In science we love citations. The whole issue about plagiarism is about use and abuse of citations. It is a core competence of scientists to properly cite the work of other persons who dealt with the same or similar topic. There are lots of conventions or ways of how to cite mostly defined by professional academic groups. How do we cite texts that originate from an AI-system? We shall have to establish ways of how to do this properly rather than to ignore the spreading practice of its use.
For the time being, we test AI-systems that provide references in addition to the text and even direct clickable links to the original work they use. The AI-toolbox is called “scite”. Your assistant by scite will draft a short note on a topic (for example: Minkowski space, see trial below) for you and provide the linked citations for follow-up. At the price of about 15 €/months it is affordable for students and young researchers. The texts generated will then, in many instances, acquire “intellectual property and publishing rights” by persons.
The ways to follow back on citations of AI-produced texts seems a trustworthy step ahead. The authors of millions of papers cannot claim more than the original ownership of the text. The academic mantra “publish or perish” has been turned into “publish and perish”. AI-enabled citations might alleviate the pain only a little bit. The profession of even university professors shifts as reviewer of texts from students to texts of machines.

Co-authorship Kafka
In science Co-authorship is a tricky issue. Therefore, many higher reputation journals list precisely who has contributed what to the paper. In the teaching and supervision of bachelor, master or doctoral dissertations it is imperative to scrutinize the original contributions of authors to the subject. There are huge differences between universities to the amount of innovation or originality that is required to award degrees or the publication of the research and results. Rüdiger Safranski published with Hanser 2024 an essay on Kafka which has 224 pages, but a 16 page long list of the sources of the copy-paste citations used from the orignal Kafka writings. By scientific co-authorship practice Kafka should claim co-authorship of the book and the costs of the „Process“ should be paid by the publishing house. However, I enjoyed the many links between comments and the originals next to each other. It is like a data analysis that sticks plausibly to the original data. AI still has a hard time to rival with these skills, although AI is catching up faster than many of us might believe or want to believe. From a social science perspective we might say the original work of maybe only 180 pages is inflated to make for a longer text of 240 pages. This justifies, probably, the publisher’s price (€26) and the marketing costs. On the other hand it becomes evident that Kafka has an enormous impact on writers and seems to take possession of them in an encompassing fashion. You move with him, but rarely beyond him. Tough lessons indeed from the publishing world.

Marketing bicycles
The marketing of bicycles has changed considerably over the course of history. Today’s narrative is more about the eco friendly impact of it. Historically the freedom aspect of free movement and emancipation of women was at the forefront. The collection of images in poster formats presented at the DTM in Berlin is impressive. The focus on women on bicycles is quite surprising for this early time around 1900. Few of the companies from the early days have survived until today. Bicycles are still fascinating children and adults today. The experience of a fragile equilibrium, your own strength and weakness in muscle power, cardiac or pulmonary strength is always challenging. It is you who is in control of speed and direction. This should be easy to sell to the masses, and it was and still is. “Bikenomics” is here to stay. Artists had the same impression and created a whole universe of promises for riders of bicycles. The long run health benefits were not even known at the time, but it was unthinkable that humans would spend most hours sitting in offices, cars and on their couches. The biking story needs to be retold to encourage people to take up the emancipating storyline again. Get on your bike again!

Bikenomics
There is a whole cluster of enterprises associated with bicycles. Selling a bike is only the first we might think of. Repair works are the most tricky part of bikenomics, a bit like bidenomics. In many cities during spring and summer it is even more difficult to get an appointment for bicycle repairs than for a doctor’s appointment, and that can be hard at times. Shortages of skilled technicians are pervasive in this sector. DIY for do it yourself is the best alternative. With the arrival of e-bikes and the digital connectivity the skill set has been enhanced recently as well. Insurance for bikes, lockers, helmets, airbag system or clothing including spectacles are part of the standard safety and security set of bicycle riders nowadays. Many, many job opportunities there and the willingness to pay for bicycles has steadily increased over the last years.
Berlin has just seen its 48th bicycle demonstration in 2024-6 on roads including 2 motorways with several ten thousands of participants. In a star like fashion multiple tracks met at the city center. The final meeting with stands and information was at the Deutsche Technik Museum with refreshments and repairs. The exhibition of cargo bikes and taxi bikes or “rickshaws” was another highlight. We need to rethink our mobility concepts and try to get the sharing to work more comfortably. For different purposes and activities you need a different bike. Ownership of each is no longer adequate as for example with aging alone your preferences for mobility with bikes also changes. Sharing is caring and this is also part of bikenomics.

