preserve the cultural heritage. Economic thinking in terms of scarcity of art works, competition between museums and cities or countries for tourism have entered the stages as well. Prices of entry and quantities of visitors have become additional concerns in the organization of the museum landscape. A lot to cope with and to balance multiple policy targets. Accessibility of those treasures is key. Opening up to broader audiences is costly but crucial to provide the justification of the public funds allocated. Great to see more complementary private investment in this exciting field. The prominent archers in front of the Berlin museums have moved ahead into a new round of competition in the organization of museums.

Eco-trees
This time we thought to advance with our ecological version of Christmas. We use LED lighting and instead of advocating real horse riding we opted for the wooden replacement. We reduced the size of the tree by 27.5% to further cut down on the carbon footprint of our event. As we were all feeling pretty confident that we are on the right track now, we learned from the media reports in Germany that the trees usually grown specifically for Christmas are taking away precious land where otherwise food would be grown. Much worse is the fact that pesticides are very often applied to facilitate the production of trees. (Link to study and test results).
We know that there is a problem in Germany to be frank about environmental dangers of diesel and glyphosate, but we did not want to believe that we inhale glyphosate in our living rooms after the diesel disaster in cities. We thought trees were synonymous for nature. Far off the truth. Better check the ecological impact and risks incurred even for trees. Trust and good faith seems to be utterly misplaced when it comes to nature turned into a product.

Infrastructure
For some societies and cities it is a continuous question of how much resources we should invest in infrastructure. Access to funding is a major concern. The calculation of the viability of the project needs careful examination and evaluation. Societies have very different kinds of preferences and, interestingly, about time horizons for their deliberations.
There are examples that have been built to last a century and lasted 2000 years. Other worst scenario examples are built for just one World Expo and torn down afterwards. The Eiffel tower is such an example of the latter kind, but it lasted longer than 100 years by now. We should be thinking more about time horizons as it remains an often overlooked part of investment in infrastructure. The oldest city in Germany has many buildings from the Roman occupation that still characterize the city’s architecture. This remains an important economic factor for the city of Trier as an attractive location for tourists throughout the year. Only wars or negligence may cause severe deterioration if infrastructure has been built with an emphasis on its lasting value. The narrow-minded investment in downhill skiing like in the Swiss Alps is at best expected to last 20 years. For trees to grow there again it will take 50+ years. Sustainable investment will be viable and vital in many respects. High interest rates force us to recalibrate our societal and private s again. Taking into account a longer time frame for investment we indirectly build infrastructure that should last longer. Moving beyond short-termism is necessary, particularly in the field of investment in infrastructure.

Sectoral Change
The long-term view of sectoral change in France, for example, from 1800-2022 (Cagé and Piketty, 2023 p. 128) allows us to zoom out of our narrow focus of the last few years of economic change. The decline of agriculture is the most remarkable. The reduction of employment in industry and construction has been an ongoing trend as well. Banking, insurances, property and consulting have seen remarkable expansion over these years. Public services, security and legal affairs are still on a moderate rise. Other sectors like education, health, commerce and transport manage to grow equally.
The merit of the comprehensive volume by Cagé and Piketty (2023) is that it is thoroughly data driven and based on quite unique long data series. The data on structural change and just the employment trends depicted below refocus our attention on likely consequences of these changes.
