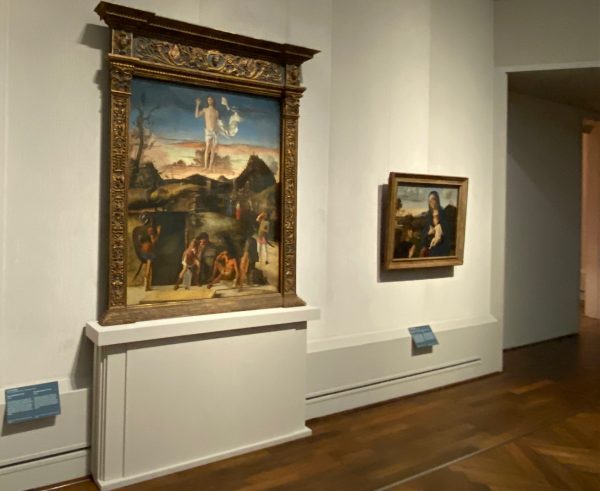
Not all art is utopia, but a lot of it. A series of talks on the issue of utopia in art (BNF) reminds us on the utopian projects many artists have pursued in the history of art. From a non-believer’s point of view, religious depictions belong to some form of utopian art. Much later art movements proposed to bring art closer to people’s lives by spreading decorative art to objects of the daily lives, like furniture, dresses, jewelry. Different forms of experimentation with materials or art styles reveal a taste for freedom of expression, sometimes of a utopian kind, at least at the time of experimenting. Abstract art opens up thought spaces which may appear like verylong shots into a very distant future. Science-fiction is of course a well known form of dealing with and representing utopian ideas to larger audiences. Maybe it is this curated space of utopia which many people seek when going to exhibitions and galleries. (Image: Giovanni Bellini, Resurrection of Christ, Gemäldegalerie Berlin).