Der bürgerliche Flaneur wird kritisch hinterfragt und erweitert erörtert im Festival DRiFT in Berlin. Das passt doch gut zu dem nötigen WALK und WALKING, welches uns schon alleine aus gesundheitlichen Aspekten von Nöten ist. Die subversive Form als kollektives Wandern, gefährlicher historisch waren die Märsche auf Rom von Mussolini, friedlicher Gandhi, aber beeindruckend erfolgreich. Ostermärche kennen wir noch als Beispiel dieser kollektiven Form des gemeinsamen Gehens und Erkundens, oder doch Beeinflussung oder gar Eroberung.
Die Idee ist alt, die Ansätze in unserer Zeit bleiben eine Herausforderung. Protestmärsche kennen viele Organisationen gerade aus den nicht-regierungs Organisationen (NGOs) und den Gewerkschaften. Präsenz zeigen und seine Meinung äußern, wenn sie nicht genügend Gehör oder Widerhall findet, gehört zum demokratischen Kanon. Eine entsprechende Wiederbelebung und Stadtteilerkundung als “Psycho-geografie” hat historische Wurzeln in Paris und Frankreich. Räumliches Vorstellungsvermögen und Orientierung ist eine Qualifikation, die messbar ist. Eine Stadt erlaufen bildet eine kognitive Landkarte der Straßen und Umgebung. Mal schwer, mal einfach, aber fast immer irgendwie anders. 
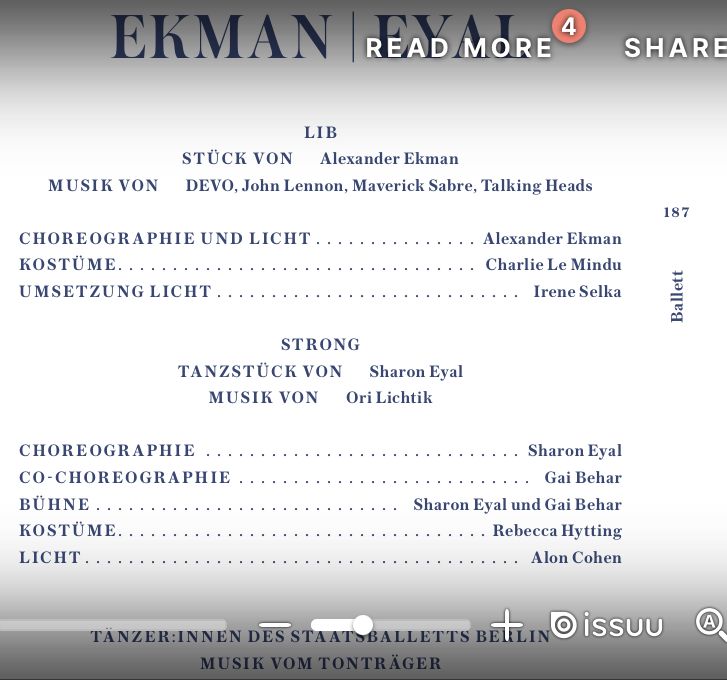
Ekman + Eyal
Die Ankündigung im Programm der Staatsoper in Berlin zur Aufführung von 2 Tanzstücken (1) Alexander Ekman und (2) Sharon Eyal im Programm spricht dementsprechend von Tänzer:innen des Staatsballetts Berlin mit Musik vom Tonträger. Das hohe Haus hat es mit den beiden Stücken geschafft, das reformierte Ballett in das 21. Jahrhundert zu retten. Dazu gehört neben neuen Bewegungsformen, die freieren Umgang mit dem Standardrepertoire des Balletts erlauben, auch die Musik der jungen Generation in die Staatsoper reinzulassen. Ja genau, dazu gehört Technomusik in der Staatsoper. Das Publikum hat sich deutlich verjüngt und so manchem älteren Herrn oder Dame fliegt da schon mal das Blech weg. Die Clubszene in Berlin hat ihre balletttänzerische Erweiterung gefunden mit ihrer Musik als Kunstform. Das gelingt besonders durch die Musik von Ori Lichtik „Strong“. Die provokanten Kostüme, die gekonnt mit Genderrollen spielen, ergänzen auf eindrückliche Weise die kraftvollen Ausdrücke der Tanzenden. Anspielungen an Maurice Béjart’s Bolero oder „Le sacre du printemps“ erfreuen Tanzbegeisterte. Gruppendynamik, Solo und Pas de Deux bauen dennoch auf dem klassischen Figuren- und Konstellationsrepertoire auf. Auch oder gerade in der Clubszene der Realität gibt es die Feuervögel, Flamingos und schwarzen Schwäne. Zur Vorbereitung auf den Tanzabend empfiehlt sich der Besuch in einem der Berliner Clubs. Gerne auch einmal wieder in den Berliner Zoo gehen und die Haarpracht der Orang-Utans in der Bewegung bewundern. Die uns genetisch sehr Verwandten haben uns in puncto Haarpracht, besonders auch im Alter, einiges voraus. Mehr Bewegungsfülle und Begeisterung für Bewegung wecken beide Stücke auf nachhaltige Weise. „Nobody leaves the room unmoved“. Ein bewegender, tänzerischer Abend Unter den Linden.
Visual
Key visuals have the potential to appeal to us like an own language. From a communication point of view the message is simple. You send a message from your visual appearance even if you do not intend to do so. Hence, better think about it briefly before you go public. The receiver might interpret your visual statement differently from you or other peers, but you offer a coherent version of your activity or appearance. Be it politicians (Merkel) or others, frequently memory allows only for key visuals to make lasting impressions or for something or someone to enter into collective memory of a decade or even a century. Repetition, also from different sources, plays a major part in this. It is surprisingly still uncommon to hire persons in charge of key visuals for a person, an organisation or a festival. Haphazard treatment of key visuals as part of marketing is probably an underestimation of the lasting impact of a coherent visual message. Stability and repetition are key here, rather than the wide-spread ad-hoc approaches to marketing. Only on the margin of the exposition devoted to Philippe Apeloig “Des esquisses à l’affiche” (BnF) this lesson can be learned. The merit of the exposition is the opening-up of the process of creation. Posters, graphics and typescripts all contribute to the overall visual message. Achieving coherence in the thousands of choices demands an aesthetic point of view. This may blend aesthetic languages of a decade and reflections on the subject. Catching an audience at the time of affluence of images, movies and accelerated rhythms of daily life remains a challenge. For the “Fête du Livre” Apeloig has achieved this in a memorable way, well worth a tiny exposition of donations from a master in visual communication. 
Mobil
Mobilität geht heute schon anders als für meine Generation oder vorherige Generationen. Selbst wenn Autos noch für viele in den Vorstädten und auf dem Land schwer verzichtbar sind, ist der Stadtverkehr im Wandel. Erst die Teslas, die einen scheinbar unaufhaltsamen Aufstieg als relativ saubere Alternative zu den Verbrennern darstellen und jetzt der Quantum aus Bolivien, wie der Wall Street Journal am 27.4.2023 berichtet. Sehr klein, noch ohne Heizung, gemütliche Stadtgeschwindigkeit als Maximum und knapp 100 km Reichweite für 3 mittlere Personen plus Chihuahua oder Dackel für gerade mal 7.500$. Das kosten 2 gute, flotte E-Bikes auch, nur werden die noch schneller geklaut als damit gefahren wird.
Für viele Städter sollte der elektrische Einkaufswagen genügen, dieser steht ja sowieso die meiste Zeit. Kleine Ausflüge ins Umland unternimmt der Städter eher selten, vielleicht noch zum Sport in jüngeren Jahren. Fernreisen werden meistens anders bestritten. Bus und Bahn bieten wieder wachsende Reichweiten, wenn es sein muss nachts. Hier kann weniger groß (auf 4 Rädern) wieder zu mehr Beweglichkeit führen, egal ob als Eigentum oder besser noch als Sharing-Variante. Von den großen Reichweiten mit Fußwegen in deutschen Städten sind wir noch weit entfernt. Das wird sich hoffentlich bald ändern. Bis dahin drehen wir Runden in kleinen Parks und verkehrsberuhigten Ecken. Wem es draußen mit dem Fahrrad zu gefährlich, kalt oder nass ist muss auf den Heimtrainer umsteigen. Mal sehen wie lange es noch dauert bis sich kollektive Vernunft durchsetzt. Verhaltensänderungen sind bekanntlich schwer und dauern wegen Rückschlägen lange. Wir bleiben dran am Thema der nachhaltigen Mobilität,  um unserer (Enkel-)Kinder willen.
um unserer (Enkel-)Kinder willen. 