For the 2 authors we should redirect our attention much more to the implications of these trends (like rising inequality) on political conflicts and power struggles. Democracies are at risk, if we continue to ignore these seminal changes of industrial structures and shifts in employment. The traditional strongholds of trade unions and progressive forces in the manufacturing and construction industries as well as in public transport seem to have unaccounted implications for our political systems as well. The volume by Cagé and Piketty (2023) will soon be available in English and reach broader audiences just-in-time for the European Parliament elections in June 2024. Particularly the spatial implications and how the neglect to take into account the fundamental differences between the rural development and structural change needs urgent reconsideration. After the time for reading and working with the data (LINK) is the time for action to preserve our European Dream of peace and social development. 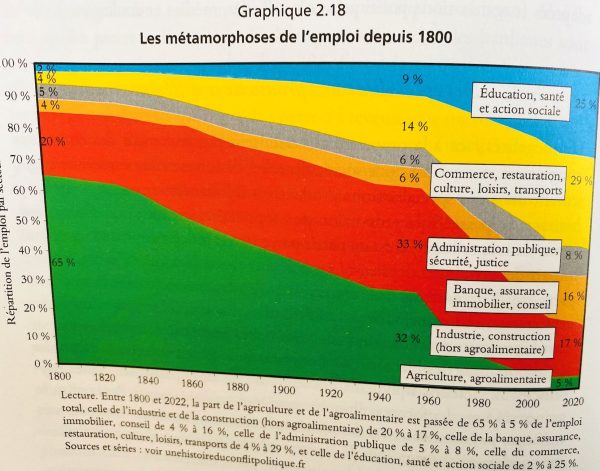
Arms trade
The sustainability of war depends a lot on the availability of arms. The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) publishes regularly updated data on arms trade. The report ranks countries who are the most important exporters as well as importers of arms (from 2018-2022). The lists show for exporters that the U.S has been at the top of exporters with 40% of the global export share followed by Russia with 16%. France 11%, China 5.2, Germany 4.2 come next on the list. Taken together Italy, Spain and the U.K. reach another 10% jointly of global exports. South Korea and Israel come in with shares of 2.4 and 2.3 respectively. The top ten serve allies but also more broadly the world arms trade and race. New dynamics have started to come into force. The Russian aggression and war on Ukraine territory will have an impact to the extent that Russia is probably exporting less and shift to a more importing state.
Among the importing countries India is leading the ranking followed by Saudi Arabia and Qatar. More generally Asia and the Middle East were the most important buying countries. Importing arms might be interpreted as an indicator of perceived threat to a country. Long cycles of arms renewal may also drive statistics of arms trade, but new threats like cybersecurity and space technology have created new fields of potential attack and defence.
All in all, yet another rationale attributed to Clausewitz seems to play a role in driving the arms trade. “If you are perceived to be weak, an enemy will use this to attack”. Well, this also means that buying arms, producing or importing them, could deter a military aggression. That form of deterrence of aggression is known from the nuclear arms race as well. In the realm of conventional weapons, we have thought, it would no longer apply. We were mistaken in this respect. The dividend of peace has come to an end for many countries. The SIPRI report (2003, summary p.9) shows the continued rise on the global level of the arms trade. Why are we so scared of each other? Russia has reverted to imperial politics using conventional weapons. Containing such disrespect of internal law needs our full attention to avoid a spreading to other areas. The link of diplomacy and trade needs close scrutiny. 
Preference
In societies it is not easy to derive collective preferences of citizens. Elections every 4 years tell sometimes nothing on specific issues which were not debated or of sufficient relevance at the time of the election. Dealing with snow and slippery sidewalks is hardly an issue at all. However, the preference to clear roads meticulously rather than bicycle and pedestrian paths in a dead end road reveals preferences for „s‘heilig Blechle“ the holy tin box (car) in many cities. Our orthopedic units in hospitals are crowded at such times and those costs are hardly attributed to the source of human negligence for fellow humans. We would expect that aging societies start to address such topics but little change has occurred so far. Hence we claim airbags for pedestrians and cyclists😂. Preferences probably have changed already but implementation is slow and faces strong opposition as well. It’s always easier to lock frail persons into their apartments at such snowy times. It feels a bit like corona where it was also easier to restrict mobility for pedestrians and children than to deal properly with the virus. Aggregation of preferences in societies remains a challenge and sociology has a lot to offer in this regard.

Energy Storage
News agent Reuters has published an analysis of the setback for short peak coverage of electricity by power plants fueled with gas. Conclusion: economically no longer viable. Investors draw back even from contracts already signed. What is the game changer technology here. Batteries that store energy just like the batteries of millions of cats that have a storage capacity to supply energy for a whole household for more than 2 days. Other giant batteries cost only half the price compared to 5 years ago equal to $150 per kwh. In five years solar energy doubled its share of energy production to now reach the same amount as energy provision by gas.
Reaching a critical turning point in energy generation, investors flock to the more profitable medium or long-term investment. Good news for the planet. Wind and the sun are all around us. We have only started to cover roof tops of office buildings, car parks and other shelters. Start thinking about your energy storage as of now and reserve a suitable space for it. Costs are coming down rapidly in a few years or maybe only a few months. 