Law Nature
There exists a rather complicated relationship between law and nature. It is part of constitutional law to check whether nature figures at all in a state’s constitution as part of the fundamental legal principles. On a global scale the nations or people living in the closest relationship with nature most often do not have written constitutions. In the same vein, animals or biodiversity do not figure in most constitutional documents (nice project to substantiate this claim). The philosophy of law has line of literature devoted to “Naturrecht” which is more concerned with human beings and their differentiation than the millions of other species.
Administrative law is probably the domain with most of the legal judgements with relevance to nature or the environment as for example any larger scale construction is either land, water, air or biodiversity grabbing. Rights and limits need to be defined precisely. In this field the role of law as “appeasement” is widely applied. However, this is more complicated in cases when a whole population of an island in the ocean is threatened to disappear due to the rise of the sea level like in the case of the Torres Strait Islands, next to and part of Australia.
The UN Human Rights Committee (UN-HRCee) in Geneva has made a decision on the claim of these people to have rights that the nature of the islands as low-lying islands is threatened by disrespect of their fundamental rights of existence and survival. The claim has been received by the court, but the court deems that the threat to their culture and survival is not imminent. In practice, therefore, the sword of law is rather weak and time until the disaster is used as a right to continue the usual economic exploitation of earth as before despite the deferred consequences for the planet in a rather unequal way.
(Image by AI copilot designer 2024-6-2 “5 judges in red gowns sit in a flooded courtroom”, 2 propsitions) 
Cars electrified
It is not only cars, but the whole automotive industry that got somehow electrified. The U.S. have imposed a 100% tax on electric cars produced in China recently. Europe is feeling the heat as well (compare Fressoz in Le Monde 31.5.2024). Production of cars is not a for fun activity. It is firmly embedded in our economic system which believes in profit maximization even at high environmental costs. Therefore, the production of cars follows the logic to build cars that generate the highest profits. Bigger cars yield bigger profits and this has been known for decades. Why should we expect our car producers to deviate from this logic. Investors push hard in this direction as well. Small e-cars generate small profits. This can only be economically valid if large numbers are produced. China’s home market has the market size and air pollution levels that make this a viable strategy also for the lower income people. If not sold in the US or Europe, the home market is able to absorb huge amounts of electrified cars. Downsizing of cars needs to happen particularly in inner cities. The implementation of this is not going to be easy and without resistance.

Library Search
Libraries have not only lots of books on shelves and in storage places, but scientific research makes use of lots of scientific journals as well. The direct access to these journals shortens the search for information. We tend to focus on certain sets of journals, which we follow regularly as well as some random choices. Libraries like the Staatsbibliothek in Berlin have the advantage of access to multiple scientific disciplines under the same roof. This facilitates cross-disciplinary research with access to the best available knowledge. This resembles university libraries where also a broad spectrum of disciplines is taught.
Moving from paper-based publishing to electronic publishing, it is obvious that libraries are part of this move. Printed journals disappear and the electronic versions are made available to the readers. 2 issues arise: (1) adapt your search strategy to e-search and reading on screens and (2) accept that your research leaves traces (and potential tracking of your activities) of what information is really used. User statistics are likely to have consequences in the medium term. All libraries want to know who are my readers and what kind of search strategies do they apply. Similar to some of the best scientific results that are an outcome of by chance findings the search in libraries is enriched through „random effects“ of search. On-shelf access to printed copies allows a rapid overview of a whole year of issues beyond the abstracts always available online anyway. It is so much faster than the online search that we shall miss the paper-based issues of journals for quite some time. At the time of artificial intelligence everywhere reading and writing might be overvalued as economists might say. Our search algorithms and use of libraries is evolving at the same time. The by-chance or random inspiration might move to other places.

Democracy celebrates
With all the bad experiences of Nazi-Germany and the failure to defend democracy in Germany against its fascist enemies in the 1930s, it was a pleasure to celebrate democracy in Germany together with a huge crowd. 3 days of information and party around the major institutions of democracy Parliament, government, federal governments, constitutional court and all ministries joining in with pavilions in the parks nearby allowed a bottom up feeling of democracy. Visiting the chancellery as well as the parliament in a single day shows the openness of these institutions and the ease of access to our political system. People of all ages and all walks of life strolled around and enjoyed the day. Freedom to voice your opinion was easy and many took their time to do it. Civil society organizations were a natural part of the show. We seem prepared to stand up for our democratic values and principles. This will be tested in all the forthcoming elections.

Competence Gardening
Primary Schools in Berlin have the possibility to participate in the “Gartenarbeitsschule”, the school with learning goal of gardening. It is an interesting option to go out into the real world and deal with nature, sustainability, consumption, climate and many other topics. Voltaire could complement the curriculum in philosophy with his biographical links to gardening. The access to the fields is easy next to one of the central train stations and a larger urban reforestation project as just one example of the 15 overall in Berlin in 2024. (Südkreuz, Südgelände). Hands-on experience of gardening can address multiple forms of problem-solving competencies. Beyond the use of AI, a major advantage is the possibility to train collaborative problem-solving. Beyond the multifactorial approach in determining what to plant, the organization of the implementation and individual contributions towards the realization, all these elements are learning goals. The scope of learning qualifies gardening for learning well beyond primary school as well. It is a nice example of lifelong and lifewide learning even a hundred years after their wider applications in Berlin.