Polypharmacy
Each specialist treats a person or patient in her/his field of competence to the best of current knowledge. Well, marketing of pharmaceutical products is also a field of special competence. Medical doctors and pharmacists are largely competent intermediaries between the world of medical and pharmaceutical research, commercial interests and patients. As persons age, so-called multimorbidity is creeping into the daily life of many persons. After a certain age (75+), depending on country of residence to some extent, we all become patients. Although the basic problem has been known since the phenomenal rise of the pharmaceutical industry, little research is devoted to patients receiving multiple treatments with medical prescriptions from several specialists. In addition, we know there is a rather severe issue with compliance to prescriptions, for example, taking antibiotics for the whole prescribed period, to name just one. The interactions between several prescriptions and molecules administered to patients are very difficult to monitor and scientific tests of those are expensive and no pharmaceutical company really has an interest in such studies that might further add to the already long list of potential side effects. However, the study published by Daunt et al. (2023) reiterates the warnings that treatment of multimorbidity can have unwanted side-effects we do not really know about. General practitioners will have to take on the role for medical stewardship for their patients. Monitoring a patient’s digestion of a combination of medications becomes a prime role as of the age of 75, the paper specifies. Whereas a common believe tells us, taking more, will help more, the “daunting” truth might be, less can be more. (Source: Daunt, R., Curtin, D., & O’Mahony, D. (2023). Polypharmacy stewardship: A novel approach to tackle a major public health crisis. The Lancet Healthy Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(23)00036-3. 
Pastiche
Die lange Tradition der “Pastiche“ (BnF, 2023) der französischen Presse ist nur wenig über Frankreich hinaus bekannt. Sicherlich kennen viele den wöchentlich erscheinenden „Canard enchainé“ oder die Satire-Zeitschrift „Charlie Hebdo“. Die witzigen, fälschenden Plagiate von bekannten Zeitungen und Zeitschriften, Pastiche genannt, haben einen Kreis an Liebhabenden, die sich ihren Humor nicht nehmen lassen. In Gesprächen gilt oft die humorvolle Sichtweise auf Politik, oder das tägliche Leben, als intelligent. Eine andere, unübliche oder gar verbotene Perspektive auf einen Sachverhalt kann ja bekanntlich zu einiger Erheiterung beitragen. Was sich seriöse Medien nicht erlauben, darf dann schon mal in den Pastiche vorkommen. Wie weit darf Humor gehen bis Humor verletzend oder gesetzeswidrig wird. Diese Grenzen sind je nach Kultur und politischen Gegebenheiten verschieden. In Frankreich lässt man/frau sich nicht den Augenzwinker verbieten. Übersetzen lassen sich die oft indirekten Anspielungen nur schwer. Viel Hintergrundwissen, oft nur von kleinen Gruppen von Personen, ist zum Verständnis nötig. Da wird vielfach erst auf den 2. Gedanken gelacht oder geschmunzelt. Die Bestände der BnF daraufhin zu sichten oder überhaupt die Kategorie zu führen, sogar als eine Literaturgattung, ist beachtlich. Nachrevolutionärer Karneval ist eben 365 Tage Narrenfreiheit. Das Recht und Gesetz dazu, wird wohl gut definiert sein. Majestätsbeleidigung wird es da nicht mehr im Strafbuch geben, was zu überprüfen ist.
Hannover Messe
Es war wieder einmal Hannover Messe. Das jährliche Treffen der Industrie mit samt der neuesten und manchmal auch älteren technischen Lösungen bietet eine eindrückliche Plattform zur Repräsentation von technischen Problemlösungen (offizielle Bilder LINK) . Da gibt es Lösungen für Probleme, bei denen wir noch nicht einmal wussten, dass wir sie haben oder einmal haben werden. So überrascht es nicht dort einige Firmen gelistet zu sehen, die ihre Dienste und Produkte anpreisen für die Unterstützung mit künstlicher Intelligenz, aber eben auch das Erkennen von Mogelei unter Zuhilfenahme von künstlicher Intelligenz. Also so ähnlich wie auf einer Automesse gibt es auch eine Abteilung die Rettungs- und Krankenwagen präsentiert. Technische Lösungen denken, wenn sie gute Lösungen sind, eben immer gleich ihr eigenes Versagen mit. Es bleibt letztlich nur die Frage, wie viele Versagensschleifen mitgedacht worden sind oder mitgedacht werden können. Der menschliche Faktor (als Fehlerursache) ist dabei ein sehr schwer auszuschließender Problemfall. Das musste nun auch die Hannover Messe als Ganze erfahren. Wenn die Menschen, die die Menschen hin- und wieder wegbringen vom Messegelände streiken, dann kommt das nahezu einem GAU (größtem anzunehmendem Unfall) gleich. Es gibt nicht nur menschliches Versagen bei Maschinenabläufen zu berücksichtigen, sondern auch mangelnde Kooperationsbereitschaft oder gar Böswilligkeit. Dabei sind wir nun aber schon in der Science-fiction oder James Bond 007 gelandet. Artificial Intelligence wird nicht frei von diesen allzu menschlichen Schwächen sein. Ein paar Gedanken sollten wir als Interessenten einer Fortbestehung unserer Spezies schon haben. Zwischenzeitlich lasse ich ChatGPD mal die Frage beantworten, wie Angestellte der Deutschen Bahn effektiv ihre Forderungen durchsetzen können. Kein Wunder, dass autoritäre Länder bereits mit dem Regeln von künstilicher Intelligenz begonnen haben. Ich zumindest habe viel Energie und CO2 gespart, denn der Messebesuch in Hannover fand virtuell statt. Deswegen dann auch keine eigenen neuen Bilder. Zur Produktion von Fake-Images oder recycling-Bildern früherer Messen (Photoshoppen) fehlt mir die Lust, Zeit und wohl auch die künstlerische vielleicht sogar kriminelle Energie.
Printing
Printing is a more than 5 century-old industry. The invention of the printing press is mostly attributed to Johannes Gutenberg from Mainz. However, the Asian precursor of mobile type letter printing of Cai Lun of the Jikji dates back to 1377 in Korea. These early masterpieces of the inventors of print can be inspected at the Bibliothèque nationale de France (BnF). The summary term for this technical innovation by historians is the “age of start-ups”. The procedure for Gutenberg to have 2 financing rounds with his “business angel” Johann Fust, who is later claiming even almost the full rights of the printed volumes, resembles the start-up spirit of today as much as that of the 15th century. Not belonging to the Patrician families, it was very difficult to defend your rights in courts of the gilds. The printers also became a very powerful intermediary themselves. They either sold pre-ordered books or had to take the risk of assessing the market for their product. The editors of today do much the same in the trading world of books and rights of authors and translators. Merchandising products of the church and later churches (protestants Luther Bible) had a particular value to both the clergy and its devotees, not to mention the shop keepers in-between as well. Pilgrimage business was another start-up industry still going strong in the 20th and 21st century and popular in all religions. The early prints and typographs applied are fascinating in themselves, but there is a lot to be learned about the foundation of a new industries that still employs millions of people and is at the origin of learning revolution similar to the one we are living with the digital technologies today. The European languages with respect to printing had a certain competitive advantage, based on 26 letters of the alphabet, far fewer types were needed to print books than the more than a thousand different signs for printing a Korean text. In terms of printing this is cost-reducing and probably you do not need to be able to read yourself to be a printer or it makes proof reading more accessible favouring benefit margins. After all, the age of industrialisation probably had a precursor in the printing industry. The potential of the printing industry was only exploited much later to the full extent. Comparable to “peak oil” we hope to have reached “peak paper” at last as well for the sake of our planet and our own survival. 