Beer Temple
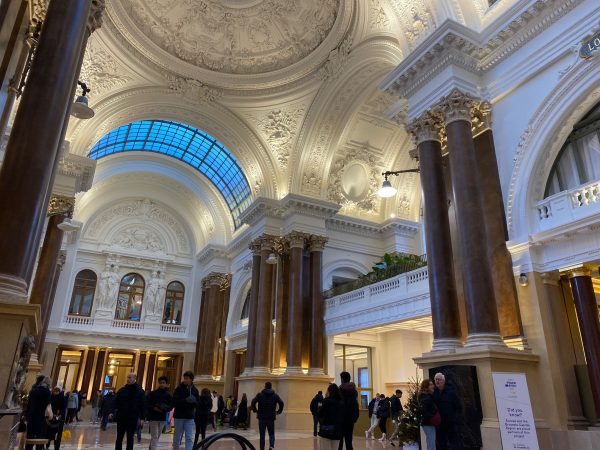
Brussels has recently opened a new attraction. A splendid temple-like building devoted to the unnamed God of beer-drinking. The renovation over several years of the centrally located “Bourse” has created a new popular attraction right in the centre of Brussels. From the outside the building reflects the classical temple architecture from Greek and Roman times. Although the building was for a long time the trading place of shares, obligation and currencies and thereby very closely linked to a country’s wealth and economic fate, it has found a new destination to represent the diverse and spirited culture of the people or peoples of Belgium through the lens of a beer glass. Of course, this is surrealism à la Magritte et al. (Museum and galleries within walking distance). The shifting fate after a financial crash to transform the “Stock Exchange” into a temple of surrealistic experiences is great idea and its realisation as popular move to transform the stock market into a temple to worship beer, beer drinking and conviviality a great idea. Without joking, the restaurant in the temple proposes good food that can be matched with a selection of 30+ kinds of Belgian beer (including 4 non-alcohol-containing beers).
Framing beer drinking culture differently from the image of beer and football hooligans is hard to achieve. Public images of beer drinking on television are all around us, anew every weekend. The Brussels stock exchange is a great place to reflect on shareholder versus stakeholder issues. Brussels has opted for a popular conversion of the building. Paris has gone for the upmarket more exclusive transformation of the previous stock exchange (Bourse commerciale) into a gallery of modern art from the private Pinault foundation.
The museum of beer in the upper ranks of the building in Brussels offers even tastings we were told. Well, beer drinking and stock trading (gambling) have both addictive potentials. Ruining yourself, the one or the other way, is equally disastrous not only for yourself but potentially others.
Know your limits is easier said than done. It is a behavioural phenomenon for individuals as well as regions or whole countries. With the apparent “Limits to Growth” for our planet or our ways to trade, even praying in the renewed beer temple is unlikely to solve the bitter-sweet issue. Perhaps discussions in the new Brussels temple will spur new coalitions and stimulate new ideas to overcome the locked-in political trading positions. Maybe the European Parliament should have a futuristic surreal session in the historic site. The only problem is, they would no longer want to return to their usual forum for debates.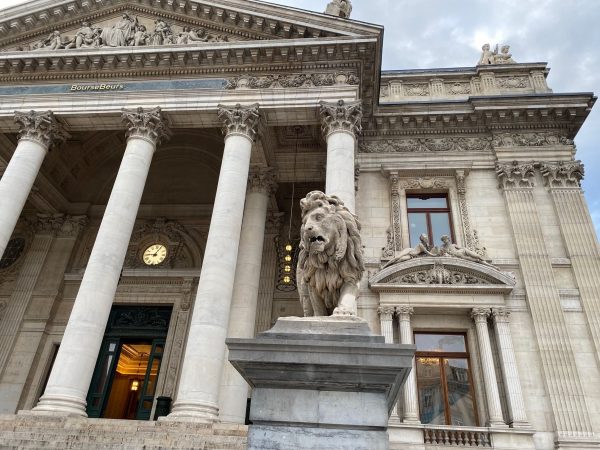 

CO2 Footprint of Books
In view of the worldwide size of book publishing we should also keep an eye on the CO2 footprint of book publishing. The Italian association of publishers gave a brief overview of the likely CO2 footprint the printing of a book causes. Their best guess is at ½ a kilo of CO2 on average. For simplicity of calculation and assuming that an editors’ association is unlikely to overstate the amount, let us assume it is 1 Kg CO2 per book. The most CO2 is consumed not in the book production but in the transport of the items, machinery and personnel involved in producing, editing, selling etc. Of course, paper is recycled to a large amount. Certified sustainability of paper from trees has become a standard in most countries.