Competence Handwriting
The acquisition of handwriting as a competence has been important for centuries. In primary schools this technique is exercised as a foundation for the performance in other cultural techniques like language writing and even calculus. Therefore, it has been beneficial to make sure children acquire basic competences in handwriting. This has not changed much, although the time devoted to perfection of the technique has been reduced over generations. We still have some memories of people who have made the handwriting or the pencils used a case of distinction. At the enlightenment period a lot of authors drafted their thoughts and manuscripts in handwriting and our museums or biographies are proud to show off handwriting of authors, artists or composers. In some of those we are able to retrieve the thought process behind the writing. The editing, crossing out, adding sentences or correcting words are traces to dive deeper into these creative processes.
Currently, we are less sure, whether in the age of AI we should still rely much on this old technique of handwriting. If we just treat it as one of many competences to be or become creative yourself, we are on the right track. The PISA studies by OECD include problem-solving as a crucial competence. Handwriting or drafting first steps of a solution might still be useful. A handwritten sketch of a solution might guide the elaboration of the more encompassing solution.
Another interesting feature of handwriting is the cross-cultural element of it. We feel easily compassion for a handwritten document. The psychomotor competence of handwriting is fascinating across continents. It has distinguished us from other species as well. The evolutionary steps are important elements of a learning process. Nostalgic feelings about handwriting do not help anybody, but children are well-advised to still keep an eye on their handwriting competence as part of or first step in problem solving, even if it is just to formulate the question they are interested in. 
Patient Empowerment
The empowerment of patients is a well-established practice in the treatment of diabetes. Measuring your own blood sugar and adjusting your medication to the self-monitored data is common practice. For patients with high blood pressure this patient empowerment is less prevalent. A medical study carried out in Valencia (Spain) by Martínez-Ibáñez et al. (2024) has tested the effects of such a self-monitoring and self-medication experiment.
The results publishes in (JAMA) gave rise to considerable attention in the profession as the empowerment of patients is one way out of the likely increasing shortage of medical professionals in aging societies. Whereas other studies found that total costs to the medical system might increase, the study in Spain provides evidence of the cost-reduction effect of such an empowerment. 24 months after the beginning of the trial. After the establishment of a “medication based on an individualized prearranged plan used in primary care” the self-administering participants achieved a significant decrease in their blood pressure that lasted until the end of the study after 2 years. The drop-outs of the study seem to follow a random pattern.
The conclusion gives support to the potential of patient empowerment in the widespread treatment of higher blood pressure beyond the regular visits of medical doctors. The monitoring of changes in lifestyle add to this to keep the costs of health care under control in aging societies. 
Image History
The archives of the history of movies and/or television show to us the multiple ways how images capture our attention and memories. Visual narratives are an own category of our personal and collective memory. The wide range of visual experiences are a powerful way to influence. Not only the movies and stories matter, but the whole range of images associated with the cinema world. Poster collections, newspapers and today the so-called social media multiply the original images. The Deutsche Kinemathek allows a special, critical understanding of image history as Germany has been using and abusing images and movies in a very manipulating manner historically. The message is: do not take images for face value. The ways and techniques to manipulate images have been widely used and are all around us today. Whereas the mass media in previous decades have dominated the collective memories we have entered into an era with many more subcultures that evolve within their own bubble of images. An original attempt to cut 65 movies of German film history into less than 4 minutes is presented in the exhibition (Milkowski and Simbeni). It focuses on gestures and “les regards”, “Blicke”, how the actresses and actors seem to look at us. Eyes capture attention, and this as soon as we open our eyes as children. Our brain works as image recorder and our memory algorithms tend to favor image recognition while processing images continuously. We do not know much about our own image sorting algorithm or algorithms yet. Research on aging of the brain gives some hints. With declining short term memory the images stored in long term memory take the upper hand. This makes an understanding of the history of images even more important.


Deutsche Kinemathek
Just in the vicinity of the Potsdamer Platz in Berlin you’ll find the Deutsche Kinemathek, the museum movies, actors, actresses, directors and the history of cinema in Germany. There is a small specialized library in the Kinemathek that allows to dive not only into journals and books, but also video material, scenarios and accessories. Of course, you will find a lot of material on all sorts of movie stars (heroines) over more than a hundred years. The “Divas” of the industry take up a large part of the exhibition. “Marlene Dietrich” much more than “Hildegard Knef“, the former born and the latter lived for a long time in Berlin-Schöneberg (Berlin-Pretty-Hill as some locals call it nowadays). The 2 Divas probably caused the funny translation. Anyway, the hall in the Kinemathek which is exclusively devoted to Marlene Dietrich impresses with a lot of glamour and mirrors around.
For those with not only a biographical, but also life course interest in cinema cherish the public access to the library. The most impressive table there is the desk with access to the Ukrainian movies and about cinema in Ukraine. A list with QR-codes allows you to readily approach the recent developments before and during the Russian aggression on Ukraine (See image below). After all Potsdamer Platz in Berlin was a hot-spot of the cold war period in the divided Berlin. A little bit of a “Metropolis-atmosphere” can still be felt. The Kinemathek explains well what this is all about. 
Killing me softly
The problem with pollution is, it is killing you softly from inside. It is almost impossible to escape air pollution as it is pervasive in cities, but also in the countryside where you do not expect it that much. This is the result of the study by Kuzma et al. (2024) published in “The Lancet Regional Health Europe”. Based on a data set of 8 million persons from Eastern Poland the effects of air pollution on myocardial infarction incidence was analysed. The use of the “European Union’s Earth Observation Programme” contributed data on air pollutants like PMs, BaP (benzo(a)pyrene), SO2 and NO2 concentrations. The multi-level data of 5 voivodeships, 101 counties, and 709 communities in Poland allows to differentiate the effects of damage to the heart tissue on cardiovascular disease. The other well-known factors are arterial hypertension, diabetes, obesity, chronic kidney disease, hyperlipidaemia, and smoking as most of us know already. The effects of BaP (benzo(a)pyrene) is shown for rural areas despite the lower observed traffic density in these areas. The killing occurs softly from within our bodies by just breathing in and out, and in and out continuously. The disease burden in these regions is observed with “recorded 63,154 hospitalizations and 5921 in-hospital deaths (9.4%) due to STEMI; and 76,543 hospitalizations and 4079 (5%) in-hospital deaths due to NSTEMI”. In short, the need to reduce air pollution further is an urgent demand that saves lives eventually.
(Image from public domain wikipedia or “do-it-yourself” here).