Photo Album
There have been many attempts to write a history of photography. Susan Sonntag’s account of photography and photographers remains the most successful one in my opinion. It includes a critical view on the medium just as much as capturing the power-related element of images and particularly photos. “Ouvrir l’album du monde” traces the history of photography from 1842-1911 starting with the invention by Louis Jacques Mandé Daguerre of the “daguerréotype” (Great press dossier Link to pdf-file). The attempt to “de-center” the history from the dominating western perspective is interesting as it reflects the spread and acquisition of the new technology by various “ruling groups” across the planet. Images like photos served and still serve often as proof (so easy to produce fakes and fake news nowadays). Proof of variety of existence of species, mankind, land acquisition and landscapes. Images of religious ideation, frequently forbidden, have been captured on photos. Many photos use up-front and profile perspectives on the same face, like police registry or the ethnographic documentations. This puts the visitor in an awkward position of “complice” to the process, judgement or documentation effort of a ruling more powerful class or colonial occupier. Historical embedding is necessary to balance the voyeurism of the camera. The film “Der vermessene Mensch”, reviewed in The New York Times recently, is a timely warning, how science and photography have served to create hierarchies of people, despite the fact, that “all men are created equal”. 
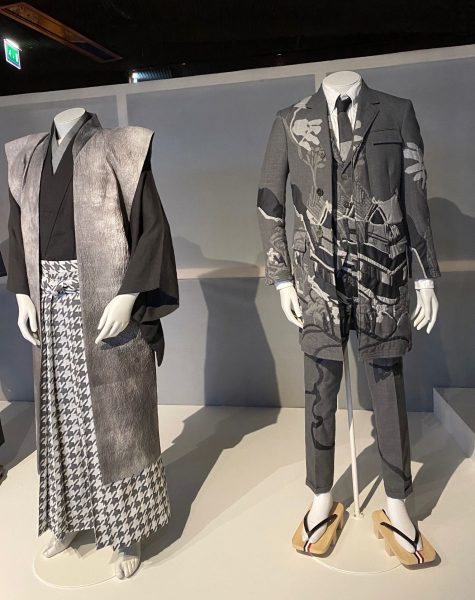
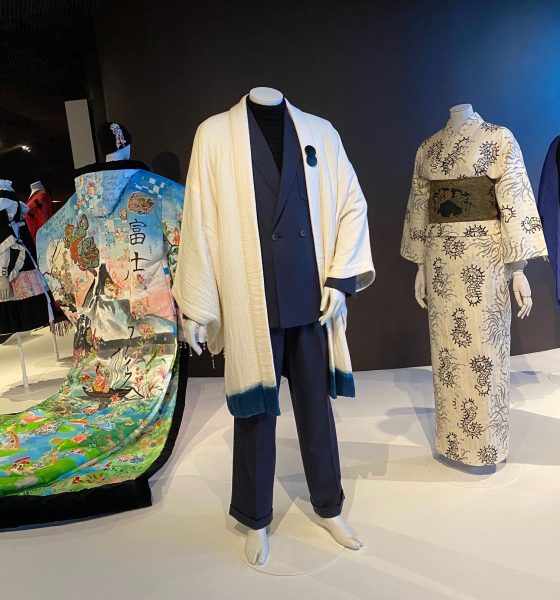
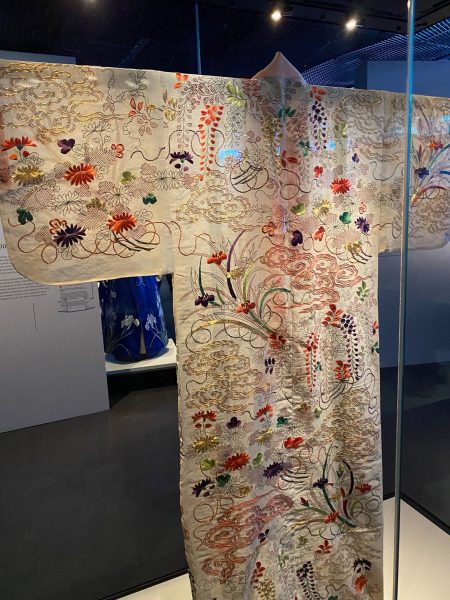
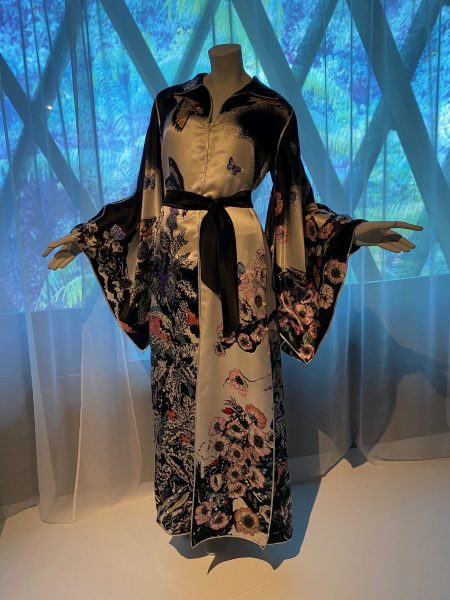
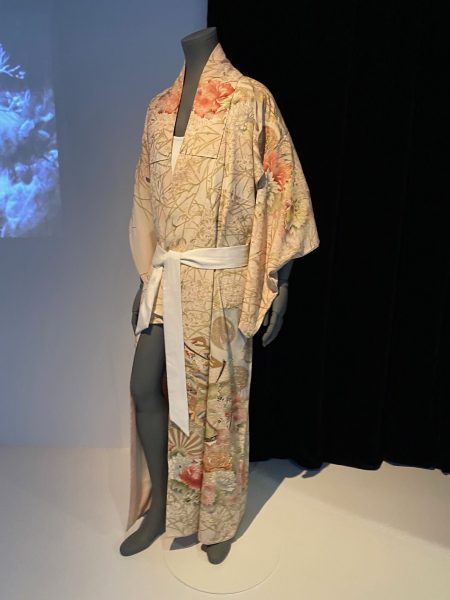
Kimono
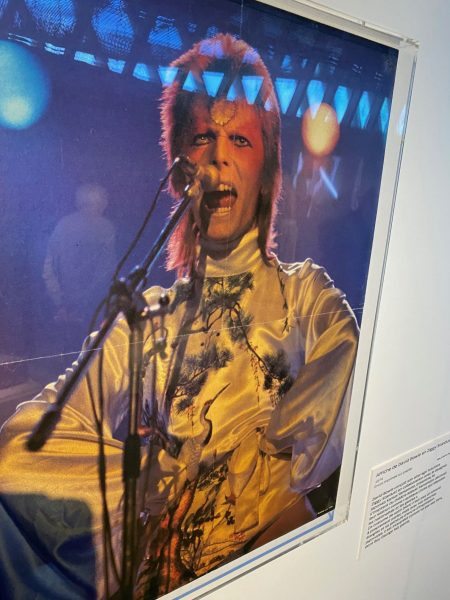
Die Ausstellung zur Geschichte, Kultur und Vielfalt des japanischen Kimonos ist beeindruckend. Natürlich kennen wir alle den Kimono aus Kinofilmen oder Fernsehen. Eine kleine, feine Sammlung wird noch bis Ende Mai im “Musée du quai Branly“ gezeigt. Die Betonung liegt dabei auf der Adaptationsfähigkeit des klassischen Kostüms. Selbstverständlich war der Kimono immer schon ein Gewand der sozialen Distinktion. Kleider machten und machen Leute, nicht wahr? Für das deutschsprachige Publikum ist der Rat der Designerin Shibasaki Rumi, die ihre eigene Marke Rumi Rock in Japan hat, interessant. Der Kimono könnte auch problemlos mit Birkenstock Sandalen kombiniert werden, für alle, die keine „japanischen Geta Sandalen“ und passende Socken im Schrank haben. „Cross-cultural fertilisation“, der Kimono ist wandlungsfähig und bringt nach wie vor exotischen Touch mit sich. Damit lässt sich vortrefflich überraschen. Das wusste schon Pop-Ikone David Bowie in den 1970-ger Jahren für sich zu nutzen.