Nice twist to the issue: your own library at home has become a CO2 storage, if you keep them or lend them or pass them on to others. Reading can be a little bit addictive and buying books as well. Reading online or electronic books reduces your CO2 footprint. The best way to imagine the reduction of your CO2 footprint, however, is to buy or to borrow a book on travelling which replaces the actual journal by reading on the couch. Yes, being a couch potato is good for the planet, and if you want to buy a book, walk to the book shop or the library if possible. If you enjoyed flying previously shift over to buying books on planes, airports, clouds in images or stories that involve extensive travelling instead for the sake of your own CO2 footprint and future generations.
Even a book will need somehow wood as input, many alternative ways of leisure time or professional activities are worse in terms of CO2 footprint. Any e-book, e-journal or e-newspaper is even better for the planet, especially if we think of the millions of paper copies across the world that are printed but never sold. Knowing your market is crucial to reduce misallocation of ressources. E-books are so much easier to store as well using regenerative energy for the content servers around the world. 
Book traders
Some book traders have a mission. They assemble little corners on their book shelves or in tiny cupboards reserved for their passion or mission. In some book shops you’ll find a corner devoted to a specific language or translations, in some a world region is represented as a specific predilection. The choises are as numerous as there are books. Of course, from an economic point of view national and international bestsellers will be shown in the most prominent places. Second come books for children, cooking, life and travel guides. All those are the cash cows for book shops and traders.
But beyond those, it is always worth the effort to search for those little carefully curated corners in a good bookstore that derive from the vision or mission of the book trader, employed or owning the shop. In some areas this contributes even to a small community building. Readings of authors add to the function of book sellers to build a relationship to their non-random book buyers. I keep going back to my favourite book stores and libraries with those curated corners for decades and across countries to find inspiration and updating of special topics.
There is a danger that we are going to lose all this professional work of thousands of well-trained book traders that guide readers in addition to publishing houses, literary critics, numerous awards and huge marketing campaigns of derived products (as with Harry Potter). Living up to your mission while running a book store must be a great experience. If is really increases the buyers and readership for the topic, would be a great result. However, I suppose many bookshops manage to keep their little curated areas despite economic pressure to go with the mainstream marketing campaigns and top selling books and gadgets.
With the decline in the number of smaller book shops (in Germany from ca 5000 to 3000 in about 20 years) we see a parallel increase in number of franchises of the big book sellers (Thalia.de 500 stores in D). Big chain increase seems to cause fewer professionally trained book traders (-10% in D) within a country. For younger generations TikTok (BookTok) has taken over large parts of the “book counselling” of book traders previously. This was a big event at the Frankfurt Book Fair 2023 as well.
Time to rush to your local bookstore and book trader before it is taken over by a big chain or simply disappearing silently. We are likely to lose many of those book traders with a mission to make this world a better, more beautiful, more tasty, enjoyable or inclusive place. 
Taxing Europe
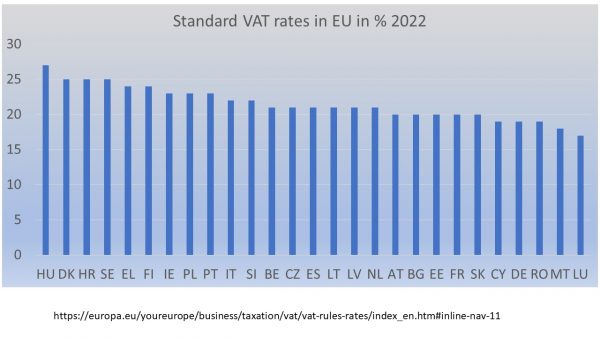
From time to time it is helpful to compare basic tax rates, for example value added tax, across the EU to understand the different economic and social policy approaches. The range of VAT from Hungary 27% to Luxembourg 17% is astonishing and it does not really feel like we are together in a common market. Okay, the illiberal, authoritarian state of Hungary is taxing the most, a clear message to visitors from another European country that this authoritarian state is relying on tax on consumption of its own people and visitors to foot the bill of state expenditure.
It is also interesting to realise that some countries with lower VAT rates have disproportionate public debates about supposed tax burdens. Tax levels are a political choice and much depends on redistributive appropriate use of tax receipts to the benefit of all or specifically those most in need. The potential for redistribution to parents, children, pensions, the poor or green investments also relies to some extent on the overall budget. The most surprising thing is the absence of a debate about tax rates, the size of the tax base and the ample exemptions or reduced rates. Of course, most of us complain about income taxes, but we all agree that it is nice to see that someone is taking care of the abundant autumn leaves or lighting of streets in the darker seasons. Even Adam Smith wrote in favour of the “night-watch state” that assures sufficient security levels. Taxing Europe to ensure that this role of the state can be taken seriously is still a common denominator across Europe.