Attune Spheres
In Berlin it is easy to walk through the history of art to up-to-date contemporary art installations. Just walk from the Alte to the Neue and then to the Contemporary Nationalgalerie. With the installation and performance in the monumental Hamburger Bahnhof the artist Alexandra Pirici succeeds in an extraordinary way the combined impression of several art formats. I felt particularly attracted by the sound and resonance that the dancers achieved in the huge historical hall of the former train station. Embedded in a choreography that spans the whole hallway and the top of a sand dune, the ideas of „Attune“ bring in demonstrations of scientific experiments as well. We are reflecting on how structures, biological, physical or geologic processes coexist. It is another example of the intersection of biological, psychological and social phenomena. The links between science and art are more direct than what most people tend to believe. This encompassing experience catches all our senses and our mind. It is very likely that this intense experience in the museum space, which attunes our sensory perception of the artwork, sticks with us for longer than many other pieces of art. The 21st century will reveal an even more powerful language of art as it incorporates even more formats to grab our attention and imagination. The research of how patterns are formed is an important question for social scientists as well. All approaches to the subject are welcome and each one reveals our knowledge gaps despite remarkable progress. (Image: Hamburger Bahnhof, Berlin 2024-5-11, Alexandra Pirici) 
AI Racing
AI has entered the racing of cars after we have been racing horses, dogs and camels for many decades. The fact behind all these races is the huge market for gambling. Anything you can bet on will do for juicy profits in that industry. The recent “Abu Dhabi Autonomous Racing League” is the latest addition to the racing craze. Moving online with 600000 spectators at its peak on video and gaming platforms the investment seems promising. The only problem, AI is not yet ready to really compete with the world of real drivers. The progress, however, is astonishing. Just one lap of 2 minutes on the circuit yields 15 Terrabyte of data from 50 sensors. These are closed circuits so no person can enter or animal can get in their way. The challenge to integrate more data and faster processing as well as algorithms for fast decision making is steep. Great learning opportunities for advances in robotics. The hype has not been able to live up to the expectations as no real racing took place yet. We have replaced the gladiators of the Roman empire with Formula 1 drivers. It is only fair to retire those drivers soon and let AI race cars against each other. It feels like a computer game on screen and it is as we shall most likely watch these races on a screen as well. Hence, what is the point. Watching youth on TWITCH play racing games will probably not change the viewing behavior of the masses. The programmers have nevertheless great learning opportunities and will find their way rapidly into the job market. The other challenges of ASPIRE seem more important for humanity like human rescue and food for the growing world population. In the meantime let the boys play around with cars and learn about potentials as well as failures of AI-programmers and dealing with both.

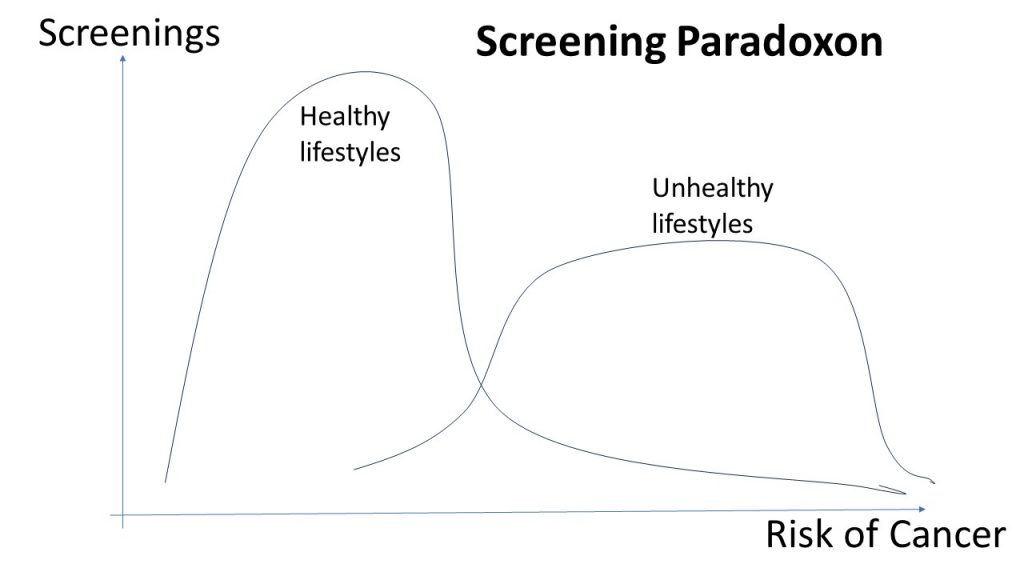
Screening Paradoxon
In the field of public health the screening paradoxon is a well-known feature of large scale programs to check for and contain the large increases in cancer among populations. A recent medical study underscores the necessity to curtail the screening paradox in Europe. The screening paradoxon is defined as “the underuse of screening by those with unhealthy lifestyles and high risks”. The opposite cases, “the overuse of screening by those with healthy lifestyles and low risks” only cause a problem for the costs of the health system as those unlikely of attaining a form of cancer make extensive use of screening. In terms of social inequality we have to be concerned about both ends of these distributions. The publicly available screening programs are skewed towards the higher educated with risk awareness as well as healthy life styles. More of them participate in screening. The other distribution of actual risks and detection of cancer is skewed towards the other end of the risk distribution. The 2 probability distributions overlap to an extent that is most likely co-determined by cultural factors like general attitudes towards prevention.
With the increase in cancer rates generally and due to demographic aging of societies, we shall need to target our resources devoted to health more precisely rather than spending too much on screening of people with very low risks. Increasing the duration between screenings might not impede detection rates of those with healthy lifestyles, but could allow to devote more resources to those people who are hard to reach by screening programs so far. Evaluations of such programs are necessary to judge the need for more targeted programs.(Image own representation inspired by Ola et al. 2024)
Barbie Chemical
Chemistry is sometimes perceived to be uninteresting, but only until you realize it might be beneficial to know more about some underlying chemical processes. The Royal Society of Chemistry has finally found a topic in chemistry to give chemistry a popular push. The Barbie hype is far from over as we all learned in the recent past. Now conservationists have found a topic with chemical processes involved to demonstrate the usefulness of chemistry knowledge for the conservation of your treasures or collections of plastic dolls or puppets in general. Most plastics PVC was not intended to last, but the deteriorated forms have a long lasting effect in form of PVAS or microplastics. So aging research has reached popular concerns like the aging of Barbie, who is believed to be “forever young”.

