Inclusive societies can build on many tools including AI to lower language barriers. It is not only a question of translation, but many other forms of language come to mind. Sign language or easy language are necessary to facilitate broader access to public services. Reading out texts on webpages or Braille translation for the blind to interact through keyboards are additional forms that are available in digital communication as well. The audio description of videos and images is well advanced (reverse engineered through AI) and allows people with limited vision to fully participate in society. Audio messaging and transcription are used by almost everyone by now. Public services will open up to these channels of communication as well. The technology around languages is much more than just translation and AI-assisted learning of languages (talkpal for example). The new lingua franca is language technology, because it enables us to speak many languages at the same time even dialects or lost languages and in many voices. (Image: Extract of Josef Scharl, the newspaper reader, 1935, Neue Nationalgalerie Berlin)
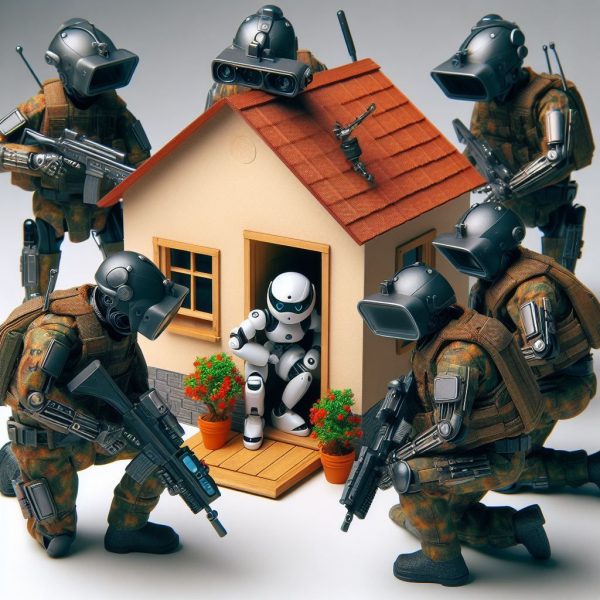

















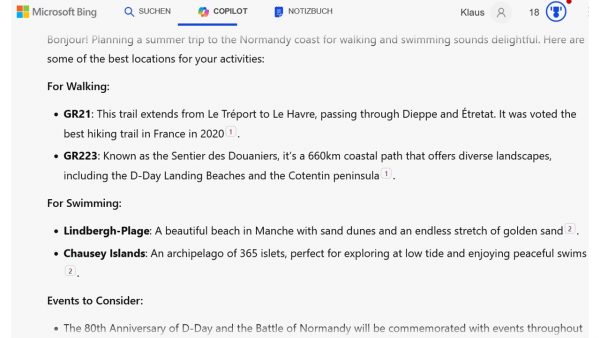

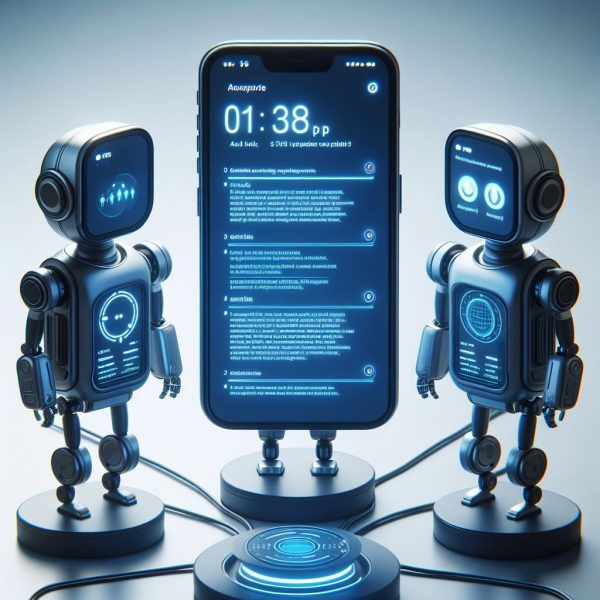
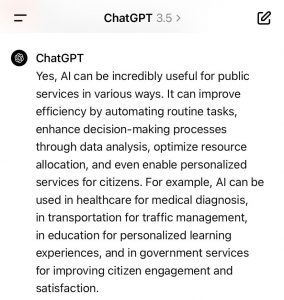 The AI ChatGPT is advocating AI for the PS for mainly 4 reasons: (1) efficiency purposes; (2) personalisation of services; (3) citizen engagement; (4) citizen satisfaction. (See image below). The perspective of employees of the public services is not really part of the answer by ChatGPT. This is a more ambiguous part of the answer and would probably need more space and additional explicit prompts to solicit an explicit answer on the issue. With all the know issues of concern of AI like gender bias or biased data as input, the introduction of AI in public services has to be accompanied by a thorough monitoring process. The legal limits to applications of AI are more severe in public services as the production of official documents is subject to additional security concerns.
The AI ChatGPT is advocating AI for the PS for mainly 4 reasons: (1) efficiency purposes; (2) personalisation of services; (3) citizen engagement; (4) citizen satisfaction. (See image below). The perspective of employees of the public services is not really part of the answer by ChatGPT. This is a more ambiguous part of the answer and would probably need more space and additional explicit prompts to solicit an explicit answer on the issue. With all the know issues of concern of AI like gender bias or biased data as input, the introduction of AI in public services has to be accompanied by a thorough monitoring process. The legal limits to applications of AI are more severe in public services as the production of official documents is subject to additional security concerns.
 (See image). ChatGPT provides a more careful definition as the “crowd” or networked intelligence of Wikipedia. AI only “refers to the simulation” of HI processes by machines”. Examples of such HI processes include the solving of problems and understanding of language. In doing this AI creates systems and performs tasks that usually or until now required HI. There seems to be a technological openness embedded in the definition of AI by AI that is not bound to legal restrictions of its use. The learning systems approach might or might not allow to respect the restrictions set to the systems by HI. Or, do such systems also learn how to circumvent the restrictions set by HI systems to limit AI systems? For the time being we test the boundaries of such systems in multiple fields of application from autonomous driving systems, video surveillance, marketing tools or public services. Potentials as well as risks will be defined in more detail in this process of technological development. Society has to accompany this process with high priority since fundamental human rights are at issue. Potentials for assistance of humans are equally large. The balance will be crucial.
(See image). ChatGPT provides a more careful definition as the “crowd” or networked intelligence of Wikipedia. AI only “refers to the simulation” of HI processes by machines”. Examples of such HI processes include the solving of problems and understanding of language. In doing this AI creates systems and performs tasks that usually or until now required HI. There seems to be a technological openness embedded in the definition of AI by AI that is not bound to legal restrictions of its use. The learning systems approach might or might not allow to respect the restrictions set to the systems by HI. Or, do such systems also learn how to circumvent the restrictions set by HI systems to limit AI systems? For the time being we test the boundaries of such systems in multiple fields of application from autonomous driving systems, video surveillance, marketing tools or public services. Potentials as well as risks will be defined in more detail in this process of technological development. Society has to accompany this process with high priority since fundamental human rights are at issue. Potentials for assistance of humans are equally large. The balance will be crucial.