Image: own presentation based on EU-data from 2022 LINK.
Bidenomics
Some American presidents become famous due to specific economic policies they managed to formulate, get approved and implemented them. Reaganomics, of previous U.S. president Ronald Reagan, was coined in connection with an open market doctrine, favouring monetary policy instead of fiscal stimuli. Bidenomics, of incumbent president Joe Biden, is characterised by his “produce in America”, Inflation Reduction Act, and fiscal stimulus provided for green and social investments.
Whereas Reagon sat more with bankers and central bankers, Biden is keen to stand with unionised workers even on the picket line. Investments that favour good jobs, jobs that apply pay scales agreed upon through collective bargaining are part of the Bidenomics that seems to work to raise the wages of the middle-class people. In the medium-term there might even be effects to lift the lower wages in other sectors of the economy as well. However, this is the tricky part of the equation to support the middle-classes and somehow the median voter.
American elections are won in so-called swing states that have voted democrats or republicans by narrow margins. Many of these states are in the “Rust-belt” states that have or had a strong manufacturing base. Bidenomics works hard to make the economy work for those people in these states, who have felt threatened by declassification, job loss and undercutting of wages due to migration. Substantial wage gains from $32/h to $40/h over 4 years is a landmark achievement in the U.S (see New York Times below). Non-unionised firms like Tesla, Hyundai or BMW and Mercedes in the U.S. will be isolated if they do not follow General Motors, Ford and Stellantis in the coming months or years.
It is not just about cars and trucks and wages, but about the chances of Biden and the Democrats to stem the renewed populist tide in the U.S. German car makers appear to be in the camp with the Tesla X-Man avoiding to negotiate with trade unions in the U.S. If Biden stays on as president after the next election, Bidenomics will gain further support and production of batteries and cars will be favoured locally with good paying, unionised jobs. Despite the high interest rates currently it is astonishing to many economist that the U.S. has not fallen into recession like for example Germany in at least 2 quarters of 2023. (Image: extract of Ney York Times 2023-11-2)
Nobel Literature2023
Jon Fosse has been awarded the Nobel prize for literature in 2023. Alfred Nobel donated the original funds out of his entrepreneurial empire build on the patents for dynamite. The explosives have ample use in peaceful times, but especially at times of war with noisy and destructive explosions. Experiments, with the tragic outcome killed together with 4 other victims his own brother. It did not stop him to pursue his entrepreneurial endeavour. In 2023 the Russian aggression continues to use explosives to kill innocent civilian victims. The sound of bombing continues to traumatise or destroy existences. The Nobel Prize for literature awarded to Jon Fosse does not bring those killed to live, but it is yet another reminder that silence or the absence of Alfred Nobel’s noise is invaluable. Norwegian Fjords and the water all around surely inspired Jon Fosse.
The scope of his writing ranging from theatre, prose to poetry and children’s books is comprehensive and impressive. This is probably all well known to many theatre-goers and readers beyond their mother tongue. For Germany there is an additional feature to the literary work of Fosse. Hinrich Schmidt-Henkel is the almost exclusive translator of the German language editions. This is already an impressive amount of work and long-term commitment to and from a translator as well as the publishing house Rowohlt. The Wikipedia entry for Hinrich Schmidt-Henkel shows the numerous works as translator of Jon Fosse as early as 2001 and still more to come. Additionally, Hinrich Schmidt-Henkel translates other classic authors from Norwegian into German in collaboration with the publishing house Guggolz located in Berlin-Schöneberg.
Besides the passion for translation Hinrich Schmidt-Henkel is active to defend the rights and salaries of translators. The threat to professional translation work by AI-programmes is imminent and just like authors and actors (not only in the USA) face continuing challenges for proper remuneration of their work. Being the German “voice” of Jon Fosse, it depends very much on specific contractual arrangements, whether a translator will also benefit not only from the popularity, but also in financial terms from the “windfall” profits reaped by authors and publishers. This constitutes probably a rather explosive issue, but worthy to be addressed eventually by the Nobel Committee. It is a “winner takes all” system just like with explosives, at least until next year’s awards. (Image Hinrich Schmidt-Henkel presenting Biermann in Staatsbibliothek Berlin 2023-9). 