Comparative Advantage
In economics all students go through the calculus of comparative advantage. People, regions or whole countries tend to apply comparative advantage to their production systems and ensuing internal or external trade. The basic rationale developed by David Ricardo has not changed that much over 200 years. The fields of application, however, are continuously expanded. Lindsay and Gartzke (2020) have applied the comparative advantage rationale to military strategy. The paper quotes 26 times Clausewitz and demonstrates the links of strategy to the basic economic and social rationale of comparative advantage. It is the politics of production that even the presence of trade may override the rationale of comparative advantage to favour local production of “operational domains” or military equipment.
In Russia’s aggression and war against Ukraine own production and trading of weapons has returned to the forefront of the concerns. In addition to the production of ammunition, the provision of drones has dominated the international arms trade related to the Russian aggression. Resources and time for production are additional factors that have an impact on availability of weapons at the right time at the right place and with the sufficiently trained persons to operate them.
The strategies that cross domains or combine domains seem the most promising. The careful analysis of your own comparative advantages or disadvantages needs to be the basis of any strategic decisions. This has been known for 2 centuries at least and is still valid in many fields of application. Additional considerations for “home production” might add to the complexity of the issue. Sustainability has also found its way into the field of comparative advantage at last. This may alter the analysis of comparative advantage of operational domains as well. Lots of unresolved puzzles still around. It will need years to sort this out despite the urgency of the Russian aggression on Ukraine.(Image: AI Copilot.2024-4-30 2 political leaders deal weapons. One has a comparative advantage in ships. The other one has a comparative advantage in aircrafts. they deal together)

AI Disruption
Many scientists started to question the disruptive potential of AI in, for example, the military’s domain. The Journal of Strategic Studies featured 3 papers on AI and autonomous systems more generally. The major argument by Anthony King is the reliance of autonomous systems on other systems mainly human operators even in the background to get these systems off the ground and maybe back again. Not only logistic support but also satellite communication is needed to guide and protect the operations. In quoting Clausewitz, Anthony King stated that war is a “collision of two living forces”. Strategy and counter-strategy will co-evolve as will attack and defence.
Jackie G. Schneider and Julia Macdonald (2024) advocate the use of autonomous and unmanned systems for their cost effectiveness. Economic costs as well as political costs are lower for these new strategic weapons. Mass fire power from swarms of drones is much cheaper than nuclear warheads and the home electorate is assumed to be more willing to accept and support limited and more precisely targeted unmanned missions. The disruption potential of AI is huge but it is most likely an addition to the arsenals than replacing them. (Image 2 swarms of drones fly in the air above tanks, created by AI – copilot-designer 2024-4-29).
Hospital Bias
Asking people about differences between private and public hospitals, you are most likely getting answers that the private hospitals deliver superior patient outcomes. Whereas private hospitals seem to have a positive stigma attached to them, public hospitals commonly have a negative stigma. Scientific evaluations are helpful to set the record straight again. The study published in “The Lancet Regional Health” in 2024 shows that in the simple descriptive statistics on several patient outcome indicators, this is what the data showed between 2026 and 2019. However, a more precise statistical analysis reveals that there is also a selective admission to the private and public hospitals in England. Using so-called instrumental variables approaches that account for the selection process between admission to the 2 types of hospitals (private versus public) most of the differences between the hospital types disappear. The underlying mechanism is a sorting of different patients into the private or public hospitals. Put in easy words, for a routine intervention people tend to chose the private hospital, but the more rare and difficult operations were more likely admitted to public hospitals. The number of co-morbidities (heart disease) is also of importance as they might negatively affect patient outcomes. Jumping to conclusions and reinforcing stigma about public or private provision of services hinders progress and an equitable provision of services.
The analysis of a potential selection bias can reveal the “creaming” effect of private provision of (health) services. Just caring for the “easy” or routine cases and avoiding the more difficult and costly cases has economic advantages, but for society as a whole the costs overall remain the same. A good public service in health is a definite asset.
(Image: Exposition Isa Genzken 2023 in Neue Nationalgalerie Berlin)