Musée quai Branly
“Musée du quai Branly – Jacques Chirac” receives relatively few visitors compared to the much more popular art museums in Paris. The proximity to the Eiffel tower, however, allows easy access within walking reach from the most visited tourist attractions in Paris. A cheeky impression of the design of the building and surrounding gardens of the Museum resemble to me a shadow of the Eiffel tower in the afternoon sun in Paris. Some might even say with a westerly wind the tower would fall exactly on the museum. No, of course the tower is not tumbling. In the shadow of the tower there is superb place to meditate in the gardens or enjoy the many exhibitions of cultures from across the world.  In remembrance of former President Jacques Chirac, Asian cultures have had a strong impact on the collections and the organisation of the garden. Very different from the French park “à la Le Notre” at Versailles or Fontainebleau, the garden of the museum du quai Branly follows a completely different design focusing on bio-diversity. The architect “Jean Nouvel”, is quoted having said, that the garden is not a complement to the museum, but the garden is the museum. Hence, it is possible to have very unexpected views not only from the museum buildings, but also of the Eiffel tower nearby. It is possible to view the Eiffel tower through different continental perspectives on it. To the extent that you might not even recognize the massive tower in the neighbourhood being immersed into wild life. Then try one of the special expositions or the permanent exhibition, if visiting for the 1st time. We travelled continents without devastating CO2 effects. Additionally, Paris is easy to reach by train. You may complement the intercontinental experience by visiting the headquarters of UNESCO, at least the book shop, in Paris also nearby.
In remembrance of former President Jacques Chirac, Asian cultures have had a strong impact on the collections and the organisation of the garden. Very different from the French park “à la Le Notre” at Versailles or Fontainebleau, the garden of the museum du quai Branly follows a completely different design focusing on bio-diversity. The architect “Jean Nouvel”, is quoted having said, that the garden is not a complement to the museum, but the garden is the museum. Hence, it is possible to have very unexpected views not only from the museum buildings, but also of the Eiffel tower nearby. It is possible to view the Eiffel tower through different continental perspectives on it. To the extent that you might not even recognize the massive tower in the neighbourhood being immersed into wild life. Then try one of the special expositions or the permanent exhibition, if visiting for the 1st time. We travelled continents without devastating CO2 effects. Additionally, Paris is easy to reach by train. You may complement the intercontinental experience by visiting the headquarters of UNESCO, at least the book shop, in Paris also nearby. 
Bauhaus Haus
Zu den Ursprüngen des “Bauhaus” in Weimar gehört das Haus, welches die Feder von Georg Muche entworfen hat. Auch wenn das Bauhaus überwiegend mit Walter Gropius assoziiert wird, ist die Parallele von Georg Muche zu dem französischen Maler und Architekten Le Corbusier frappierend. Beide waren geprägt durch die eigene Malerei und Zeichenkunst. Die Entwürfe für Häuser oder Villen folgten Zeichnungen, die wiederum einer “cognitive map” mit Prinzipen der Konzeption und der Konstruktion folgten. Treu den Ansätzen des Bauhauses verwirklichte Muche bereits in 1923 sein Musterhaus. Modulare Bauweise, preisgünstige Erstellung, aktuelle Technologie, perspektivische Blickwinkel und Lichtspiel. Eine gewisse Parallelität zu der Villa La Roche und Jeanneret von Le Corbusier besteht nicht nur in der zeitlichen Dimension, sondern auch in dem Einfluß von kubistischem Spiel mit Perspektiven in Haus und auf das Haus. Die von der Malerei herkommenden Architekten entwerfen ihre Räume mit “The painter’s eye“. Vielleicht kommt nicht zuletzt daher der Traum vom Eigenheim, der so prägend bleibt in ganz Europa und der westlichen Welt. Geprägt von den 1910er und frühen 1920er Jahren war kostengünstiges Bauen eine wichtige Rahmenbedingung. Relativ kleine Grundrisse, modular erweiterungsfähig, preiswerte Baustoffe sorgten trotz Schwierigkeiten für rasche Realisierungsmöglichkeiten. Eine gewisse deutsch-französische Parallelität drängt sich auf. LeMonde vom 6.4.2023 beschreibt ausführlich das Dilemma des 21. Jahrhunderts. Der Traum vom eigenen Haus wird für die nächsten Generationen schwieriger zu realisieren sein. Rohstoffpreise, Grundstückspreise, Arbeitslöhne, Kreditzinsen schnellen in die Höhe. Der Traum vom Eigenheim bleibt ein Traum älterer Generationen oder der glücklichen Erben solcher Häuser, fast unerreichbar für Durchschnittsverdienende. “Gemeinsam statt Einsam” ist die noch gültige Schlussfolgerung, die bereits Henning Scherf formuliert hat. Die neue Herausforderung für den Bau war, ist und bleibt die soziale Frage, der wachsenden Ungleichheit entgegen zu wirken. 
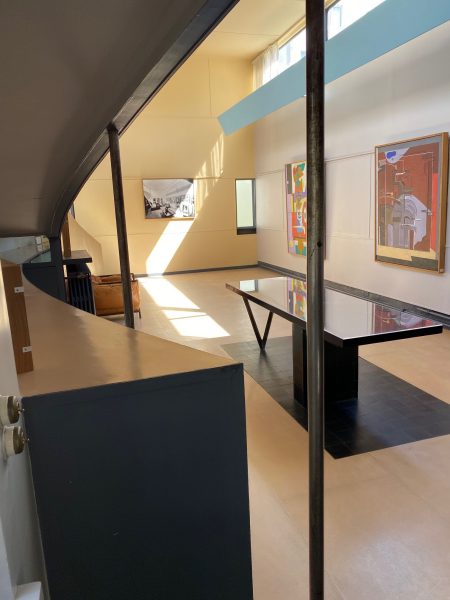
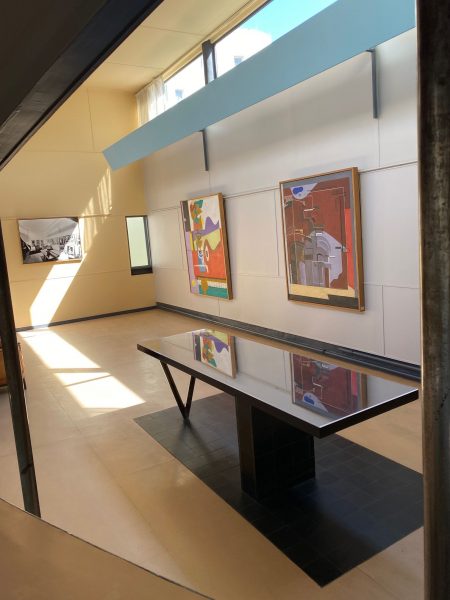
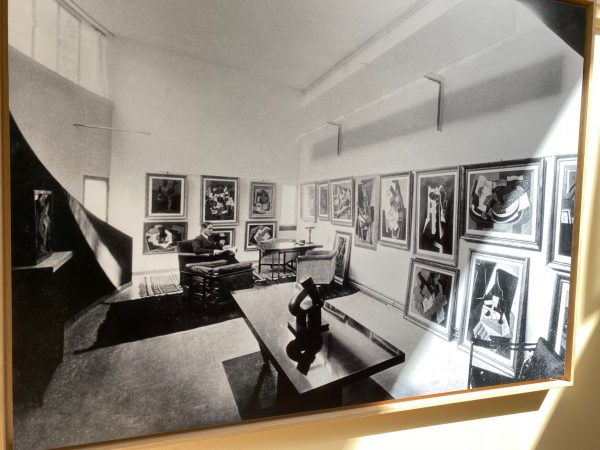
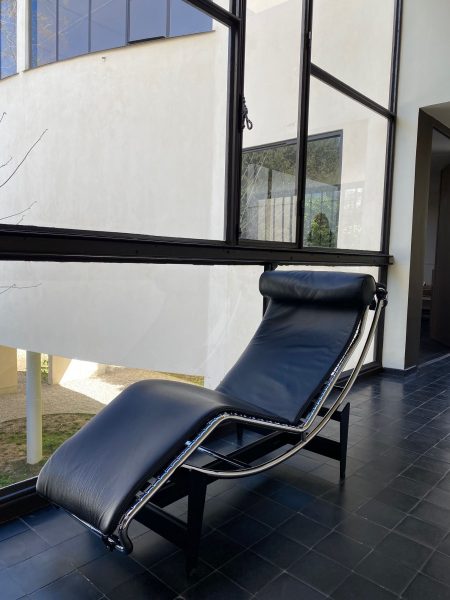
Corbusier
Le Corbusier (1887-1965) chose his artist’s name instead of his lengthy original name of Charles-Édouard Jeanneret at the age of 33 (in 1920) after having moved from Switzerland to Paris in 1917. He established a theory of modern architecture often summarised in his 5 major principles of modern architecture: 1. Pilotis as grid of pillars, 2. freeing ground floor design, 3. more open facades, 4. windows stretch horizontally, 5. garden, terrace on the roof. All these principles allow a more healthy living environment due to more light, less humidity in buildings and ease of circulation. The house Le Corbusier designed features surprising effects of light and lightness of living. “Les maisons La Roche et Jeanneret” date from 1923 and was completed in 1925. These purists Villas breathe thanks to the impression of abundant empty spaces despite relatively small surfaces. One Villa is designed for a small family, the second for a single person (Raoul La Roche) with a collection of paintings to be exposed in a small gallery. The focus on essentials of living, health, light, water, air and art combine to a relaxing and inspiring atmosphere. Despite many of his convictions to build affordable housing for many people, which received mixed success, his “maisons bourgeoises” in Paris and elsewhere remain masterpieces beyond the 1920s and the 20th century. Le Corbusier was concerned about tuberculosis. Today the corona-crisis has reached comparable health concerns. Architecture might react to the latter crisis in re-considering the lessons from the former. Relaxing in a Le Corbusier Chaise longue and meditating in front of a Picasso, Braque or Léger painting is indeed more than a little bit elitist. But copies of such images or your very own slide show or museum VR-clip in this surrounding make this experience more affordable and compatible with living arrangements for millions of people of the middle class as well.
