The 20th century has told us many lessons. History does not repeat itself, but it appears that new variants of old themes keep coming back. Slowly passing the century like a movie in decades instead of episodes, we witness socio-emotional tides. The first decade, the 00s intensify the beginning of urban planning and social revolutions. The 10s show the arousal and subsequent extinction of masses of people in trenches. The 20s were described as the Carefree Twenties. In the 30s we observed the rising tides of fascist organisations followed shortly afterwards by the disastrous 40s. After the Shoah and the World War the 50s were fabulous viewed from the U.S. and Western Europe. The 60s propagated sex, drugs and rock n’ roll spreading across continents. The wild 70s became almost inescapable through the continued rise of mass media. The 80s were depicted as the colourful 80s as the 2 previous decades had set the scene for psychedelic colours. The 1990s have been coined as the gay 90s by some. Coming out as a gay person became easier and Western societies more sensitive and open to diversity. The back cover of the recent publication by Aurélien Bellanger “Le vingtième siècle” (The 20th century) speaks of the book as “roman polyphonique virtuose”. I look back on the 20th century as “polyphone” in many respects. It would be an illusion to believe we can only keep the nice sounding harmonies without the tensions or dissonances. 
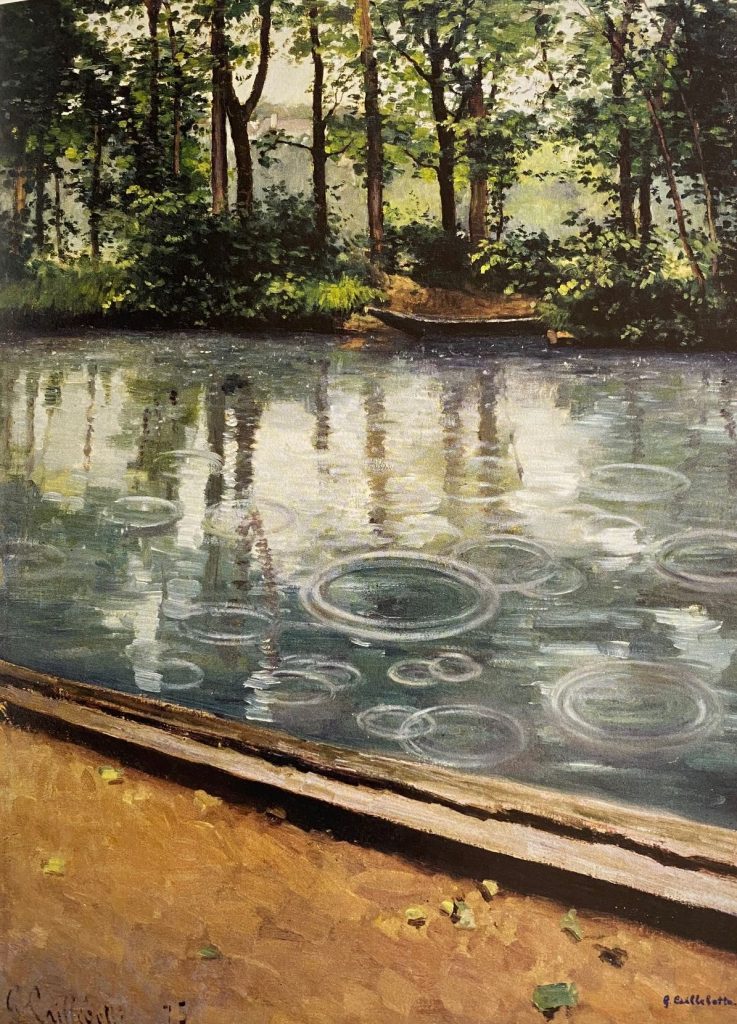
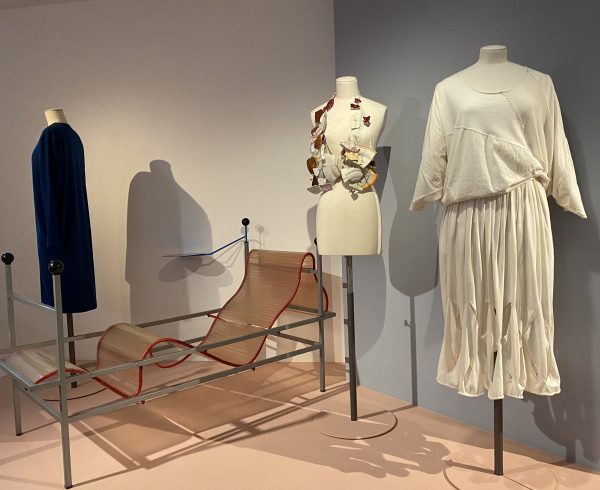
Caillebotte
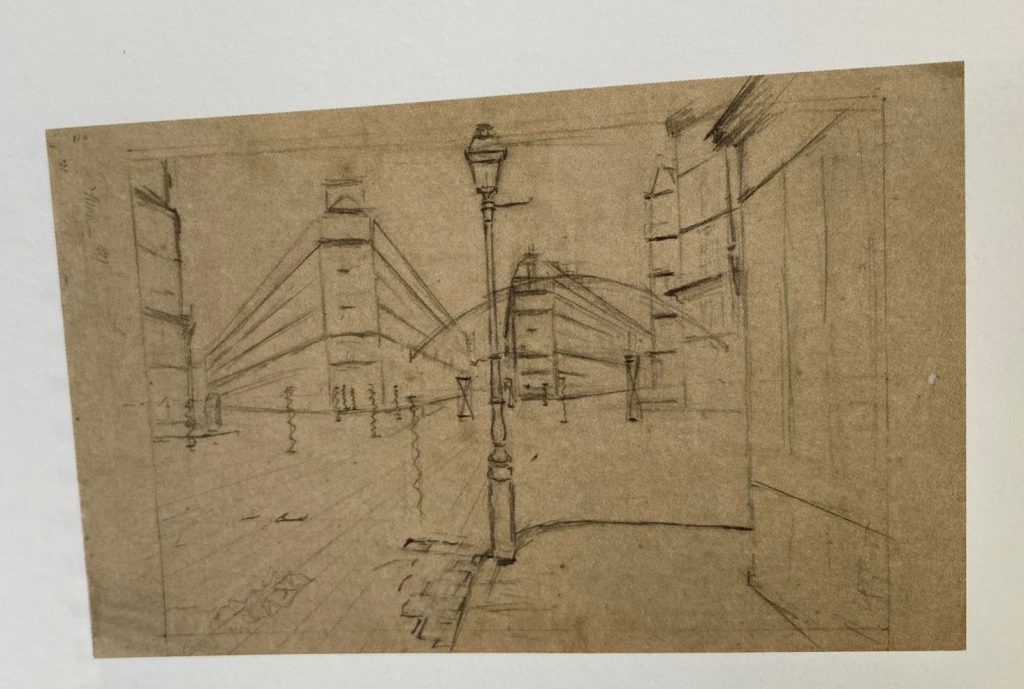
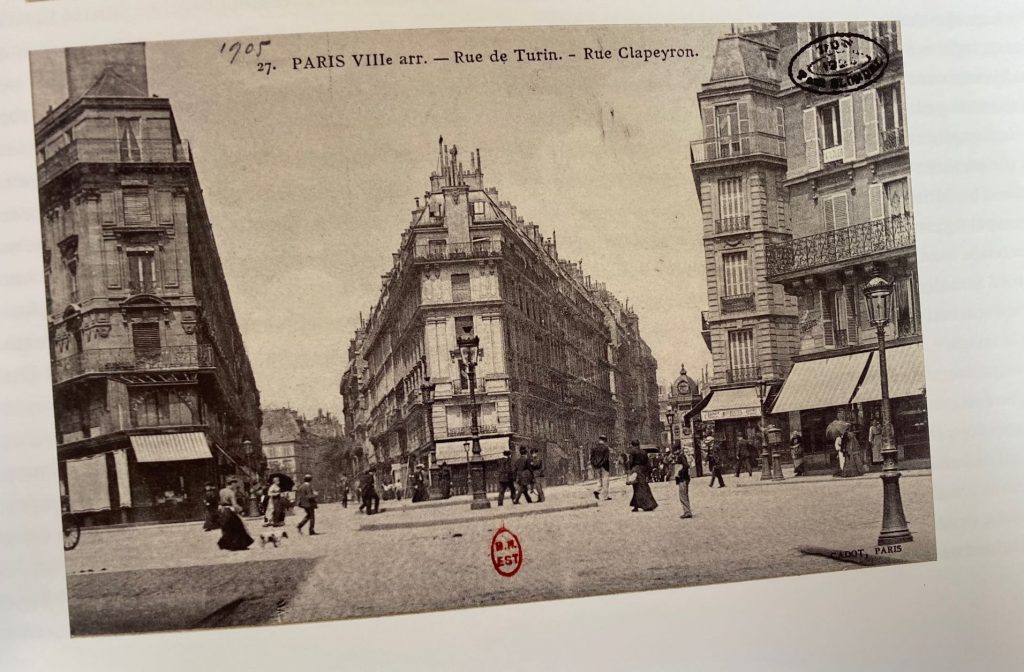
Gustave Caillebotte has done it again. Son of a great beneficiary of war efforts himself. He started with support from his father’s fortune on a painting career. Soon after his father’s death, he joined the group of “alternative artists”, later called the impressionists in France. On the 1.2.2023 the Musée d’Orsay acquired a key painting of Caillebotte for 43 Million € with the help of a donation by LVMH. Where does the hype come from? A catalogue of the exhibition of the painter “Gustave Caillebotte, The painter’s eye” from the National Gallery of Art in Washington from 2015 established Caillebotte again as a key person of the impressionist movement. Rich in diversity of motifs, the painter and supporter of the impressionists (Philantropist) has foreseen the challenge photography could bring to painting. The painter’s eye is well explained by Michael Marrinan (pp.22) in the catalogue. In fact, the spatial depth of the views of the streets of Paris is a precursor to many photographers and movies of several decades later. Caillebotte’s images of Paris depict well the mixed feelings about a daunting city size and the isolation of people captured in their own little inner circles with little communication despite or because of the noisy surroundings. Misty atmospheres allow to focus on impressions. Almost meditative walking in the city is his modern topic. Reflecting on painting as profession versus painting as artist is somehow an impressionist’s sociology of professions. Gustave Caillebotte did not have to paint for money and he was aware of social class differences as son of a factory owner. It did not spoil his artistic view with social facts, but rather tried to reveal the intrinsic beauty not only of landscapes, but ordinary working people. Other impressionists painted beautiful ballerinas, Caillebotte painted workers and sometimes more challenging parts of Paris in his early years. With climate change near Caillebotte’s home in full swing, we shall “adore” the rainy days in Paris even more. And in the countryside, too. The painter’s eye reveals a visionary view of the modern and post-modern world. 
Patient
The pandorra’s box is wide open. With ChatGPT applications the discussion has started to use it for more medical applications. As for much research having assistants to support you in routine tasks in your research is a standard procedure. Now the medical profession is also discussing the use of ChatGPT for the boring and time-consuming task to draft reports. The first study, published in the Lancet Digital Health, evaluates in a preliminary form the patient-sensitive form of communication between clinics and patients. Beyond chatbots, which organise information from calling persons, the obvious application is the use of ChatGPT to draft patient clinic letters. The example in the study is the skin cancer reporting. Lengthy reporting back to patients of lots of “hot and cold spots” might be done by AI with sufficient reliability. All depends on the correctness of the data base, the screening and samples taken. The communication between clinic and patient can then focus on other issues. ChatGPT just like neuroflash has its strength in being able to control for the “level” of the language. In addition to the choice of the output language it is possible to use, as it is required in the U.S., an average understanding level of patients. In other words, easy language rather than medical expert language is an option or even a requirement. Anecdotal evidence and the PISA for adults studies show how difficult it can be to talk the same language even if you talk the same language. There is ample scope for improvement and ChatGPT or neuroflash for German applications of AI are prime candidates to fill this gap in clinic patient communication. Considering that our mobile phones (can) do already most of the scanning of skin cancer dots and AI is used in pre-scanning the images and recommends to consult medical expertise, the next step to improve health delivery seems feasible. Whereas the statistical analysis explains 62% of “median humanness”, the score of 37% of explained variance of median correctness is a surprise as the basis of the model to explain deviation from correctness should be as low as possible. Medical data, like many other data, is not simply binary. The way forward is most likely relying on a “human-in-the-loop” approach for some time. A limited human input might reassure many patients as well.