Hannover Fair
The annual science fair at Hannover is a kind of a show of things to touch and of those things that come to the public market in the near future. Most of the annual hype is about potentials of production. Rationalization, using few resources or innovative solutions of digitization are high on the agenda. Create your digital twin, save energy, make production more safe or cyber secured.
Robotics is another reason to visit the fair. Some 7 years ago I had my Sputnik experience there. The robotics company KUKA had demonstrated live the that assembling a car from pre-manufactured components takes just 10 minutes for the robots. Shortly afterwards the whole company was bought by Chinese investors. Roughly 5 years later we are swamped by cars from China. It was not that difficult to predict this at that time. Okay, we need to focus on more value added production and take our workforces (not only) in Europe along on the way. Reclaiming well-paid, unionized jobs in manufacturing, as Joe Biden does, will not be an easy task. Robots and their programming is expensive, but skilled workers, too. Hence, the solution is likely to be robot-assisted manufacturing as a kind of hybrid solution for cost-effective production systems.
Following the proceedings of the 2024 fair we are astonished to realize that visiting the fair is still a rather “physical exercise” walking through the halls. After the Covid-19 shock we expected a lot more “online content”. Instead we keep referring to webpages and newletters rather than virtual visits and tours. The preparation of the visit in advance remains a laborious adventure. However, the in-person networking activities in the industry are largely advanced by ease of exchanging virtual business cards and the “FEMWORX” activities.
This year’s Sputnik moment at Hannover is probably most likely related to the pervasive applications of AI across all areas of the industry and along the whole supply chain. Repairing and recycling have become mainstream activities (www.festo.com). Robotics for learning purposes can also be found to get you started with automating boring household tasks (www.igus.eu).
Visiting Hannover in person still involves lengthy road travel or expensive public transport (DB with ICE). Autonomous driving and ride sharing solutions might be a worthwhile topic for next year’s fair. Last year I thought we would meet in the “metaverse fair” rather than in Hannover 2024. Be prepared for another Sputnik moment next year, maybe.
(Image: Consumer’s Rest by Stiletto, Frank Schreiner, 1983) 
AI Defence
For those following the development in robotics we have been astonished by the progress of, for example, rescue robots. After an earthquake such robots could enter a building that is about to collapse and search the rooms for survivors. A recent article in “Foreign Affairs” by Michèle A. Flournoy has started its thinking about the use of AI in the military with a similar 20 year old example. A small drone flying through a building and inspecting the dangers of entering for persons or soldiers. Since then technology has advanced and the use of AI for automatic detection of dangers and “neutralising” it, is no longer science fiction. The wars of today are a testing ground for AI enhanced military strategies. It is about time that social scientists get involved as well.
Warfare left to robots and AI is unlikely to respect human values unless we implement such thoughts right from the be beginning into the new technology. An advanced comprehension of what algorithms do and what data they are trained on are crucial elements to watch out for. According to Flourney, AI will assist in planning as well as logistics of the military. Additionally, AI will allow a “better understanding of what its potential adversaries might be thinking”. Checking through hours of surveillance videos is also likely to be taken over by AI as the time consuming nature of the task binds a lot of staff, that may be put to work on other tasks. Training of people and the armed forces become a crucial part of any AI strategy. The chances to develop a “responsible AI” are high in the free world that cherishes human rights and democratic values. Raising curiosity about AI and an awareness of the dangers are two sides of the same coin or bullet. Both need to grow together.
(Image created by Dall-E Copilot Prompt: “5 Robots disguised as soldiers with dash cams on helmet encircle a small house where another robot is hiding” on 2024-4-23) 
Digital Estonia
The progress of Estonia in going digital is quite advanced. The electronic identity card which allows data to be linked to health data and accounts or banking gives an impression of how far-reaching digitalization may go. Great steps have been taken to guide the population on the way to move towards the digital (only) world. Learning and coaching of a huge amount need to take place so that people do not abandon or get lost on the path towards “everything digital”. For the so-called digital natives, who have grown up with the sound of their smartphone at the bedside all the time, this move feels “natural”. Some experienced or silver workers got on track, if they were accompanied in suitable forms. The 65+ population might find it harder to adapt to the permanent use of digital devices for not only getting around in your city, but also to do your tax declaration, pay your dues and vote in elections.
Digitalization is not a goal in itself. It has advantages to reach communities in remote places or islands, but it might alienate older persons that have no other person around to assist them in the digital only world. An easy way to get some social science data to inform the debate is to refer to Eurostat and the surveys with information about the “overall life satisfaction” of people (EU-SILC). Checking for some major countries of the EU and neighbours of Estonia with less digitalization the differences are rather small. In terms of overall life satisfaction (16+ years old) Estonia has been catching up to the EU-average mainly between 2013 and 2021. Since then, stagnation at the EU-average is what the data tell. A quick testing of the hypothesis that the older persons (65+) might not see the past evolution as rosy is reflected in the EU-data as well. Good pensions seem to drive the “happiness” of older persons in the EU more than good digitalization. Eventually the two features of a society will have to go hand in hand to improve life satisfaction to higher levels. (Image: Data Eurostat EU-SILC Life satisfaction 65+, selected countries 2013-2023, retrieved on 2024-4-23, comparison with table all ages here, Data source)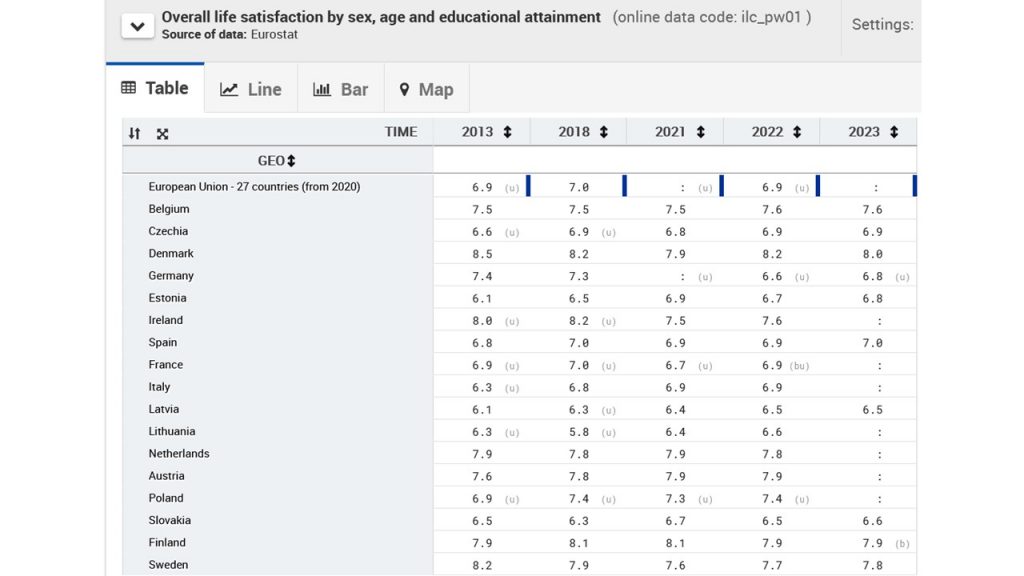
Electricity
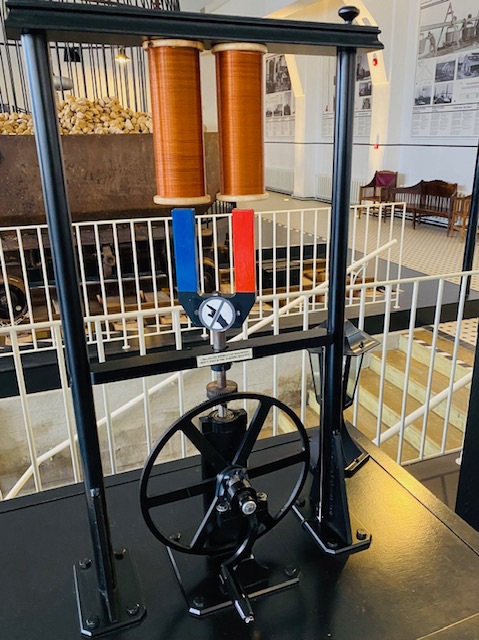
We all use electricity, not only daily but continuously. But do we really know or remember how it works? Surprisingly, we care very little about the energy provision or the physics behind it. Therefore, from time to time it is useful to dive into the details of generating electricity and thereby energy and how it arrives at our doorsteps or desks. In science museums you can literally walk through the history of power generation. A fine example is the Energy Discovery Centre in Tallinn, Estonia. Even for those you did all at school turning the handles of generators is a playful reminder of the basic principles of electric power generation. The efficient use of it, is a topic that needs to be covered as well. Searching the web for demonstration videos is fine as well, but the physical activity of moving induction coils and releasing sparks is difficult to rival. Opening up your mind for the physics of our lives yields a better grip on the challenges of electricity grids and local production of electricity. Are you already a prosumer? Combining electricity production and consumption in one household is surely a forward-looking strategy. Raising awareness for these topics concerns all generations. Take time for a power play, it is truly enlightening. For teaching professionals or want to be there are exciting programs out there, too. Just one suggestion for 2024 in Colorado, US.