Architecture
Architecture is all around us. However, we rarely consider the build environment as “conditioning” feature of our life. Architecture is contributing extensively to our perception of “social space” (Bourdieu). Inner cities, suburbs or spacious residential areas have diverse impacts on our perception of, for example, security, modernity, health or sanitary sensations. The corona-crisis has made it clear to most people that a healthy environment is a very essential part of our perception of comfort. Here the psycho-social perception of living and/or working space enters into the co-creation of housing people. Technology is a big driver of change in housing, urban spaces and rural imagination. In order to avoid corona infections a new culture of working from home for the masses become a health-driven imperative. Payment without contact, home delivery of meals, food, books, medicine have changed the living style of many people. Too little movement for our bodies has caused another silent pandemic of obesity. Enough reasons to rethink architecture from a sociological perspective on it. This probably starts with speaking of architecture as architectures. By this we mean to think of architecture from its social origins, functions, impacts and perceptions. Great historical examples of architects have implicitly or explicitly formulated a social theory of architecture or space as the basis of their “concrete” realisations. The sociology of professions of architects and the many construction-related professions needs empirical foundation beyond the cliché of socialisation as artist versus technician. Still recent forms of participatory democracy as part of urban and rural planning as well as realisations. Participatory individual or community housing are likely to stay with us. People want to get involved in co-creating their living and working space as their social environment. Architecture as social process and specific layer of the network society will be the new mantra. It has always been there, implicitly. Up to us to strengthen the social discourse on architecture. 

Wasser im Wald
Wasser im Wald hat viele Funktionen. Historisch erleichterten Wasserstellen an denen sich Wildtiere genüsslich im Morgengrauen laben, die Jagd des erschöpften Monarchen. Einfache Ziele, die jeder Jagende sich zu nutzen machen kann. Kleine Seen dienen aber auch als Wasservorrat beim Löschen von Waldbränden und nicht nur den Badenden im Sommer. Viele kleine Seen in Frankreich leiden an erheblicher Wasserknappheit. Wasserstände, die sonst im Spätsommer erreicht wurden, nach Trockenheit und Verdunstung, sind im Frühjahr 2023 berreits erreicht. Ein Waldbrand könnte kaum mit vor Ort vorhandenen Wasserreserven gelöscht werden. So hängen Feuer und Wasser im Wald recht eng zusammen. Austrocknende Seen vernichten zusätzlich die Biodiversität im Wasser, denn weniger Lebensraum im Wasser hat Konsequenzen. Das heizen mit den Motorrädern im Wald, hab ich selbst gemacht vor vielen Jahren, ist heute eh schon verboten. Aber Verbote und Jugend sind ein eigenes Thema. Wir haben der Jugend die Freiräume geraubt, die wir noch hatten und jetzt beschweren wir uns über die stubenhockenden Jugendlichen mit ihren Computerspielen und Social-Media-Aktivitäten!?! Ein völliges Überdenken des Wassermanagements ist von Nöten. Das sind wir den nachfolgenden Generationen schuldig. Welche Arroganz besitzen wir, dass die Jugendlichen von Heute viel klüger und noch schneller erwachsen sein sollen als wir selbst in diesem Alter. Aus Fehlern lernen wir, aber wir scheinen das Lernen, den späteren Generationen überlassen zu wollen. Leider funktioniert das so nicht, wir müssen schon an unser Verhalten ran und von uns verursachte Schäden selbst reparieren. Das Fegefeuer brennt schon, ob wir es noch rechtzeitig löschen können? 

Feuer im Wald
Das sogenannte grüne Lunge kann immer öfter ihre wichtige Funktion der Klimaregulation nicht mehr wahrnehmen. Waldbrände begleiten den Klimawandel. Bereits 2018 gab es ein großes Feuer im Wald bei Paris. Im “forêt de Sénart” in der Nähe der Städte Montgeron, Yerres und Brunoy (nahe Paris) hat sich der Wald seit dem Feuer im Hitzejahr 2018 noch nicht erholt. Geld für Reparatur der Schäden fehlt und so lässt die notwendige Aufforstung auf sich warten. Der Verlust der Biodiversität durch den Brand lässt sich schwer bemessen. Brandrodung, gängige Praxis im Amazonasgebiet, hinterlässt auch bei uns mehrere ungewollte Folgewirkungen. Die Bewirtschaftung des Waldes hat die Schäden abgeschrieben, aber Zukunftsinvestitionen lassen auf sich warten. So heizt sich die Region Ile de France eben weiter auf und Millionen Käufer von Klimaanlagen. Die befördern in naher Zukunft das Wirtschaftswachstum, aber beschleunigen den Klimawandel. Wir wissen, dass es so nicht weitergehen darf. Nur der Wille, wirklich etwas daran zu ändern, fehlt an vielen Orten. Weiterso, wenn es kein Weiterso geben darf, ist die Schizophrenie unseres und des letzten Jahrhunderts. Lernen im und vom Wald ist nötig. Das ist unsere Lebensgrundlage. 