Digital Egal
In den deutschen Amtsstuben geht es Ende 2023 oft noch erschreckend analog zu. Für einen Grundbuchauszug, beispielsweise, hatte ich das außerordentliche Vergnügen das Grundbuchamt am Amtsgericht in Berlin Ringstraße aufzusuchen. Sonst nimmt man sich ja nicht die Zeit, solche Sehenswürdigkeiten von innen zu besuchen. Die Überraschungen waren vielfältiger Art. 3 Personen Wachpersonal und Metalldetektor, wie bei der Flugabfertigung. Für den Auszug aus dem Grundbuch ist selbstverständlich eine Gebühr fällig, die nur bar entrichtet werden kann. Auf zur Zahlstelle, immerhin auf dem gleichen Flur. Die nächste Amtsstube hat zwar noch einen richtig historischen Tresor, aber die Erfassung der Zahlung läuft wohl noch auf alten Geräten. Vielleicht per relativ unsicherem WLAN verbunden. Das LAN-Kabel ist jedoch schon mitgeliefert, das dann irgendwann einmal eine sicherere Netzanbindung ermöglichen wird.
Über einen Dienstleister lässt sich der Verwaltungsakt auch online erledigen unter Herausgabe der Kreditkartendaten und sonstiger Daten (Cookies) samt Unterschrift per Maus (!). Das ganze für die doppelte Verwaltungsgebühr. Dank des 49 € Tickets wollte ich mir diesen Spaß jedoch live gönnen. Wahrscheinlich werde ich das nochmals mit den Enkelkindern so als lebendigen Museumsbesuch nachvollziehen. Wer weiß, wie lange das noch möglich sein wird. Das Personal trägt es mit Fassung und dem nötigen Humor.