Transparent Publishing
New technology pushes transparency of publishing, journalism and science to new levels. Through the hyperlink structure of texts it is easy to link back to the sources of a text. What used to be long lists of references at the end of a text or in footnotes has become directly accessible through weblinks. Only paywalls may or may not restrict the fast and easy access to original sources. In writing online, this is a major additional feature of publishing in the last few years. Some online journals allow this for quite some time now, but there are lots of printed versions that stick to the read and be stuck approach of publishing.
In teaching I have been an advocate of “read the original sources” as the basic source of inspiration for authors. The transparency of the thought process and the evidence provided in whatever form should be traceable. In publishing this transparency allows to exclude the copying of thoughts or unreflected referencing.
However, the task to check for the validity of weblinks and the updating is an additional task. 500+ blog entries with an average number of 2 weblinks per blog entry makes this a job of its own. Testing of 1000 weblinks is something you need a software or plugin which alerts you to “broken links”. The maintenance of a webpage, therefore, increases substantially as the content increases. Reorganisations of webpages make the follow-up of links sometimes quite hard. Projects like the general archives of the web and webpages are very important to ensure the transparency of publishing in the short, medium and long run. The archives of today look more like machine rooms than the splendid archives or libraries of the past and present. 
AI Reader
In the middle of the hype around AI it is useful to take stock of the reflection and evolution of AI. In my own analyses and writings on AI it evident that a narrowing of focus has taken place. Whereas before 2022 the writing dealt more with digital technologies in general. The links to the literature on the social construction of technologies was obvious. Algorithms and AI was a part of the broader topic of society and technology.
This has changed. The public debate is focused on “everything AI now”. We look at technological developments largely through the lens of AI now. Hence, my focus of assessments of technology from a societal perspective follows this trend. In a collection of blog entries on AI we try to demonstrate the far reaching changes that have started to have an impact on us. In the last few months the all encompassing concern about AI’s effect on us needs full attention of social scientists, policy makers, companies and the public at large. We can no longer leave this topic to the software engineers alone. By the way, they themselves ask us to get involved and take the latest advances in AI more seriously.
As a “flipbook” the online reading is rather comfortable (Link to flipbook publisher MPL). The pdf or epub files of the blog entries allow to directly follow the links to sources in webpages or other publications (AI and Society 2p 2024-4-18). The cycles of analyses and comments have become faster. Traditional book writing suffers from time lags that risk to make pubications outdated rather quickly. Dynamic ebook writing might bridge the gap between time to reflect and speed to publish or inform the wider public. The first update as .pdf-file is available here: AI and Society(2).