Schaukel
Sagt die Lehrperson zur Schulklasse: Stellen wir uns alle jetzt mal alle eine Schaukel vor. Wie sieht die Schaukel denn so aus? Was gibt da so drumherum? Könntet Ihr nun bitte versuchen, die Schaukel auf ein Blatt Papier zu malen? Jeder hat seinen Bleistift und einige Buntstifte dabei. Einfach mal versuchen, es gibt keine Noten dafür. Es soll Spaß machen und wer möchte kann sein Bild anschließend den anderen zeigen. Schön, sofort wird es ganz laut in der Klasse und alle legen los. Naja, fast alle, das stille Mädchen aus einer der hinteren Bänke stockt und wirkt unruhig. Sie ist erst seit einigen Monaten in der Klasse und spricht noch nicht wirklich wie die anderen die Ortssprache. Da liegt wohl an der langen Reise, die die nicht mehr ganz so Kleine hinter sich hat. Die meisten Jungen und Mädchen erklären zugleich recht lautstark welche Schaukel sie malen werden. Die vom Garten hinterm Haus, vom Spielplatz nebenan oder sogar die Schaukel unterm Baumhaus im angrenzenden Waldstück. Bei den meisten Kindern steht rasch die Schaukel nicht mehr im Mittelpunkt der Kurzgeschichten, sondern die Freunde oder Kinder mit denen sie gemeinsam schaukeln. Nur unser stilles Mädchen erinnert sich mehr an ihren Reiseweg, bis sie dort in dieser schönen bunten Schule angekommen war. Das waren viele Stationen, von denen sie gar nicht erzählen möchte oder gar ein Bild malen möchte. Die meisten Erinnerungen war so, dass sie diese lieber für sich behalten wollte. Zu weit weg waren sie von den aufgeregten Erzählungen und fantastischen Geschichten der anderen MitschülerInnen. Doch dann hatte sie doch ein Bild vor Augen. Ein Spielplatz in einer großen Stadt, Berlin genannt, ist ihr in Erinnerung geblieben. Als sie diese Schaukel grob, ohne Farbe nur mit Bleistift auf das Blatt skizzierte, keiferte der Banknachbar schon: So sieht doch keine Schaukel aus! Die Neue kann noch nicht mal eine Schaukel malen. Das stille Mädchen blieb weiter still, wusste sie doch genau, dass ihre Schaukel eine Überraschungsschaukel war. In der großen fremden Stadt war ihr diese Schaukel aufgefallen, denn sie war fast so schön, wie die Schaukel an dem starken Ast des Baumes, im Garten ihrer Großeltern. Dadurch verknüpften sich ihre vielschichtigen Erinnerungen zu einem Bild.
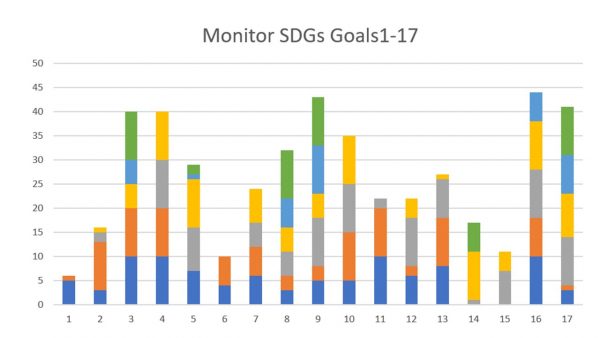
Monitor SDGs7
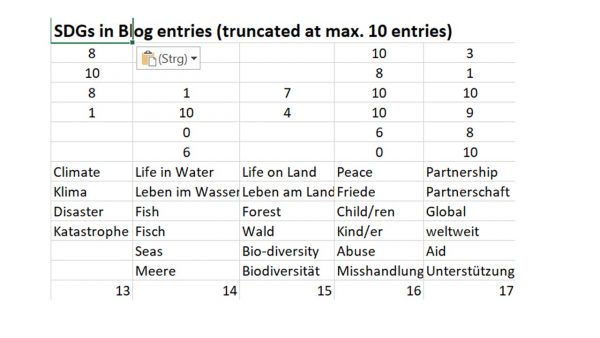
The complete monitoring of the SDGs of the UN for global development shows a surprisingly large coverage of topics. The search function is indiscriminate of some contradictions or returns the same entry twice like in sustainable industry. However, the simple check reveals frequent and less frequent entries. Entries 1 = Poverty, 6 = Water and 14 + 15 = Life on Land and in Water received less attention. The agenda for the coming weeks is set. 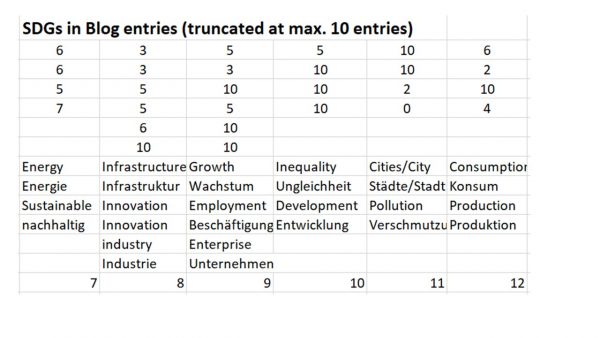
Pressure
Pressure or stress, in most humans, contributes to higher blood pressure. Sources for pressure are manifold and that is the basic problem. As it is hard to identify the major sources of high blood pressure, we often use a summary term “life style” in order to avoid shaming particular substances, (tabaco, red meat, alcohol to name just a few). Among life style elements is the daily rush to work and back home or bringing children to school and home again. Work itself is a major contributor as well. Leisure activities are not free of pressure in order to perform at a person’s best. As in many health topics, the balance does the trick. This is common knowledge beyond the Asian world as in their health philosophy of Yin and Yang. The Western world is proud to have the best and highest availability of medical treatment and hospitals for their populations, accepting some inequality in access nevertheless. For countries with less means for curative practices they have no choice and have to focus on preventive strategies (Lancet Study Link). Rural China, therefore, is a good case to study access and willingness to apply western medical type treatment of high blood pressure is too expensive and just not available in sufficient numbers. The good news is, with a preventive programme based on nurses rather than medical doctors the prevention of high blood pressure works reasonably well. Community health workers are therefore a cost-effective alternative in reducing blood pressure. Sitting is the new smoking, and driving around in a car rather than walking or cycling are health risks, even if the car or the chair is a very nice one.
Menschen
Im Bundesarchiv in Berlin sind einige Fotos zu einer Variante der Vermessung von Menschen ausgestellt. Nicht nur in den Kolonialregionen wurden Menschen zu rassenideologischen Studien vermessen. Die Kurzbeschreibung dazu und die 2 Bilder reichen, um diese scheinbar wissenschaftliche Praxis zu dokumentieren. Zurecht wird auf den Skandal mit der weiteren Verwendung dieser Daten bis 1981 hingewiesen. Es gab Kontinuitäten von Wissenschaft die heute noch erschrecken lassen. Kritischer Umgang mit jeglicher Art von Daten gehört zu dem Curriculum guter wissenschaftlicher Praxis. Diese darf nicht vor ethischen Fragen Halt machen, auch wenn das die weitere Verwendung der Information blockiert. Der Kinofilm “Der vermessene Mensch” hat dafür erneut sensibilisiert. Ethnologen und Ärzte wurden vielfach in den Dienst von Ideologien gestellt oder haben sie willentlich vorangetrieben, oftmals aus persönlichen Beweggründen. Skandale in und um Archive gehören zur Weltgeschichte, wie die geschichtliche Erkenntnis selbst. Mediale Verbreitung und Bestätigung von Klischees werden schon lange verurteilt, aber mit wenig Erfolg, wie der Deutschlandfunk Kultur selbst berichtet (Link Sendung Fazit). Die Kitas und Schulen haben ihre Hausaufgaben ebenfalls schlecht gemacht (Link). Wo ein Wille ist, ist meistens auch ein Weg, aber wenn der Wille fehlt aufgrund von Stereotypen wird sich wenig ändern.
Goals SDGs
The Strategic Development Goals (SDGs) date back to 2015 for their enactment. The goal setting is a routine procedure for the UN and its subsidiary international organisations. This makes a lot of sense, because if you do not name the problems, you are unlikely to address them in a systematic fashion. Quantifying the goals is then a much more difficult task and that then already part of the ensuing discussion about idealist, illusive or realist goals. Most diplomatic exchanges focus on this goal setting and scheduled monitoring as well as more comprehensive evaluations of goal achievement. The SDGs comprise another strategic twist. Rather than concentrating on national governments, non-governmental organisations and businesses were encourages to actively participate in the implementation of the goals. After more than 7 years the achievements of intended improvements should become visible. Well, goal setting and monitoring over the last seven years is likely to reveal failure on several of the 17 indicators. Covid-19, disruption of supply chains, wars causing recessions and high inflation are major factors to explain failure. However, knowing the reasons of failure is a substantial part of improving in the next coming years. Returning to cooperation rather than confrontation could do the trick. Even after wars cooperation to organise relief is the only way forward to come closer to achieving the SDGs.
