Gas consumption in the EU has been reduced by about 20% since the beginning of Russia’s war on Ukraine. This is a considerable accomplishment and has been sustained for 2 years now. The major element in this has been the reduction of gas consumption in industry, but also households have successfully managed to reduce heating of rooms and water with gas.
Diversification of provision with sizable increases in the provision by the U.S.A is another element in the beginning of a trajectory of gas reduction in Europe. Germany as a major consumer of this type of energy supply is also making strides in shifting consumption. This is my short summary of the report by IEEFA.org in 2024-1. All electric devices like heat pumps could speed up the gas reduction further according to the policy recommendation by IEEFA in 2024-2 reducing costs of living and CO2 emissions further.
Data from Eurostat allow to compare monthly data across Member States. The overall trend is a market decrease with differential patterns of refilling supply capacities. Big countries in the EU made and continue to make a real difference compared to previous years (see table below). 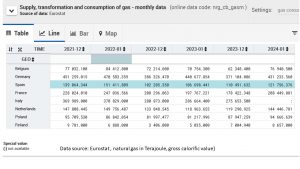 The comparison of December and January figures across years reflect the months with high sensitivity of the public for heat and cold. Further reductions of gas consumption is feasible due to the mild winter months of 23/24 which allow to reduce heating costs for many households and offices. Good news for the planet and hopefully a move in the right direction to shift away from heating with gas.
The comparison of December and January figures across years reflect the months with high sensitivity of the public for heat and cold. Further reductions of gas consumption is feasible due to the mild winter months of 23/24 which allow to reduce heating costs for many households and offices. Good news for the planet and hopefully a move in the right direction to shift away from heating with gas. 