Source: Stephen R Ali, Thomas D Dobbs, Hayley A Hutchings, Iain S Whitaker (2003). Using ChatGPT to write patient clinic letters. Lancet Digit Health 2023 https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00048-1 
20s
In retrospect from the 1930s and in prospect from the 1910s, the 1920s may well be described as “The tumultuous Twenties”. Several other summary notions are attributed to the 1920s. “Les années folles” in the French speaking world, “The Jazz years” within the U.S. or the “Wild 20s” in Germany coined the decade after the disillusion of the 1st world war. The economic and cultural revival after the period of atrocities has seen thriving city centres and comparatively little economic hardship until the Wall Street crashed on October 24th in 1929 the so-called “Black Thursday”. The party was suddenly over and a lengthy economic crisis spread globally. It was within this free spirit of the 1920s that the Fascist counter movements of the 30s started to take roots.
The 20s saw the skyscrapers soar and the credit-financed speculation was at its highest. Pierre Boudon (1991, pp. 137) characterises the architecture of the 1930s as “l’inversion des signes”. The Bauhaus of the 1920s was later forced into emigration. The film of F. Lang “Metropolis” (1927) prolonged the constructivist lines of the 1920s to a haunting vision of big cities with its daunting acceleration of economic and cultural experiences.
Walter Benjamin later referred to the method of technical reproduction as one of the major foundations for the mass movements and mass culture, which turned the relatively prosperous early and mid 20s into the disastrous 30s. Indeed, many scholars combine the 20s and 30s into one historical period as the rise and decline between the 2 world wars of the 20th century.
Certainly in terms of economic development many countries witnessed a steep rise in prosperity in the 20s followed by deep recession in the 30s. What went up in spectacular terms in the 20s, economic development, democratic participation, came down in the next decade due the rise of Fascist movements.
100 years later in the 2020s we still struggle with many of the same issues. Poverty and “Existenzminimum” were topics of the 2nd International congress of modern architecture in 1929 in Frankfurt. This reflects the lasting need to address “social issues” throughout decades, if not whole centuries of mankind. 
History
Approaching history with a personal touch is a powerful way of attracting persons into learning about others and themselves. The use of some personal belongings as part of a “history box” can be the beginning of an historical journey into the 30s, 40s, 50s or any other decade. It is an empowering tool for learners of all ages. Digging deeper into personal histories, societal constellations and societal change becomes alive through tiny little things. Communicating about these artefacts blends old and new narratives, just as much as the life courses of the “common woman or man” with the celebrities of the time. “Getting personal” is the hype in the time when social media want to define our life though endless nudging. Reflecting on origins is not what we tend to do, PhotoAPPs create retrospects for us, take it, or leave it. History is catching up on us. The fashion world reinvents history on a seasonal basis. After all, a bag is a bag is a bag. Or is it different from the one a person took to Auschwitz.
Economic Narratives
Joseph Stiglitz (2003) provided a detailed description and interpretation of the economic history of the 1990s in his book on the roaring nineties. As a member of the Clinton Administration serving as a Chairman of the Council of economic advisers, he had first hand access to the information, debates about interpretations and conclusions drawn during the period. In the preface (2003, p.XII) he provides some of the lessons this work has provided him. “Today, the challenge is to get the balance right, between the state and the market, between collective action at the local, national, and global levels, and between government and non-governmental action. As economic circumstances change, the balance has to be redrawn. Government needs to take on new activities, and shed old ones. We have entered into an era of globalization in which the countries and peoples of the world are more closely integrated than ever before. But globalization itself means that we have to change that balance: we need more collective action at the international level, and we cannot escape issues of democracy and social justice in the global arena.” The surprising approach by Stiglitz, as a winner of the Sveriges Riksbank Prize, to present no data in tables or figures demonstrates the need for telling convincing stories beyond throwing images and shuffled data at your audience. However, this is probably only feasible once you won a quasi-Nobel prize to not lose credibility among economists. Nevertheless, the issue is larger. Stiglitz manages to address the much larger audience of non-economists who construct or constructed their own “collective memory” of the legacy of the nineties as the “global 90s”.