Bold initiatives like the Marshall-Plan for Europe in the 20th century made it possible to rise from the ashes. Countries that have been in ruins at that time, now have important roles as financial contributors to support other regions. The goals remain the same, the challenges as well. 
Repair 2
Ever since the visit to the exhibition “Care, Repair, Heal” at the Martin Gropiusbau in Berlin the image of flying protheses rests with me. Repairing the human body is feasible in many fantastic ways. The inner wounds, however, are less visible and sometimes hurting even more. In recognition of the thousands of victims again in the Russian war on Ukraine’s territory and the atrocities causes by mines to injure humans, we have to assist in caring, repairing and healing. This has not changed since the Great War or the Nazi-induced mass murder and mutilations. Humanity is unable to bann such landmines despite international conventions trying to achieve this.
The strong image produced by the protheses as clouds in the sky (Kadar Attia) remind us of the lasting effects of war. Images we had associated with the mutilated soldiers and civilians of the 2nd world war, many still around us in the 60s or 70s, are coming back to Europe. Writing about the 20th century, Aurélien Bellanger described in words a similar traumatising vision of flying protheses in his story of the lonely poet and philosopher. We cannot repair history, but we can work towards reducing useless additional suffering. It is part of the absurdities of our world that technology has created masterpieces to assist us and reduce suffering, but at the same time technology is applied to create the worst suffering as well. Rather than thinking of this relationship as 2 sides of the same coin, I prefer to hope for dialectic evolution towards a better synthesis solution using enforceable international law. Yes, I still have a dream! …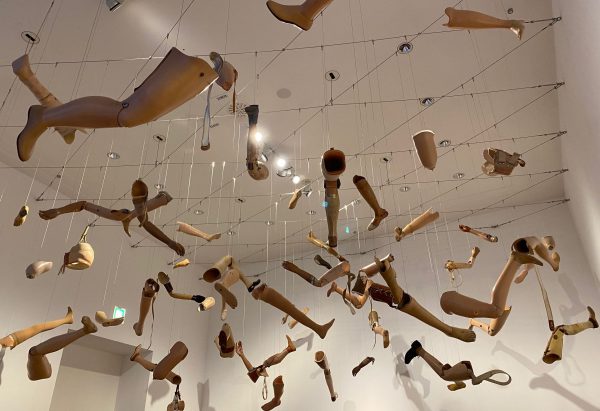 
Technology
Over the 20th century technology has pushed forward in many fields. As there were huge investments needed the public campaigns to support new technology without much further reflection of potential consequences have pulled many western societies into risky technologies. Except the Club of Rome there were very few to question the naïve beliefs that technological change will make societies rich and potentially even more equal. The recent report “Climate Inequality Report 2023: Unequal Contributions to Climate Change” has debunked both of these claims. More flying across the planet, particularly short city hopping, has allowed few persons to reap the benefits of the jet-set world, but contributed to climate change in excessive quantities. This is a fact when we compare major world regions among each other as well as within each country. It has to be the wealthy countries that have to shoulder the biggest share of the costs. It has to be the wealthy that pay higher contributions for their pollution. Society has to reign in technology more than ever before. Moreover, we still have to get the income and pollution distribution organised in a better way. It is not only an implementation challenge, but the major question of the 21st century to repair the damage largely caused throughout the 20th century. 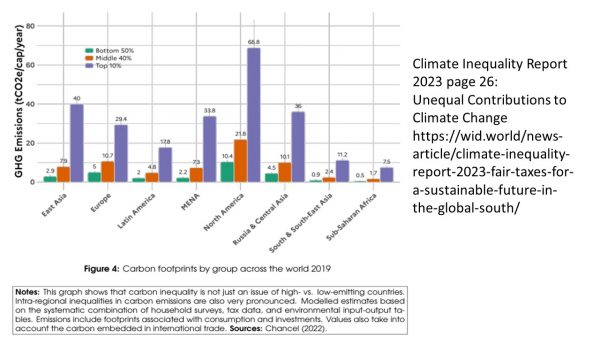
20th Century
The 20th century has told us many lessons. History does not repeat itself, but it appears that new variants of old themes keep coming back. Slowly passing the century like a movie in decades instead of episodes, we witness socio-emotional tides. The first decade, the 00s intensify the beginning of urban planning and social revolutions. The 10s show the arousal and subsequent extinction of masses of people in trenches. The 20s were described as the Carefree Twenties. In the 30s we observed the rising tides of fascist organisations followed shortly afterwards by the disastrous 40s. After the Shoah and the World War the 50s were fabulous viewed from the U.S. and Western Europe. The 60s propagated sex, drugs and rock n’ roll spreading across continents. The wild 70s became almost inescapable through the continued rise of mass media. The 80s were depicted as the colourful 80s as the 2 previous decades had set the scene for psychedelic colours. The 1990s have been coined as the gay 90s by some. Coming out as a gay person became easier and Western societies more sensitive and open to diversity. The back cover of the recent publication by Aurélien Bellanger “Le vingtième siècle” (The 20th century) speaks of the book as “roman polyphonique virtuose”. I look back on the 20th century as “polyphone” in many respects. It would be an illusion to believe we can only keep the nice sounding harmonies without the tensions or dissonances. 
1900s
1900 marks the year of the 5th world exhibition in Paris. The Eiffel tower, built for the 4th exhibition in Paris remains the iconic attraction despite the new architecture that is added to Paris as the Petit and Grand Palais as well as the 1st Metro line. Art Nouveau style adds to already impressive architecture in and around Paris. With the planning horizons of several years in advance of events, urban planning with all its facets of urban infrastructure and architecture becomes much of a defining scientific discipline for decades and for most of the time of the century. Grand urban architecture and design constitute just another form of competition between nation states. Most of them want to show off their imperialist acquisitions and, what they define as “curiosities” at the time.
Habib (2005, pp.502) singles out Arthur Schopenhauer and Friedrich Nietzsche as “heterological thinkers” who coin major thoughts in the late 19th century that shall influence the beginning of the 20th century right from the year 1900 onwards. “The world should be formed in your image by your reason, your will, and your love! And truly, it will be to your happiness you enlightened men!” (Nietzsche. Thus spoke Zarathustra 1978, p.110). In retrospect from the 21st century we shall doubt this overly positive approach to human intentions and their will to form the world according to their abstracting ideas only. Tensions between technology and society became visible and it took many decades before society became conscious that it is up to society to choose technologies they preferred.
The planning for the Brussel Expo 1910 started right after the previous Expo 1905 in Liège. Protests in Brussels accompanied already the choice of terrain for the Expo, but the governors and shareholders of the enterprise decided 1906 for a site near the “forêt de Soignes”, where trees had to be cut for access to the construction site and for future visitors under local protest. Women workers were present to exhibit the low pay of women in industries. Child labour was documented with shocking images. Around the globe labour movements started to raise attention. In the U.S. the National Women’s Trade Union League (1903) was founded as well as the National Child Labor Committee (1904). “Bloody Sunday” in St. Petersburg (1905) saw the killing of peaceful protestors in front of the Zsar’s palace, which ignited the Russian Revolution of 1905 and the creation of the Russian Parliament. Some of these issues (child labor) keep returning to our social agenda well into the 21st century.
Einstein’s publication of the theory of special relativity (1905) as well as challenges from social philosophy reflects the huge discrepancy between advancement of the sciences and the living conditions of the masses. Social theories and science advances foreshadow the violent turbulence throughout the 20th century.
(Sources: (1) Max Welch Guerra et al. (2023). European Planning History in the 20th Century: A Continent of Urban Planning. Routledge. (2) St. James Encyclopedia of Labor History Worldwide: Major Events in Labor History and Their Impact, Neil Schlager (2004). (3) Images from I. Van Hasselt(1980) Bruxelles Expo 1910: l’incendie / de brand. J Stevens. 