Bisher kannte ich die Diskussion über die Digitalisierung der Verwaltungen mehr aus wissenschaftlichen und technischen Diskursen. Jetzt kann ich so richtig in das Jammern darüber einstimmen. Produktivitätsfortschritte lassen sich hier in ungeahntem Maße erzielen. Einer geht noch: Was ist das längste Wort in dem Amtsvorgang und wie viele Buchstaben hat es?
Gerichtskassenstemplerabdruck (auf der Quittung).
Aging Challenge
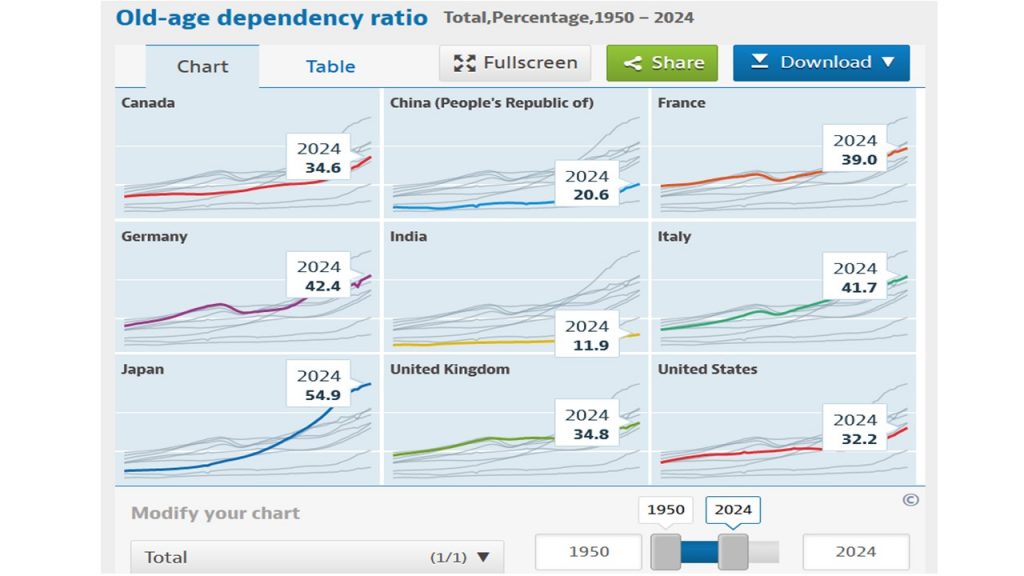
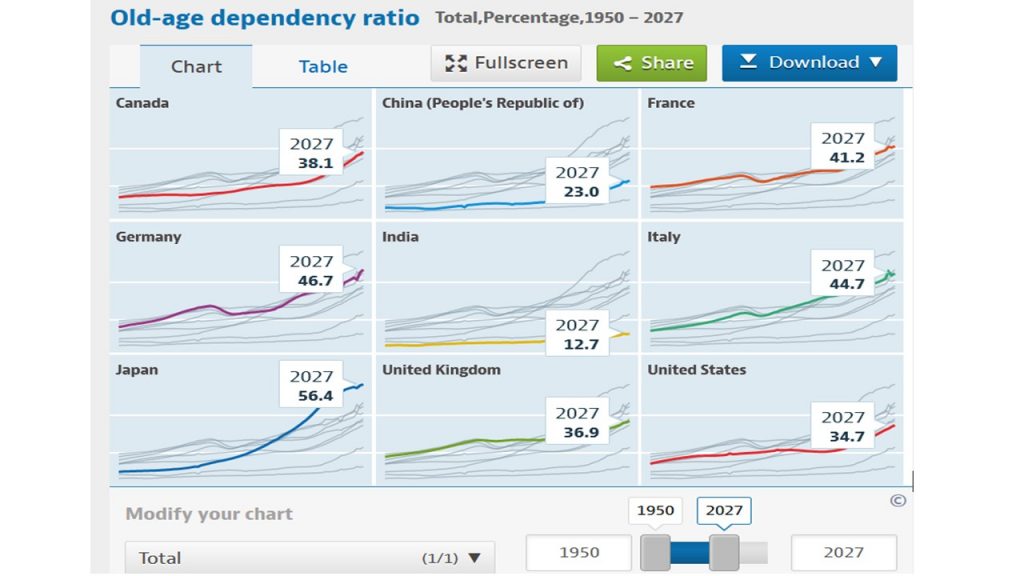
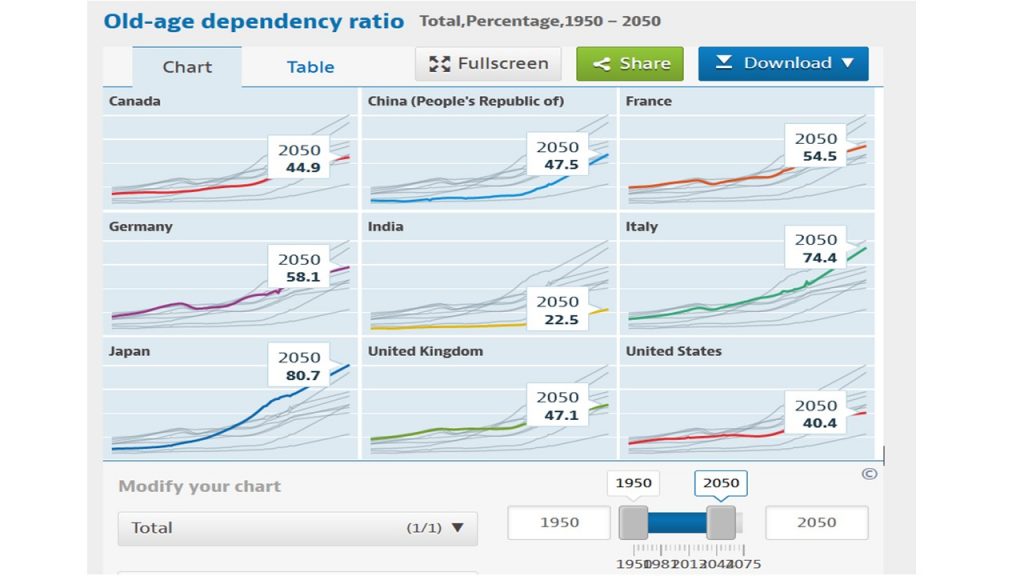
Several countries face an aging challenge now and in the near future. The OECD provides some basic data, figures and projections. All data to calculate the aging challenge are more subject to change than they used to. The Covid-19 rise in mortality rates has implications as the number of premature deaths of the elderly (65+) has risen even in the economically advanced countries. The so-called old-age dependency ratio is a widely used indicator to assess the charge or pressure on the working-age population (20 to 64) to finance those in retirement (65+). demographic ratio is defined as the number of individuals aged 65 and over per 100 people of working age defined as those at ages.