The narrative of the 1990s grossly neglected the value of the biosphere. Asymmetric information (his shared prize winning issue) was and is still used in the market of natural resources to keep polluting the planet and push ahead with careless deforestation. The Exxon case is just one piece in the puzzle of asymmetric information and misinformation. Misguiding economic narratives play a powerful role. Maybe we need to write more about the “roaring failures” of economics and public policies across several decades in the 20th century. (red dots = forests lost on our planet A early 2000s, and there is no planet B) 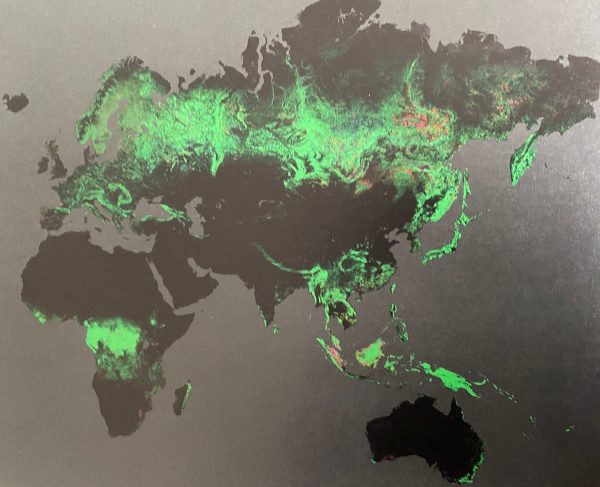
Time5
The social sciences deal with time either as part of social theory and as part of social measurement in the broadest sense. The entry of time in “The encyclopedia of social theory” (Ritzer, 2006, p.837-41) reminds us that since the age of Augustinus, believing that time is a God-given concept, we have evolved with Kant’s notion of the “Ding an sich” that time exists within our experience, but also beyond our experience of it. It is Durkheim who sees time as a social institution and raises the issue of a social construction of the concept(s) of time. In the process of civilisation, Nobert Elias leads us to think of time as an evolving social process which allows us to reach higher levels of civilisations. Despite wars and other backlashes, the basic premise remains an eventual improvement on previous situations (Time 3). The phenomenological method applied by Husserl points at the “inner time consciousness” of persons, which finds its literary expression for example in Proust’s writings.
In addition to time as the object of social theories, we find frequent implicit use of concepts of time as a component of social theories. Life courses, social change, social mobility, social integration, learning, all these concepts are conceived with “time stamps” attached to the them. Their temporality, i.e. location in time and space, durations, sequential orders and interlinkages form huge fields of research. Whole societies have attempted to define when is the “normal”, “right” or “best” time to do something for the individual or the society as a whole. Social desirability is linked to time and space and varies accordingly. The 1960s probably were a decade where the questioning of social desirability was most obvious.
Social measurement of time and the location of social phenomena in time leads us to the empirical field of studying time or the treatment of time as a basic dimension in and of social processes. “The encyclopedia of social measurement” (Kempf-Leonard, 2005) list the sampling of time as a basic entry to the topic. Frequency of sampling, (yearly, quarterly), level of sampling (person, household, region, country), repeated surveys (prospective, retrospective) of same person or rotating samples of persons have their specific strengths and weaknesses. Analytical methods rely on the concepts of the measurement of time. It seems to be a fair observation that (Clarke and Granato, 2005, p.836) the future of time series analysis lies in the linkages to theory. After all, the 2 worlds of theory and empirical measurement are linked through the concept of time, despite the tendency to abstract from it or assuming a large overlap in the concept of time (and space) referred to. Clocks seems to be ticking differently in different places.
Image: Dali Paris. R. & N. Descharnes Salvador Dali Sculptures & Objects. Eccart. Ref. 615, page 238. 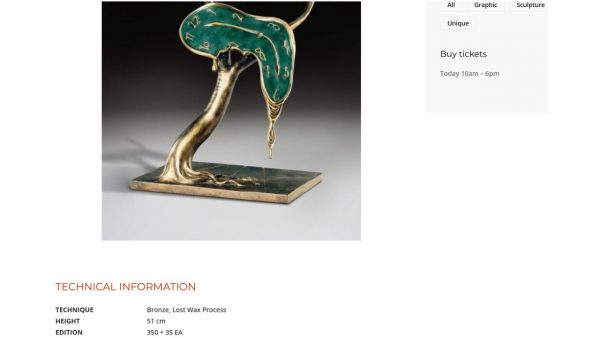
Time4
»Tempus fugit» (Latin proverb) time is flying, or time is escaping us. This is a classical quote. Students of Latin come across it in language acquisition. “Carpe diem” make the most of the day, others responded. Some even raise it to a dogma of their existence. Whereas in classical times, time was more likely to be perceived as a linear concept (v = s x t), modern concepts discuss time as “acceleration” a nonlinear concept (a = v x t = s x t²) or higher order non-linearities even (time³). Social time is embedded in such concepts of time. At some moments we perceive time as running very slowly, at other instances as running fast or accelerating. The synchronisation of time for friends, a couple, a family, lives, within a society or between societies is the big challenge. We tend to use calendars to synchronize our time acknowledging that time might be running at different speed for different persons. We have invented rituals of synchronisation like celebrating birthdays, departures at work, retirements or relative to seasons, with corresponding seasonal greetings. In between these events time fluctuates with different speed for different persons. Commonly in a kind of superficial objectivity, time is running in the same second-, minute-, hour-, day-like fashion, but considering activities or experiences, the same time span is widely different across persons. A lot of intergenerational conflicts have their origins in this non-synchronicity of time across generations. Bernard Guy (2018) reminds us of the link of time and space, as in the equations above, common in classical physics, where we could replace s with the change of coordinates of 2 GPS-signals. This space – time relationship complicates our simple reference to time. We have become used to think in time zones across the planet or within continents, however, our imagination is a bit stretched by imagining others sleeping while we are terribly busy on the other side of the globe. Global production and logistic processes have integrated the time and space framework for just-in-time delivery and optimisation of processes. As mankind we are still having a hard time to think about time and spend years “à la recherche du temps perdu” (Proust manuscript image below, BnF Paris2023).
Guy, B. (2018). Parler d’accélération, c’est aussi dire comment nous comprenons le temps. Dans : Nicole Aubert éd., @ la recherche du temps: Individus hyperconnectés, société accélérée : tensions et transformations (pp. 111-123). Toulouse: Érès. 