Construction
Construction as an industrial sector was growing strongly in the last decade. Corona crises, supply chain disruptions have slowed growth in the last two years, but the sector was still growing in terms of employment. The topic of skill and employee shortages hardened from year to year. In March 2023 the sector has more time to reflect on the somehow rapid, if not sometimes chaotic growth of the previous decade. The macro-economic scenario has changed now. Following on supply chain disruptions, we saw the high inflation rates of raw materials. The war of Russia against Ukraine caused energy prices to soar and eventually come down again. Latest worry is the increase in interest rates to finance construction projects of public, private and the business sector.
The whole sector is known for its economic role of forerunner of economic cycles, up or down. So, what are the prospects? Not so rosy, as the experts explain for example on the expert forum of the Belgian construction forum. The official from the Belgian National Bank announced a rather bleak outlook for the sector. New construction is stalling, but the renovation of buildings, especially for the purpose of reducing energy consumption is still strong and growing. Long-term reduction of emissions keeps the sector busy, thanks to the EU green deal in my opinion. The public, private and business investments in buildings all keep growth from turning negative. 2 big worries remain: (1) skill shortages and the lack of employees signalled in job openings in the sector is high and still rising; (2) the scarcity of women employed in the sector is still trailing most other sectors. Most companies have seen earnings grow over the last decade, sufficient time to build up reserves for the tougher quarters to come. Skill shortages and gender biases are harder to overcome. The Construction Forum in Brussels addressed both topics and tries to convince employers and the younger generation. Construction companies have to work on their male-dominated image was one of the take home messages Hélène de Troostemberg, the Director of Build Up pronounced.
It is not certainly not enough to have a woman as moderator of a panel and an all-female singers group accompanying the presentations. Women as architects, technicians and builders will make the sector even more attractive for the next generation of men as well. Aging of employees in the sector is another tough issue waiting for innovative solutions. Digitalisation of every step in the value chain is an additional necessary step. The leadership and trade unions in the sector are well aware of these facts. Maybe next year women engineers will pilot the robotics demonstration rather than being in charge of building a nice atmosphere with their songs. I must admit I liked the intro song to the Forum: “We build this city on rock ‘n role”, but I am less sure whether rock ‘n role will solve the gender and recruiting issue of the sector. However, naming and framing the problem(s) is already part of the solution.

Spring2023
Spring has sprung, a little bit early in 2023. On the 16th of March in the vicinity of Paris, where Caillebotte designed his impressionist garden. It is still 4 weeks until Easter. The spring flowers will hardly survive until then. Hence, we prepare for an early summer, nice because of less heating, but the vegetation is suffering in the region due to the lack of rain. Hay fever for millions of persons will start early this year as well. The damages from a fire in the nearby forest “Sénart” from 2018 have still not really disappeared. It is expensive and needs a lot of workers, equipment and knowhow to avoid the same old mistakes of planting mono-cultures of trees again. When will they ever learn, when will they ever learn.
Patient
The pandorra’s box is wide open. With ChatGPT applications the discussion has started to use it for more medical applications. As for much research having assistants to support you in routine tasks in your research is a standard procedure. Now the medical profession is also discussing the use of ChatGPT for the boring and time-consuming task to draft reports. The first study, published in the Lancet Digital Health, evaluates in a preliminary form the patient-sensitive form of communication between clinics and patients. Beyond chatbots, which organise information from calling persons, the obvious application is the use of ChatGPT to draft patient clinic letters. The example in the study is the skin cancer reporting. Lengthy reporting back to patients of lots of “hot and cold spots” might be done by AI with sufficient reliability. All depends on the correctness of the data base, the screening and samples taken. The communication between clinic and patient can then focus on other issues. ChatGPT just like neuroflash has its strength in being able to control for the “level” of the language. In addition to the choice of the output language it is possible to use, as it is required in the U.S., an average understanding level of patients. In other words, easy language rather than medical expert language is an option or even a requirement. Anecdotal evidence and the PISA for adults studies show how difficult it can be to talk the same language even if you talk the same language. There is ample scope for improvement and ChatGPT or neuroflash for German applications of AI are prime candidates to fill this gap in clinic patient communication. Considering that our mobile phones (can) do already most of the scanning of skin cancer dots and AI is used in pre-scanning the images and recommends to consult medical expertise, the next step to improve health delivery seems feasible. Whereas the statistical analysis explains 62% of “median humanness”, the score of 37% of explained variance of median correctness is a surprise as the basis of the model to explain deviation from correctness should be as low as possible. Medical data, like many other data, is not simply binary. The way forward is most likely relying on a “human-in-the-loop” approach for some time. A limited human input might reassure many patients as well.
Source: Stephen R Ali, Thomas D Dobbs, Hayley A Hutchings, Iain S Whitaker (2003). Using ChatGPT to write patient clinic letters. Lancet Digit Health 2023 https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00048-1 
20s
In retrospect from the 1930s and in prospect from the 1910s, the 1920s may well be described as “The tumultuous Twenties”. Several other summary notions are attributed to the 1920s. “Les années folles” in the French speaking world, “The Jazz years” within the U.S. or the “Wild 20s” in Germany coined the decade after the disillusion of the 1st world war. The economic and cultural revival after the period of atrocities has seen thriving city centres and comparatively little economic hardship until the Wall Street crashed on October 24th in 1929 the so-called “Black Thursday”. The party was suddenly over and a lengthy economic crisis spread globally. It was within this free spirit of the 1920s that the Fascist counter movements of the 30s started to take roots.
The 20s saw the skyscrapers soar and the credit-financed speculation was at its highest. Pierre Boudon (1991, pp. 137) characterises the architecture of the 1930s as “l’inversion des signes”. The Bauhaus of the 1920s was later forced into emigration. The film of F. Lang “Metropolis” (1927) prolonged the constructivist lines of the 1920s to a haunting vision of big cities with its daunting acceleration of economic and cultural experiences.
Walter Benjamin later referred to the method of technical reproduction as one of the major foundations for the mass movements and mass culture, which turned the relatively prosperous early and mid 20s into the disastrous 30s. Indeed, many scholars combine the 20s and 30s into one historical period as the rise and decline between the 2 world wars of the 20th century.
Certainly in terms of economic development many countries witnessed a steep rise in prosperity in the 20s followed by deep recession in the 30s. What went up in spectacular terms in the 20s, economic development, democratic participation, came down in the next decade due the rise of Fascist movements.
100 years later in the 2020s we still struggle with many of the same issues. Poverty and “Existenzminimum” were topics of the 2nd International congress of modern architecture in 1929 in Frankfurt. This reflects the lasting need to address “social issues” throughout decades, if not whole centuries of mankind. 
Fukushima 12
12 Jahre nach der Kernschmelze im Atomkraftwerk der technologiebegeisterten Japaner stellt sich immer noch die Frage nach der Entsorgung der verstrahlten Reste und Kühlwassers. Laut eines Berichts und den veröffentlichten Bildern zu dem Kernkraftwerk Fukushima staunen wir über das weite verseuchte Umfeld und die riesigen Lagerstätten für den verstrahlten Abfall. Geothermie, Wasserkraft, Windkraft und Solarenergie könnten auf der Fläche sicherlich riesige Mengen von nachhaltigem Strom produzieren. Das hatte bis vor 13 Jahren niemand denken oder aussprechen dürfen. Heute nach 18.000 Toten und vielen Folgeschäden durch Krebs und geschädigtes Erbgut wird der Unsinn weitergehen. Da sind sehr starke Interessen am Werk, denen es nicht um Menschenleben geht. Atomkraft, koste es was es wolle. Die Einleitung eines Teils des verseuchten Wassers ins Meer ist wohl bereits erfolgt. Noch mehr wird folgen müssen. Über die Fische als Teil der Nahrungskette werden Menschen dann mehr Radioaktivität aufnehmen. Das war schon so mit den Pilzen nach Tschernobyl. Fukushima bleibt ein abschreckendes Beispiel weltweit, da helfen jetzt zum 12. Jahrestag ein paar Solarzellen als Trostpflaster wenig. (Bilder aus ARD Tagesschau 11.3.2023. Auch bei uns ist es leider schmal Glück gewesen, dass nichts Schlimmeres passiert ist (Link Radiobeitrag DLF 2023-4-17)