From time to time waste from so-called highly developed countries is making headlines and then it is forgotten again. Huge amounts of plastic waste gets shipped for example from the USA to Malaysia in containers regularly (NYT 2025-7-1). The dumping of waste in other countries where it is cheaper to waste the waste is a cynical practice. Not only is the potential for reuse and a circular economy disregard, the little control that is exercised how the waste is treated afterwards is neglected. Some might just end up in our oceans later on or find its way in our food chains. The recent discovery of lots of nuclear waste at 5000 m depth in the sea in another extreme example of this practice to dump waste affecting all of is when profits have been accumulated inn the hands of a few enterprises and states. Such external effects as they are called in economic theory are part of the standard economic thinking. The challenge is to detect such behavior, persecute or better prevent it. This calls on countries who produce the waste to check for the contamination potential and treat their own waste. Fukushima has lots of barrels of nuclear waste waiting. The pervasive nature of this waste will make it last for thousands of years. “Beggar thy neighbor” with your waste is a major default of our current economic and social model. It remains an unresolved puzzle why mankind continues to work towards its own extinction. (Image: Le grisou, Constantin Meunier, MRBAB, Brussels).





 The flowering season starts earlier in Europe and bees start earlier ro their collection of nectar and their service of pollination to other flowers. In early April 2025 in France near Paris we observe wild bees already in their daily routine. However, the risk of cold nights is still there, albeit those building their homes below the surface are a bit less at risk during a frosty night. Seeking a clever shelter is a good strategy for survival particularly at times of global warming. Some kinds of wild bees seem to sense this already changing homes from one season to next one. Humans remain their toughest enemies as they restrict their choices quite severely. Man-made pollution and herbicides are beyond bees’ control and cause havoc in the ecosystem of bees. Apiculture is an interesting science also for social scientists as this forerunner species of the matriarchy has evolved into a well-organized productive society. They are a bit harsh to each other and communication is rather unidirectional, but an interesting social cosmos of its own kind.
The flowering season starts earlier in Europe and bees start earlier ro their collection of nectar and their service of pollination to other flowers. In early April 2025 in France near Paris we observe wild bees already in their daily routine. However, the risk of cold nights is still there, albeit those building their homes below the surface are a bit less at risk during a frosty night. Seeking a clever shelter is a good strategy for survival particularly at times of global warming. Some kinds of wild bees seem to sense this already changing homes from one season to next one. Humans remain their toughest enemies as they restrict their choices quite severely. Man-made pollution and herbicides are beyond bees’ control and cause havoc in the ecosystem of bees. Apiculture is an interesting science also for social scientists as this forerunner species of the matriarchy has evolved into a well-organized productive society. They are a bit harsh to each other and communication is rather unidirectional, but an interesting social cosmos of its own kind.



















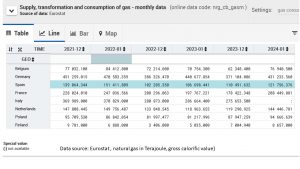 The comparison of December and January figures across years reflect the months with high sensitivity of the public for heat and cold. Further reductions of gas consumption is feasible due to the mild winter months of 23/24 which allow to reduce heating costs for many households and offices. Good news for the planet and hopefully a move in the right direction to shift away from heating with gas.
The comparison of December and January figures across years reflect the months with high sensitivity of the public for heat and cold. Further reductions of gas consumption is feasible due to the mild winter months of 23/24 which allow to reduce heating costs for many households and offices. Good news for the planet and hopefully a move in the right direction to shift away from heating with gas. 