Know how
The construction of a knowledge graph is like an exercise in visual thinking or image thinking. A common method in design, visual thinking uses graphical tools to visualize ideas and develop the ideas on the basis of these visuals. So, let’s take our ABC of notions running from action … over nature … to zero. We place these notions in the core of the knowledge space and develop the satellite combined notions around the core. Visually this is easily reflected in the figure below. Content-wise a lot of thinking has to fill the combinations and check empirically this mind map of the knowledge space. Abundant complexity will let us search for digital tools to accomplish such tasks. On this webpage we find already a cloud of words that is empirically showing biggest the words with the most entries of the same key word. This shows us visually what this blog is mainly about. Europe and democracy appear fairly big. Additional analytical tools will clarify what are major or minor links to this pair of notions. “There’s something on my mind”, something which I might not even be aware of. Just an empirical question, should be easy to solve, eventually. 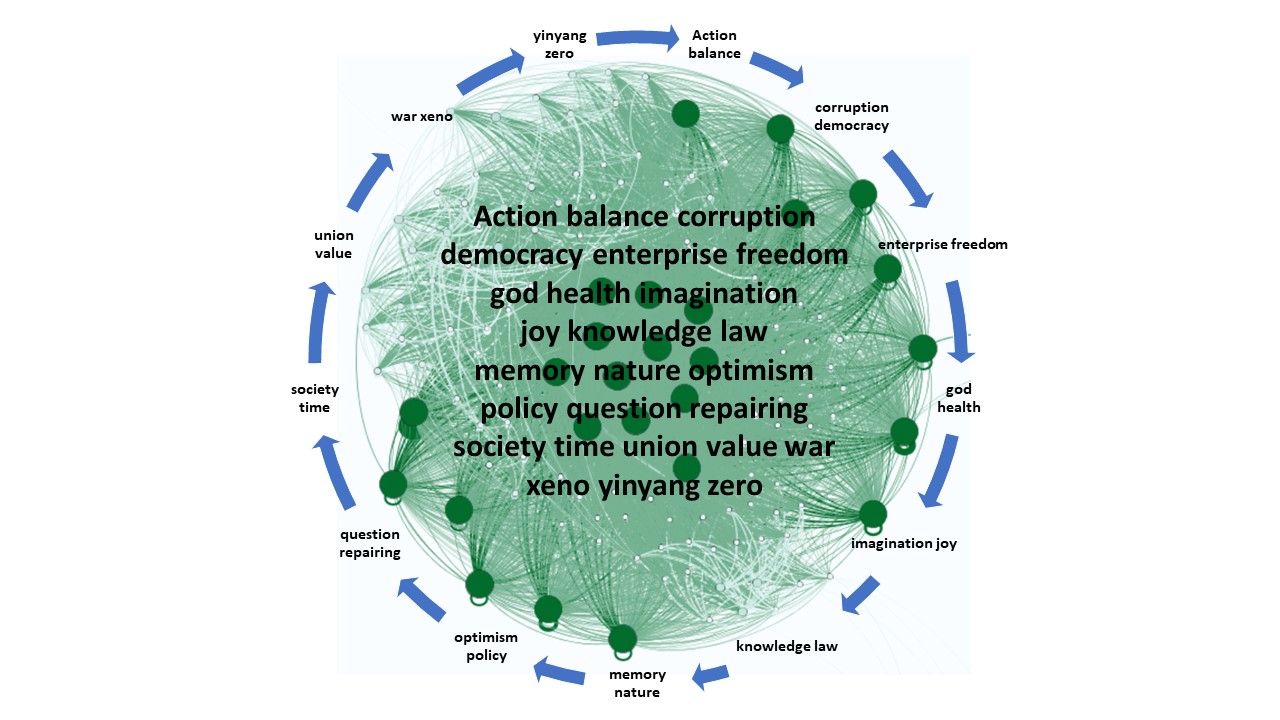
Bio-medical-sociology
In family histories we like to look on tree-like linking structures. Most frequently the choice is the descendant perspective (Top down). X, Y, Z have been the children of A and B and so on for a couple of generations. Bottom-up perspectives are equally feasible and modern patchwork families have more widespread representations of their families. Those representations were easy to do as families were lifelong bonds. Shorter family bonds, previously mainly caused by pre-mature deaths, are more common as people might have different partners and off-springs at different periods of their life course. Drawing family trees then looks more like a network structure of several families. History and literature is full of stories of how families aimed to keep their genealogy simple to the outside world. Modern days are no exception to this. Law had to adapt to these societal facts and changes thereof. Comparing decades over the last century there is, in my view, the remarkable trend to allow for more complexity in family histories, even after the 60s leading to many complete ruptures of family ties and links throughout the 70s and 80s.
With reducing fertility rates in most, not only western regions of the world, medical demography is back on the agenda. Similar to family trees, new forms of identifying promising pharmaceutical products have moved to more data-driven disease insights. Historically the local medical doctor had an overview about the likelihood of diseases following family’s medical histories over generations. Data-driven analyses, supported by data analytics and/or AI support, can learn permanently about potential and actual risks. New links of diseases are discovered this way extending the family doctor’s view of risks to watch out for in patients. Additional remedy and marketing potentials of existing drugs are also detected this way, beyond anecdotal evidence. Research published in the “Journal of biomedical semantics” by Vlietstra et al. (2020) classifies disease trajectories to construct knowledge graphs of biomolecular interactions. What previously a medical doctor in region could infer from his medical records in a less systematic way, can now be analysed on big data sets of countries, continents or even the global scale. Data is knowledge, and some already know, that this data-driven knowledge is worth a lot of money. Linking previously and seemingly unrelated facts or events, just like becoming aware of more complex family trees through DNA-analyses is the medical part of history. How we deal with this as families or societies as a whole, is the trickier part. Structural changes of societies are marked by decades-like changes, but specific events like “Fukushima”, Tschernobyl or other man-made rather than natural disasters have created new forms of contamination and the spreading of it. In addition to family trees we need broader consideration for knowledge bases to demonstrate, for example, the spread of cancer in the networked society. Additionally this evidence should have a stronger recognition in courts as prove of contamination lines. Statistical reasoning is more likely to become court-relevant. Hence, train the legal profession beyond what “statistical discrimination” is like. Causal mechanisms are manifold. Some are more likely than others. Semantic knowledge graphs remind us of the presence of reverse causality many relationships. Scientists need an optimistic state of mind to abstract from many intervening processes on health, be they tiny micro- or bigger macro-level societal effects. 
Flotow Potpourri
Über das musikalische Thema der Flotow Oper „Martha“ gibt es der heutigen Popmusik vergleichbar spätere verkürzte Versionen. Zu einiger Beliebtheit ist das Potpourri zu den Motiven von Martha gekommen. Kleineres Orchester und ein melodisches vereinfachtes Arrangement konnten für kurze Konzertabende verwandt werden. Der Komponist und Arrangeur Spasny Op. 65 hat Flotows Melodien aus „Martha“ publiziert (desgleichen von Wagner und Verdi). Die Kopie in der KBR Bruxelles ist ein kompletter Orchestersatz datiert von 1886 und 28.7.1894. Aufgeführt wurde das Potpourri im Kursaal von Ostende, wahrscheinlich für die Sommergäste in der Hafenstadt mit naheliegenden Erholungsgebieten und Küstenorten. Neben einigen schönen handschriftlichen Kopien für Violine (5 Seiten) oder Pauken (1 Seite, viele Pausentakte) ist die Partitur für die 1. Violino als „Conducteur“ (assisté?) ausgewiesen und sehr abgegriffen. Interessant sind die Anmerkungen und Einfügungen, wahrscheinlich zu wichtigen Parallelstimmen. Die komplette Streichung ab dem Larghetto am Ende der Partitur, anfänglich in Des-Dur, war vielleicht zu anspruchsvoll, für das zu erwartende Publikum. Ein F-Dur Abschlussakkord vorher klingt erholsamer, zumal im Urlaub nicht wahr. Der an einem Gag interessierte Musikfreund amüsiert sich an der Kritzelei am Anfang. Aus MARTHA; POTPOURRI ist Martha, Potpourrie geworden, was so viel heißt, wie „Martha verdorben“. Der Dirigent (Assistent? Es gibt noch ein sauberes Conducteurexemplar in der Mappe) hatte wohl einen schwierigen befristeten Sommerjob angenommen. Alternativ könnten wir das aber auch interpretieren als Kommentar zu der vereinfachten, aber verdorbenen Version der Flotowschen Martha als Originalstück. Genauer wollen wir das gar nicht wissen, oder?
Flotow Europa
In der späteren Aufführungspraxis des Werks von „Fritz“ von Flotow, wie ihn seine Mutter in MeckPom nannte, sollte es für den in Frankreich ausgebildeten Jugendlichen einige Fallstricke zu überwinden geben. Bereits seine erste Oper „Alessandro Stradella“ hatte mit Produktpiraterie zu kämpfen. Der Übersetzer Gustave Oppelt (1844 Autor zu Stradella genannt BNF), mit Erwähnung auch von Alphonse Royer, hatten die Rechte des Librettos inne (Stempel des Dépôt Légal 1859 Nr 1139). Anlässlich der Erstaufführung in Brüssel am 2-3-1859 au Théâtre Royal de la Monnaie erschien das gedruckte Libretto versehen mit einem Echtheitsstempel. Bereits 1860 gab es dann Anlass, dass Gustave Oppelt mit der Unterstützung von „Frédéric de Flotow“ für seine Übersetzungsrechte kämpfen musste und dazu eine Notiz in der „La revue et gazette musicale de Paris“ veröffentlichen mussten. Autorenrechte waren und sind keine Selbstverständlichkeit. Die Lebensgrundlagen vieler Künstler, besonders der KünstlerInnen, auch heute, bleiben meistens prekär. Flotow war bereits beteiligt an Vereinen, die die Kompensation von AutorInnenrechten vertraten. Die „Dédicace“ an die königliche Hoheit Madame la grande Duchesse Douairière Alexandrine de Mecklembourg-Schwerin, née princesse de Prusse (Link Stammbaum), versteht sich dabei wohl auch als Dank für die Berufung von Flotow als Intendant an das Theater von Schwerin, gleich neben dem schönen Schloss. Mäzene konnten wohl über Stellenbesetzungen KünstlerInnen ihr künstlerisches Arbeiten weiterhin ermöglichen. Flotow brauchte auch die Unterstützung, die ihn zu seinem Lebensende nach Darmstadt umziehen ließ.