Repair Building
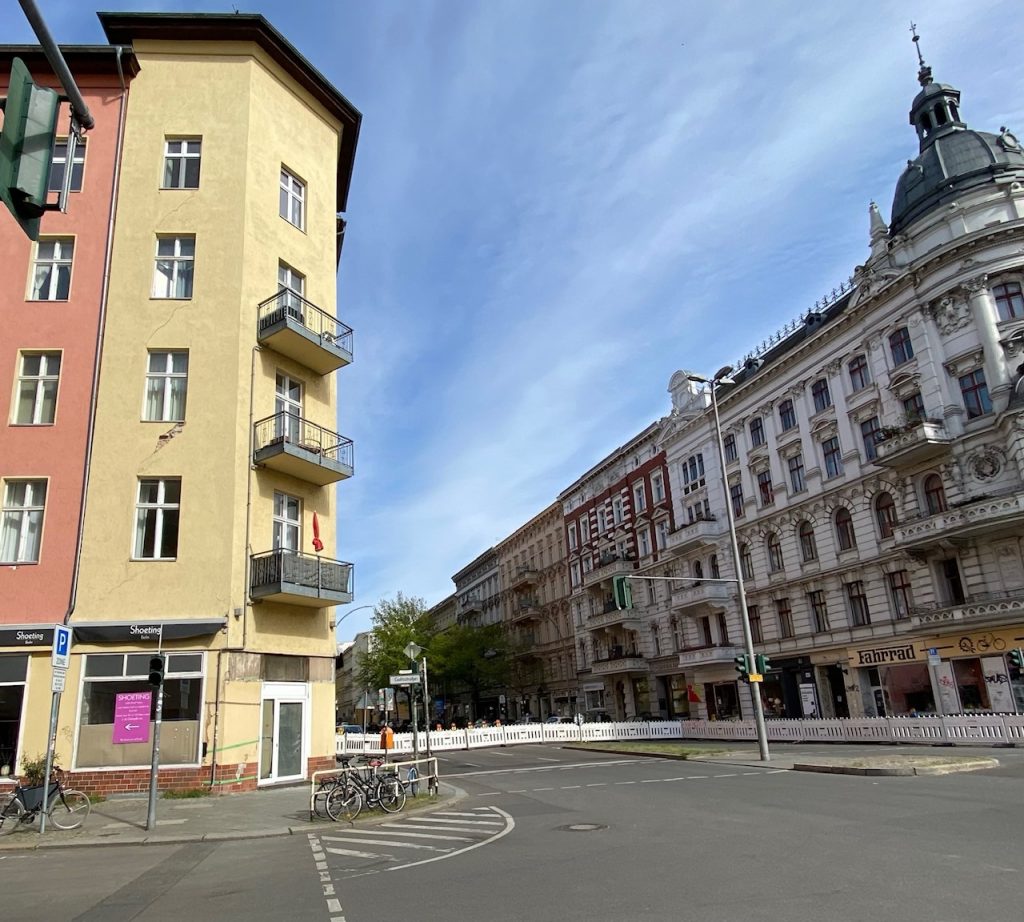
All buildings need repairs from time to time. For most of them the basic structure is solid enough so that isolation or maintenance will do. However, 100 years old buildings that have lived through 2 wars might have deep rooted deficiencies that are not visible at first glance. This can be observed in Berlin near the city center in a popular neighborhood with many visitors in „Schöneberg“ sometimes translated as „pretty hill“. The building at the crossroads seems to have been renovated only a few years ago, but the static of the building is so unstable that the city council has decided to block the whole crossing for circulation due to the danger of an imminent collapse of the building. The neighborhood has mixed feelings. It is great that the danger has been identified in time and blocking the road reduces the nuisance of traffic in the surroundings full of restaurants and cafes. The cover up of the repairs and renovation at the building is shocking as there appears to be just paint over basic structural faults. Construction work has failed to detect and prevent the static risks. An inspectorate that acts promptly to avoid bigger disasters is a societal asset.

Citizens Gardens
There are multiple ways to link citizens to gardens. Most people would link citizens to the property of their own garden. This is more the perspective of people from the countryside. The aim of citizens who can afford it have a garden, many others wish to have one and all of them enjoy public garden spaces. An intermediate version of the public versus private property of citizens’ garden is the joint ownership of groups of like-minded people to work together in the shared property or rented garden space. The recreational and health effects are well documented, if care is exercised with utensils etc. Spring is the ideal time to join projects again as the results of a little bit of gardening will be visible and enjoyable for several months afterwards. Gardens are also meeting points for people of all walks of life as in the vicinity of the European Parliament in Brussels. The Citizens’ Garden has a different function to people gardening there. When you puzzled about Europe after a visit to the Parliament or the Museum of the History of Europe, then it is time for a stroll and relax in the garden nearby.
Alternatively, the Exhibition Centre of Tour & Taxis in Brussels not too far away from the North train station has an impressive indoor garden for the times of rough weather conditions. At the time of the book fair culture in the indoor garden made a splendid combination. There is a green version of Europe. It is like a small plant. It needs a lot of time and care to grow. 
Causal Benefit Model
In the field of medicine we move more and more towards precision medicine. Previously, the term of personalized medicine was used which suggested to a certain degree that a personalization might be feasible. The budget constraints have forced us to change the term to avoid unrealistic, untenable promises. In the field of cardiology scientific advances advocate to shift from a risk-based model of treatment to a causal benefit model. (Kohli-Lynch et al. 2024 Link). Long-term benefits of a treatment are more promising, if the treatment addresses the causal mechanisms at work. It is wide spread practice to deal with general risk profiles as guidelines as the precision medicine based on a causal benefit model is far more laborious since to search the causal mechanism at work requires additional testing of hypotheses. This becomes immediately clear if genetic causes enter into consideration. Nevertheless, medical research advances more and more in this direction. Genetic testing has been shown to be useful in analyzing and treating issues like sudden cardiac arrest (in survivors). We are somehow aware that genetics may play a role here, but we shall need a lot of additional studies to make the causal benefit model a feasible option for widespread applications. Targeting research in this field will offer new avenues for precision medicine in the 2020s.