Major factors that have an impact on the ratio are mortality and fertility rates as well as migration, but also participation rates in employment for those younger than 20 or older than 65 years of age. Seminal shifts in participation of women in the labour force contribute also to reduce the old-age dependency ratio. An influx of about 1 million of refugees who have immediately a work permit like Ukrainians in Germany have a substantial impact as well. Life expectancy is expected to rise again after the years of reduction due to Covid-19. In 2024 and 2027 these ratios do not move too much. Extending the time horizon to 2050, when people born in 1985 would start to retire shows more reason for concern. Whereas in 2024 France, Germany and Italy are still fairly close to each other (2.4 percentage points), the gap starts to widen as of 2027 (5.5 percentage points). In 2050 Italy is projected to have an old-age dependency ratio of 74.4%, about 20 percentage points higher than France.
Okay, in the long-run we are all dead, says an economist joke, but changes to increase fertility or allowing more migrants in are not in sight for Italy. Therefore, the urge to react is increasing there. Younger generations might not be able or willing to foot the bill of high pension expenditure in Italy. Compared to Italy or even Japan the pressure on France is much less pressing, contrary to the national government’s opinion and policy initiatives to increase retirement age without parliamentary majority.
Source for projections and figures: OECD (2023), Old-age dependency ratio (indicator). doi: 10.1787/e0255c98-en (Accessed on 04 October 2023).
Nations Fail
Ever since Adam Smith wrote on the “Wealth of Nations” the topic concerns social scientists. The discourse around the wealth of nations has become even more fundamental these days. Beyond wealth calculated in economic terms we are convinced to add well-being of the population as well as the state of the environment into the accounting procedures like national accounts. But wait a second. Similar to the term wealth we have to widen our perspective in what is considered to be a nation. Shifting borders through wars (Russia aggression on Ukraine) or separatist tendencies of regions, (re-)unification of Germany or Korea (eventually) show that the nation is a concept in flux. Considering migrants from former colonies still as having residential rights in the colonising country shows, there is more to nations than a one size fits all nation concept.
Daron Acemoglu and James A. Robinson had published the book on “Why nations fail. The origins of power, prosperity and poverty” already in 2012. On the 3rd of October Germany celebrates its re-unification only because the Russian dominated German Democratic Republic (and the other Eastern European satellite states under Russian control) can be considered as a failed state. These Russian dominated states crushed private initiatives and build corrupt systems where party allegiance and hierarchical structures were overemphasised. Following Acemoglu and Robinson (chapter 10) the lack of diffusion of prosperity is likely to be the root cause. Even similar to the French revolution, which brought about tough measures of redistribution, the external threats to the post-revolution France demanded subscription of masses into armies to defend the young republic against aristocratic rulers in the surroundings. If monarchy in France is a failed state, the post-revolution France survives due to high identification with the republican idea. The Soviet dominated Ukraine is a failed state, but the Ukraine of today resists due to its willingness to defend its own republican ideals. To get virtuous circles of development started, inclusiveness across the board is necessary. Leave nobody behind, seems to be a shortcut summary. It is much easier said than done. Loosing younger generations in the sense that they no longer subscribe or feel part of an inclusive wealth of the nation is a highly dangerous path. Failed states have a history in failed inclusive social and economic practices. Democracies are at risks just as much as authoritarian nations. However, democracies have better institutional settings to address the lack of inclusion and in multiple ways.
When I celebrate the 3rd of October in the Federal Republic of Germany I celebrate (1) the accomplished failure of the GDR, its undemocratically elected elites, corrupt institutions and the failure of the thousands of willing collaborators of the Russia-backed regime; (2) the peaceful resistance movement, (3) the relatively short-lived humanitarian focus of the Russian leadership at the time to not send in the tanks and (4) the willingness of the FRG to support 20 million new citizens for many years to come (5) the allies of the FRG to accept the potential security threat of a strengthened Federal Republic of Germany, which might entail a shift in the balance of power in Europe.
And yet, even in 2023 we pose questions on what is the concept of failure, when authoritarian regime can still survive for sooo long and some still accomplish extensions. We keep questioning the sense of the term “nation” in modern times and across the globe. Too many wars are still fought in the name of a “nation” even if only a handful of military-supported leaders and single autocrats try to impose wars in the name of some rather vague or plainly mistaken claim of nationhood.
On the 3rd of October we celebrate that “nations can fail” opening a path into a more prosperous and inclusive society. Some nations fail, just because they were no nation in the first place. The GDR was such an artefact of international compromise as part of the overall “balance of power” and the Cold War. The result of this process gives so much hope to other divided nations (Korea) or nations under authoritarian oppressive rule.