Photo K
The self portrait is a timely topic for an exhibition of photography. As part of the European month of photography (EMOP), the PhotoBrusselsFestival offers a good overview of what photography deals with in the 21 century. The Korean cultural centre (KCC) in Brussels has a long tradition to serve as an exposition in the centre of Brussels (Sablon) and is joining this year’s photo festival. The 2023 photography festival has the “Self-Portrait” as a guiding theme. Rather than entering the debate about “portrait chosen or portrait endured” (Photographica 5,2022) the self-portrait has more degrees of freedom in it. Even if it is apparently a choice to portrait oneself, there are ample examples, where the urge to produce a self-portrait is part of a wider concern for fundamental issues.
The exhibition of 5 artists from Korea at the KCC invites us to reflect on the pervasive self-portrait practice all around us. The self-portrait is not only a tool of self-reflection, which has a long tradition in art (just think of a famous drawing by Albrecht Dürer of himself), but self-portraits are also pervasive on media and social media today. Additionally, the self-portrait is a powerful tool of thinking and imagining yourself at various stages of the life-course. For centuries it had been a social or political privilege to have your portrait taken. It still is to some extent, but only if the person taking the photograph, has a special reputation. In a market difference to the selfie, the exhibition of artists in the KCC highlights the process of self-reflection that is part of creating the portrait as well as the ensuing reflection by the spectator. In looking at the self-portrait of the photographer, we might involuntarily deal first with our own perception of the image. Danger, dreams, fantasy, sorrow, pain, self-assertion and reconstruction of the self, all these themes come to mind when confronted with the self-portraits of the 5 artists (Bae Chan-hyo, Jeong Yun-soon, Lee Jee-young, Ahn Jun, Choi Young-kwi).
KCC director Kim Jae-hwan names this collection, curated by Seok Jae-hyun, “An odyssey of images leading to self-re-flection”. In referring back to the protagonists in novels from Hermann Hesse, he points our attention to the “unique journey through images as they find themselves”. To embark on the journey visit KCC in Brussels, ask for a copy of the catalogue or start by reading the title of the exposition: “Who Am I” – it is apparently no longer a question after the journey. Is it for you? More reflection on images and photos here.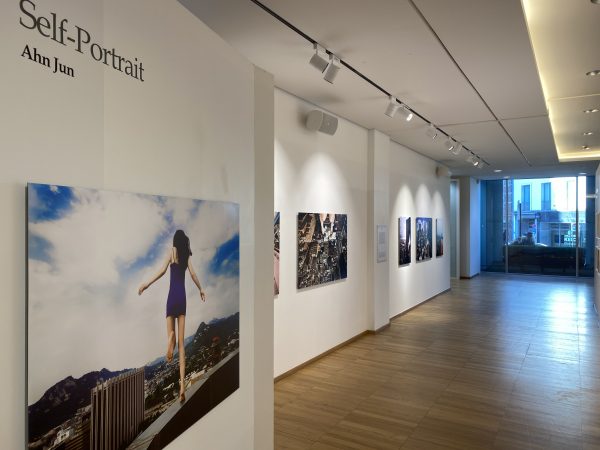 

50s
The fifties are remembered as the prosperous and booming years in the 20th century, worthy of nostalgy for some. Indeed, after the 2nd world war and its destruction the time of re-construction had come already some way, thanks to the Marshall plan of the late 1940s. Most countries had to turn huge military equipment industries into civil uses. After the Schumann Declaration, the European Coal and Steel Community was a first successful and lasting institution building in Central Europe. A mass production boom of cars, civil aircrafts, radio and the beginning of public television were landmark changes in the relationship of technology and society. The U.S. became a leading force in this evolution pushing for free trade between countries and consumerism. The deprived generations of the war period in the 40s welcomed the “fabulous fifties” (Arleen Kelin, 1978) as a dynamic and prosperous decade, despite dramatic speed to innovate new more deadly weapons. The atomic bombs were tested from superpowers and nuclear energy started to surface. Solar cells and optic fibres were also inventions of the mid-50s. Strange that we had to wait for another 70 years and multiple crises before these resource-efficient technologies achieved popular success. Integrated circuits, micro-chips, the laser, Tupperware, Coke, Lego, Mickey Mouse and global cinema came upon us during the 50s. The Sputnik effect re-opened an arms race as part of the cold war including outer space beyond airplane reach.
Families longed for and indulged in an as normal as possible family life. Unfortunately, this meant for many women, who had worked outside home during wartimes, to return to a role of housekeeping. Rock n Roll and increasing consumption of mass produced products could compensate for some of this deprivation. Higher divorce rates in the 60s and/or lack of own pensions were the dire consequences for many women. Showtime, and showing-off were the mantra of the 50s. Glamour (Magazine) rose to cult status and prepared popular culture and art. Following fashion and awareness of design spread across societies enabled by the easier access to “sewing machines” allowing more home production for the middle-class persons. The “people of plenty” (Andrew Dunar, 2006 p.167-8, referring to David Potter, 1954) were effectively sold a car culture with the automobile as an agent of change.
The atomic era was believed to continue prosperity for more decades (Expo 58 in Brussels) and a delicate, but relatively stable balance of power restricted open wars. “The End of Ideologies” during the fifties (Daniel Bell, 1960) lead to focus on Realpolitik and a race for prosperity, oblivious of the ecological consequences for many decades to come. 
60s
“Make love, not war”, is a summary slogan of all sorts of protests that have moved the sixties. With the spread of television impressive images caught attention no longer just locally, but almost across the whole world. With the inauguration of political debates on TV between Kennedy and Nixon, reaching millions of persons at once and images travelling borders faster than to translate text, spreading of new ideas and political actions was more rapid and more emotional. Commonly the 60s are described as the sex, drug and rock-n-roll period. But there is much more to it. Yes, the sex revolution got started and access to, as well as experimenting with, drugs became more widely spread. Music became a defining moment for young people from teenage years onwards. After Rock n Roll from the 50s, came the rock music and pop culture, which were able to bring together huge crowds of several hundred thousand party-goers. The Woodstock festival and hippie gatherings became a defining moment mainly for the young. Older generations still battled for affordable housing and the “Great society”, as a large-scale anti-poverty program was called.
The phenomenon of the Beatles co-defined the 60s. The Beatles captured more than just one generation with their popular songs and iconic style. Mary Quant, attributed to have designed the mini-skirt, equally co-defined a period with a visual provocation to conservative life-styles. In parallel, the sixties saw the civil rights movement grow, Black Power succeeding with peaceful actions more widespread attention, leading to the abolition of openly racist practices. The peaceful movements and happenings, however, had to face the deadly attacks on J.F. Kennedy and Martin Luther King during the 60s. The whole decade was influential in the field of education as well. Based on a new spirit of altruism and happiness combined with, but also beyond religious feelings, new forms of living together, sharing and the common good were tried out. Anti-authoritarian educational practices were influential beyond the 60s.
Books covering the 60s are manifold. In addition to Arthur Marwick’s impressive, multi-faceted volume “The sixities”, I enjoyed the book by David Burner “Making peace with the 60s”, especially his approach to burn some received wisdoms about the 60s, namely the restriction of it to those 10 years. “The withering away of philosophy”, the beginnings of postmodernism and a theory-driven or conceptual approach to the decade, amongst other topics, is the merit of Fredric Jameson (1984, p.192). “The 60s without apology” is a programmatic title well worth thinking about seriously as the editors and authors did.
Besides the ecological disasters of the 60s already, (nuclear, oil and wars), Mini Cooper cars, Lava Lamps as well as Blow or Ball Chairs, Barbies, Frisbees, Brigitte Bardot and Pippi Longstocking (Patricia Massó, 2010), all were dressed to impress. “The 60s without apology” by a group of editors nicely summarises the review of the 60s and their lasting effects on us, for better and/or worse. 2 generations later in 2023 youth is again threatening mass mobilisation in France as depicted in LeMonde 4.2.2023. It is a kind of “déjà vu experience”. 
70s
In autumn 2019 the Cosmopolitan featured a headline “Stop fighting it: the ´70s are back”. At least in fashion the 70s are still with us. Platform soles, moon boots, hot pants, all had their first appearance in the 70s. We keep seeing them in fashion shows even 50 years later. In politics, the retreat of the U.S. from Vietnam in 1972, with more than 50.000 killed soldiers from the U.S. and many more Vietnamese persons, is certainly a success of the sizable activists’ peace movement of the 60s. Willy Brandt’s kneeling in Warsaw in front of the heroes monument in honour of the Warsaw ghetto marked the beginning of a reconciliation with Eastern parts of Europe.
The oil crises 1973 and 1979 caused mass unemployment and from the beginning of the 70s “Greenpeace” started its on-site activist approach against nuclear weapons, killing of whales and dumping of toxic waste. The network of independent organisations is contemporaneous to the invention of e-mail between large so-called mainframe computers using the now common address format x@y.z. The feminist movement achieved major successes with a UN resolution to ban discrimination against women. The male dominated aggressive and excessive punk movement occurred almost in parallel. New products like the Polaroid camera for instant photos and prints, video cassette recorder, the chopper bike “Bonanza” as well as the collapsible Maclaren Buggy for children defined a lifestyle around a more mobile society. Plastic furniture, bright colours with uncommon combinations brought with it a more diverse culture. Societies exploded into different lifestyles. Some taking the new Concorde, so-called supersonic speed delta airplane between Paris and New York, whereas others walked around in “wooden clogs” as a kind of folk fashion, watched Kojak the bold police inspector, listened or sang to ABBA tunes, danced like in “Saturday night fever”. In December 1979 Pink Floyd released “The Wall” which became with 23 million sales the top seller of all 70s productions (Champ Hamish p.120). Some of these artists we can still enjoy jumping up and down on stages across the world or being honoured with a Nobel prize in literature like Bruce Springsteen.
The wild 70s are remembered for the sexual revolution, the philosophy of love and peace as well as the continued spirit of the civil rights movements (Particia Massó, 2010). The sexual revolution spurred women’s liberation just as additional exploitation by thriving borderless consumption industry. Sex sells and it sold well. The cinema and print industry cashed in on the new trends and the spreading the new trends. Social relationships became much more unstable, divorce rates increased sharply in the 70s. In response, “surviving the 70s” (DeMott, 1971) a kind of survival guide tried to give advice of how to stem the tide, largely unsuccess for some decades.
Societies continued to explore new forms of life, while some niches of conservative life styles started to shield themselves from these outrageous trends. Vasarely imitating tapestry and design invited new forms of facing your own walls. Where to go on from this liberalisation? More equal rights for all, was a claim, but it took several additional decades to achieve some of the claims. Intersectionality, viewing for example violence as an across gender, social class and ethnicity as an overall mankind issue, became a claim much later only. “All in all, it was just bricks in the wall”, a huge wall it still is. We haven’t climbed it yet. 
Time2
The concept of time has been dominated by “chronometry”. We used to take a look at our more or less reliable wrist watch for orientation in time. This is a cultural practice in all societies where such devices are readily available as consumer products. Before this time, even in the Europe, church bells or the sun played the role to locate people in time (Norbert Elias on civilization). Nowadays, even in remote areas of our planet the mobile phone has taken over to assist us to organize time. In the sociology of time, we observe multiple clocks. The personal time, social time – organized through laws, collective agreements, conventions or as behavioural features of us. So-called early birds have a specific awakening response of their cortisol level in their blood. For others this is delayed. We might conclude from this that different clocks are ticking within us. The societal challenge is to synchronize them. Starting time of schooling is another phenomenon of societal construction of life courses. Starting or ending time of a school day, week, month, year, adulthood, all are determined collectively and changed from time to time. Beyond points in time, there are durations in time to consider. Life spans are socially determined. Life expectancy varies a lot by social class and education levels. Therefore, at least in retrospect and keeping the duration constant across persons, life time clocks are ticking with different speeds for us as individual persons.
In the digital age and powerful search engines based on “web crawlers” we live more than ever in a global state of mind. Awareness of “global history of history” (Woolf, 2011) allows us to add perspectives from several parts of the world to our own version of history, historiographies and histories. Collective memories are continuously shaped and recreated. Due to easy reference to chronological time a perspective following decades has become a sort of collective mind map. This influences directly or indirectly through peer behaviour and preferences our own mindsets (Blanning, 2008 p.307). From a sociological point of view decades are at the crossroads of time, period and cohort effects, potentially mixing up all 3 effects. However, statistically speaking we might apply a spline function -´ to our otherwise / linear running of time. Thick description of decades like the 60s, 70s, 80s, is common practice in our communicative practices, preferences as well as behavioural features. A dialectic co-evolution of decades, one negating the other or one decade being a synthesis of 2 other decades are part of the critical assessment of lasting contributions to history through histories (Paul Ricoeur). 
Deconstruction
Deconstruction is a powerful tool or even method. Beyond imagineering, deconstruction in the literal sense means take to pieces. In most cases a physical object consists of several objects or parts. By deconstruction we attempt to understand the whole object as the sum of its parts. Before a new product or design is created, many scientists, engineers and artists start to deconstruct existing artefacts. Understanding how the object is assembled, for example, allows you to play around with pieces and maybe come up with an alternative way of constructing the object. The architecture of “deconstructivsm” has left us fantastic buildings. In furniture design there are also nice examples of deconstruction. Paris is a good place to study deconstruction (Explained), perhaps many still read Derrida there. It is a fruitful method beyond its engineering sense for example in law, literature or many other social science disciplines. If you are not mad yet, visit the MAD in Paris to see examples of deconstruction or construct your own deconstruction. Both have a dialectic relationship to each other anyway.
Subject/Object
The 26 notions in alphabetical order may determine a subject and/or an object in a sentence. This is just the simple grammar of a language. Add a verb and we have a full sentence subject predicate object (SPO) as they say in English. In the philosophical sense the subject-object relationship is a bit more complicated. Beyond Aristotle’s objectum and subjectum, we think of Descartes “Cogito ergo sum” as the definition of the self as subject, rather than being an object of God’s will and creation. Kant then forms the couple of object and subject in the sense of objectivity and subjectivity. Pure reasoning is the abstraction of subjectivity to achieve an interpersonal objectivity. The master of dialectic thinking, Hegel, conceives an object as objective conscience and a subject as particular subjectivity. Having defined the extreme points of the spectrum makes you think about a joinder or the synthesis. Freud adds the object as result of sexual impulse. Wittgenstein then introduces a kind of hierarchy into the S/O-relationship. Objects become ultimate elements and indescribable in content as kind of basic notions. This follows the mathematical view of objects as indirect description of a mathematical object through axioms stating the basic principles governing the object and then deduce the logical consequences. Gödel’s incompleteness theorem , however, rejects this claim. This is the basis of, for example, algorithmic testing whether deductions are true or false. Condensed mathematics has relied on this testing approach as well.
A pragmatic perspective is added by Marie Gautier (p.719 “Notions”). If we want to reach an objective, we shall need others to realize it. By way of this imagination the S/O-relationship turns into an interactive relationship. Following Habermas, we might claim that the S/O-relationship is also a part of communicative action and therefore the discourse ethics. The definition of who or what is object and/or subject needs open discourse. The arena is not only the parliament, but larger audiences or the world wide web. Beware of the Luhmann systems theory, whereby for example the definition of what is a technical object is, is left to technicians, who then ponder in their self-reflective, reflexive circles amongst themselves. Techniciens in their circles tend to neglect the prime importance of society and laws to determine technological choices. Language with its constituent elements of subject, predicate and object (SPO) is one example of a knowledge system build on axioms or negotiated conventions for grasping and exchanging about phenomena. Nice, now we play around with it.
SPO => OPS. 
Sound
Each society has its sound. Each person lives in her/his sound cloud or bubble. Cities are generally noisy places, Lots of traffic, mobility and moves leave sound bytes all over the place. Each city though has its own sound and spectrum of frequencies. Libraries, museums, places of worship, all build their special atmosphere due to specific sound design. The Singing Project by Ayumi Paul (Gropiusbau Berlin) created its own sound environment. Reminding us to consciously design our exposure to and experience of sound is welcome. John Cage started to build his very own language of music, similar to Schoenberg, from scratch. His writings Empty Mind explain his view and techniques a bit. Starting with silence and the time between sounds we recreate our own sound experience. Notation of it comes second in place. only for the potential to repeat the experience notation is useful. But it is only one form of conservation for posterity. Noise canceling is the amazing tool from sound physics which allows you to neutralize noise by adding specific frequencies to noise which cancel out each other. Design your personal sound experience beyond noise if you like. Nature recordings or familiar person voices allow you immersive experiences when and where we want. your home sound can be everywhere nowadays. 
Action Verbs
Action words are in other words called action verbs. Each complete sentence has one. Hence, they are part and parcel of the basic construction of sentences.
“The purpose of an active verb is to create a clear, concise sentence. By using an active verb, you can eliminate unnecessary words and make your writing more direct. In addition to making your writing more concise, active verbs also add punch and clarity. They can make your writing more interesting and persuasive. Additionally, active verbs can create a sense of immediacy which is often useful in persuasive writing. When it comes to writing, there is nothing more important than using strong, active verbs. Not only do they make your writing more interesting and engaging, but they also convey a sense of confidence and authority. In addition to being more descriptive, active verbs also add a sense of movement and action to your writing. Rather than simply stating that something exists, you can use active verbs to show how it exists. For example, rather than saying “there is a chair in the room,” you could say “the chair sits in the corner of the room.” This may seem like a small change, but it can make a big difference in how your writing comes across. Finally, active verbs can also help to set the tone of your writing. If you want to convey a sense of wit and humour, then using playful, lighthearted verbs is a great way to do so. On the other hand, if you’re aiming for a more serious tone, then using powerful, authoritative verbs will help you achieve that.”
After the 3rd sentence this blog entry (Link) has been written by the artificial intelligence app “Neuroflash”. They promise that it is not just copy and paste, but rather written following some instructions I gave like title, table of content, style and then selected among several choices. It makes sense to me, although it is just like many other textbook entries I have found on the web. It may well serve as an introduction. Lazy journalists, priests or lawyers in case they do little research will be replaced soon by AI, who else, who is next? Big brother drafts the brave new world for us already. 
U for Union
Union, understanding, undo, unknown, uncertainty, universe, urbanization, use, u-turn. All those u-words spark imagination. Additionally, the short forms of u as abbreviation for you, ur = your, youth and smartphone typing are creating for us abbreviations to communicate even faster and shorter via social media. Union is my favourite of this list for several reasons: (1) Marital union, passionate topic not only for family sociologists, (2) trade unions, as collective form to organize solidarity in and across societies, (3) European Union, the formidable tool to create, conserve and ensure peaceful developments in Europe. We have to prolong this list with the union jack, the united states, the united nations and …, please continue the list.
For me, in union I see a whole film running, a process proceeding, or persons uniting. Unionization, just like two persons deciding to pass more time together, has some magic in it. Match making is the modern term for it. No Union without reunion, dissolving a union might be part of the process as well, as painful it can turn out to be. Most of the times we grow throughout the process. Forming a union, in all senses of the word and of all sorts of forms, is a kind of teleological urge of us as a species. We share this with many animals but have also developed strategies and weapons to force others into union. Unfortunately, no u-word without its potential to be used in the sense of abuse. Unite to defend the union of fans of unions. (Evolution of Union of Tweets own Video 12-2022). IMG_4611
T for Time
“The times they are a changing“, end of blog entry T.
We live time forward, but we seem to understand it only backwards or in retrospect. Towards the end of each year, it is common practice to look back and review the last 12 months. Then we imagine what will the future be like. Our concept of time is past, present or future oriented. In classical physics we reflect this with a depiction of time on a linear axis. However, modern concepts of time include Einstein’s relativity theory, whereby in 2 different places time may run with different speed. Similarly, quantum physics allows that the causal relationship between 2 physical states is no longer observable in a logic that follows linear time. A particle may exit in 2 states in parallel. Hard to imagine, maybe, but demonstrations of these effects are found in textbooks for pupils already. Our grasping of the world around us is enhanced through scientific rigour.
Story-telling also plays with time frames. Analepsis and prolepsis are common techniques constructing a story, a film or any form or narrative. We tend to perceive chronological time even as boring. Our memory is also playing tricks with us on time scales. When was …? Additionally, we have multiple clocks ticking away. Time to submit a report, pay taxes, until the next medication or the psychological concept of “time until death”. Strangely enough, depending on which ticking clock we focus most, our behaviour is likely to change. Mobile time management tools have been created for centuries for us to handle all this jazz (call them a watch). They all have not changed our concept of time, only the precision to measure and cramp more activities or the same one faster into our daily life. Happier since? Test your self-efficacy, more general than time management! Try meditation to slow down the pace, use an app!? I started to clone myself with a virtual presence to experience the quantum effect of my life. Podcasts are played with 1,5x the normal speed now. Rhythm and music are the remaining traditional metrics of time. Even there, John Cage’s piece “silence” managed to abandon the time reference, partly at least. Okay, time is up, next letter, please.
S for Society
At least since the “Greek Polis” became a subject of science, the study of society has filled libraries around the world. To catch up with the social sciences view on society, we may start with foundations based on Max Weber, Niklas Luhmann, Jürgen Habermas, Ulrich Beck to then move on to my predilection with micro-level foundation of social theory based on work from James Coleman. The history of sociological ideas runs from the protestant work ethic, autopoiesis in systems theory, ethics of discourse and communicative action, risk management to “1 to 1 relationships” as pillars of theorising about society. 10.000 pages later on, you might still ask yourself the question: what practical knowledge have I gained from this. Well let’s see. Imagine you want to learn about a friend and whether s/he is really a friend. Nowadays we would start with an online-search to find profiles of a person (facebook, Instagram, linked-in, twitter, twitch, mastodon). When the first entries pop-up, we start to learn about interests, looks, friends and preferences of the person. In which social media the person is (or not) participating tells a lot. We start to build an image of the person and her/his networks and communities. Soon we start comparing the person’s world reference framework with our set of values and characteristics. Welcome to thinking about society in small, and interactions within society or between groups of society. Adding some solid knowledge about statistics and you’re ready to start the science of society.
Yet, so many still open questions. When talking about society, we have to think about the trend of individualisation and ways to keep society together despite increasing plurality of life courses. “Solitude versus loneliness” is as much a social as it is an individual based issue. Community-building with inclusion, staying-on and exclusion processes have to be studied in detail. The whole process of civilisation or the study of suicide has been a sociological topic since its inception by Emile Durkheim. Imagineering is an additional tool to speculate in a systematic way about the past and future of society. That’s where all the arts come into the picture as well. The history of art is full of perspectives on society, its splendour, the misery of individuals, communities and societies. An emotional starting point is a very valid starting point, the science of society then moves on to abstraction and generalisations as well. The challenge is, to capture audiences emotionally, with short reflections on society. 
K for Knowledge
Readers of the sociology and/or the philosophy of science or knowledge have a hard time. Each discipline is evolving at such a high speed that is terribly hard for humans to follow more than 1 or 2 fields. Perhaps the choice of Karma instead of knowledge would have made it easier here. Alternatively, in German it is easy to find many nouns starting with a capital K. Kapital, Krieg, Kritik or Käsekuchen would have been popular, I guess. Soon I shall open the comments for suggestions for additional nouns, as part of the empirical “swarm knowledge strategy” rather than the theory-driven deductive method applied in knowledge generation on my side so far.
But wait, we are already in the middle of the unsatiable quest for knowledge. On a meta-level we would deal with the multiple ways to acquire knowledge and create new knowledge. Artifical intelligence is certainly one of the hypes at the moment. New data and new combinations of data drive us forward in the expanding universe and knowledge space. We have witnessed the disappearance of the thick printed encyclopedia in most households, replaced by specilised digital dictionaries or the network society’s shared knowledge base of “wikipedia“. Knowledge is linked to the history of ideas and Peter Burke is a prominent figure to rely on as a reference in this field. 20 years after “A social history of knowledge: From Gutenberg to Diderot” he published the much acclaimed: “The Polymath. A cultural history from Leonardo da Vinci to Susan Sontag” in 2020. To synthesise across the many “monsters of knowledge” over centuries is a daunting task. I like quotes like the one from Leibniz (p.77) “the horrible heap of books that is constantly increasing” and then his own continuation: “Printing, once viewed as a solution to the problem, had become a problem itself”. The whole section is devoted to information overload. Fragmentation of knowledge into disciplines and, much worse, the manufacturing of false knowledge create new challenges to knowledge. Maybe transforming the term to “knowledges” rather than knowledge is likely to capture better the differences between artificial knowledge, created by artificial intelligence and specialised algorithms, and human based knowledge. In knowledge storage we have lost the race with computers, but in deciding what are promising combinations between different fields of knowledge, we are still a wee bit ahead of the machines. Klara tell me, where is the exit, or your synthesis of the whole lot. Meanwhile I continue to read – what? books and the like. 
G for God
God is dead, wrote Nietzsche about 140 years ago. So, is he, is she, are they? The discussion is ongoing. As science has debunked the myths surrounding birth, the jury is out as humanity is claiming freedom of choice also towards the end of life. Our cathedrals of Modernity, i.e. libraries , or Tempel of knowledge, i.e. universities, offer lots of instruction and Musea artefacts or Anschauungsmaterial to answer these existential questions. Perhaps this is just a lot of noise about “rien”, “nichts” or “Much ado about nothing“.
We might have to rethink society from scratch, starting with the definition of social backround and identity , but there are plenty of good sources to build upon, starting with basic human rights and the Schuman declaration for the construction of Europe, rising out of the ashes. Lots of hard thinking to do, Rodin thought so, too. The thinker above the “porte de l’enfer” ready for meditation in the Musée Rodin Paris 7eme arrondisement. 
F for Freedom
This choice is no surprise, or is it? Who is longing the most for freedom? People in the so-called Western world are reported to score highest in the rankings of achieved levels of freedom. However, the longing for freedom often seems the strongest in countries, or regions within a country, where elements of freedom are restricted. Then fighting for freedom becomes an intense struggle, sometimes leading to outright war or fighting back like in Ukraine. Beyond the negative freedom (free from capital punishment) there is the positive freedom to express yourself freely. Both perspectives on freedom are crucial. Being free from prosecution is often only a first step towards the goal of being free to live your way of life as you feel it. It has always been a political struggle and will remain one today as well as in future. Less consensus reigns on the topic to what extent economic freedom is a constituent part of the term freedom. Far-reaching economic inequality within societies frequently limit persons at the bottom of the distribution to fully participate in society and excercise many components of freedom like decent food, housing, health and health care. All this remains the biggest challenge for humanity for years to come. We shall need a lot more heros in the name of freedom like the famous Nobel prize winners. Fighting for freedom in a peaceful way is probably the biggest challenge for humanity also in the 21 century. 
E for Enterprise
There is a new start-up scene in development in Germany. Interesting to witness the new entrepreneurial spirit. Many of the youngsters grow out of their peer community, wanting to try new ways of working and living together. The new bottom-up or grassroots form of growing a business out of a subculture seems to be an adequate response to the growing diversity of societies and easier ways of community building through online social media. Name it “reach” today, it is similar to what you previously called having a customer base. The new element refers to a blending of cultures. Learning through being online connected to the world, yes, the whole world, allows wide-spread influences from other sub-cultures, be they American, Asian or African. The young are open-minded to new stimuli like “Ikigai” from Japan and, of course, the life histories of founders and individual biographies from entrepreneurs like the legend of Steve Jobs, Apple’s legendary founder. Imagineering has become part of the movie-influenced influencers. Short clips out of a longer story build communities. The witty comment, like at school, gets more attention than the long boring story of the preacher, teacher or the mansplainer. The experience of “flow” is all around these communities and this creates the specific magic of the start-up scene. They take each other to new levels, mutually, reinforcing their preferences and life-styles. They are well aware of the risks they are taking. “Keinhorn” German short for “not an Einhorn”, the one billion value threshold for super successful enterprises taught them crucial lessons. The “ecology of organisations” which I referred to in my courses at the now renamed “Constructor University” previously “International University Bremen”, then “Jacobs University”, (let’s see what comes next?) is an important complementary research tradition to assess the “survival” of enterprises. I still recommend this University, which I quit to start new endeavors. It carries in its several  “names” the important message:
“names” the important message:
start, fail, change, (repeat). 
D for Democracy
Stand up for Democracy. Give me a D. Yes, we are passionate for democracy. Even if we are not singing Beethoven‘s “Ode an die Freude” every day, we are well aware that we have to defend democracy at numerous places. The essay in the New Yorker by Jill Lepore from January 2020 on the manifold risks to democracy and the way forward is a great inspiration. Democracy is always a “work in progress”. It improves and in most cases rises with the challenges. However, this demands to stay alert and wither the beginnings of threats to its functioning. Beyond the external threats, internal threats to democratic values are abound. The discursive element that is highlighted in the essay remains crucial. Debating in public is key. Transparency of arguments, reasoning and values are constituent parts of democracy. Clandestine ways of corruption, bribery and threatening of violence become apparent when fractions of society retreat from the public to form insider groups. Defenders of democracy need to speak out in public, publish they work, expose and perform their arts, challenge school curricula and be active in any policy field. This is a lot to do, but we have to prevail and rise to the continuous challenges to the democratic way of life. Too many dictators and autocrats around the world would like to see democracy fail. Worse, they work actively, like in “Qatargate” in November 2022 in Brussels to spread illicit practices of corruption. We have to strengthen our “antennas” and sensors to detect such practices. Prevention is key. Tough reactions with the force of the legal system to stop the spreading is also indicated. Let’s rise to the challenge, again and again with the latest technology. 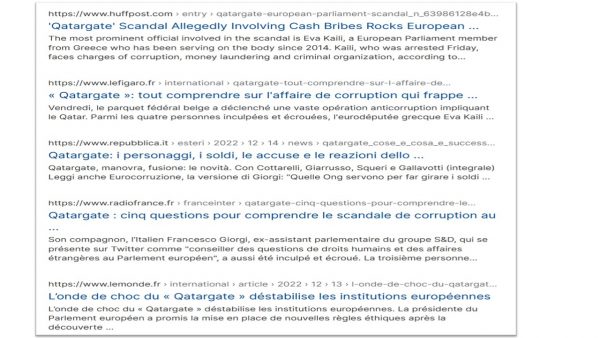
C for Corruption
After the association of C with crises of corona, climate, consumption and the church we have to come back to one of the original links: corruption. Beyond the work of describing and analysing corruption from the time of the Roman empire to the Americas of today (Link) by Thomas Strunck, the re-reading of Niccoló Machiavelli is recommended by a number of scholars (in latin here). Also, in Asia the work and writings of Niccoló have been rediscovered (Link). “non creando in veritá le cuose nove”. It needs “una ferma experienza”. As people don’t just believe in the truth of new reasons, a firm experience of them is needed. New princes cannot just pray, they have to install a new vision or belief with force (p.25) by literally forcing persons (forzare) or “fare … credere par forza” stated in Chapter 6 of THE PRINCE. If we just complement the term force by force of persuasion, or money as surrogate for both, the writing of Niccoló speaks directly to corruption in our times. History does not repeat itself. However, the history of ideas still teaches “some dogs old tricks” until they are found out by investigative journalism and an independent judiciary, which both did not exit at Niccoló’s time. (inspired by Chaudhuri, S. & Chakravarty, P. (2022) Machiavelli Then and Now: History, Politics, Literature. Cambridge University Press.)