Linking information, explanation and entertainment is the power of the world wide web. The tool used for this is the hypertext format of texts and media in general. Wittgenstein was already dissatisfied not to be able to show the steps of his thinking more explicitly. In the “Tractatus logico- philisophicus (Link to pdf-file de/engl” he uses the a cube (5.5423) to explain that we see to different facts depending on our point of departure of our vision. Try it with the logo of www.schoemann.org you should realize how our vision swops from one way of viewing the cube to another. The white corner is once in the front of the cube and appears to be in the back, when you move your vision further up. In general this leads us to be careful with the choice of our point of departure, not only for our vision. Context, some say background, is important to determine starting points. Adding the hypertext markup language to a document, like in a blog entry, allows readers (+algorithms) to see the cognitive structure surrounding a text as well. Potentially as a reader you enter into a multidimensional space with each blog entry. Any encyclopedia, glossary or index has an apparent alphabetical order to entries, but the links between the multiple entries remain hidden at first sight. With use of hypertext this has changed and each entry is turned into a 3-dimensional space, for example. Additionally, all entries have different numbers of links to other entries including dead-end entries. With the structure of links it is interesting to learn about the self-referencing just as much as about the disciplinary locus of a text, chapters, a book or a library. This helps to still see the forest despite all those trees in front of us ,or we see the geological structure of the mountain while in the middle of the forest. Happy travelling in our new knowledge space! 
Inspiration
Artists and scientists, all have their sources of inspiration. The most beautiful way of putting this is contained in a poem by Jacques Prévert. “Moi aussi, comme les peintres, j’ai mes modèles…”. The source of inspiration varies from physically present models to imagined ones. Painters and sculptors, we imagine, have their models right in front of them and build on their specific kind of observation, view and vision, seeing more or differently from others, at least since modern times. Poets and authors are believed to draw inspiration from abstraction and imaginative description and narration. Musicians tend to rely on hearing fine-tuned or creative tensions, as much as the resolution in harmonies through sequences of sound. All seem to have a sensitivity beyond the normal and a skill to find a way to transmit to others. Photographers catch representative moments or visualize artifacts and combinations of them in new ways. Scientists are not so different as we might think. Imagination of new hypotheses in established fields is part of their skill set. The transversal skill in all these processes of inspiration is the openness to cross-discipline fertilization. So-called Polymaths reached excellence in more than one field of science, “Polyartists” touch several fields of different arts. Further new innovative combinations of disciplines like they are practices in “centres of advanced studies” are a first step to brings down walls in mindsets and disciplinary ivory tower practices. It will take only a tiny little step forward to come back to the practice of royal courts. The person called “fou du roi” had an important role to play, not only in the game of chess, but in questioning and entertaining leaders. I wish universities, science centres and ministries would allow themselves more of this kind of inspiration. Inspiration is considered here as a source of questioning your own approach from another perspective. Look at your phenomenon of interest with a different model or imagination in mind. New synapses will follow. Let us welcome them to make the world around us a better or more beautiful place. Wait, is more beautiful enough already? Is this a contradiction, better versus more beautiful, or is the latter a subset of the former, or is a tautology anyway? The catalogue of the exposition “Archives des rêves” du Musée d’Orsay gives plenty of insights into images as sources of inspiration for people of all walks of life. 
Giselle
Once upon a time, not at the Opera de la Bastille, but next it, in a small theatre called Théâtre de la Bastille, the fairy tale of “Giselle…” was performed. The world-famous ballet Giselle (Karlsruhe Programmheft) is still amongst the most frequently performed magic piece of classical ballet. What is it about? In short: sex and crime. Yes, and it sells well.
Francois Gremaud tells the classic story of excitement, love, deception, death, regret, haunting and memory in a concise and witty fashion. The exemplary dancer is at the same time the narrator of the story as well as the critic and art historian accompanied by a 4 musicians strong orchestra. The educational piece with a “womanxplainer” on stage is great entertainment, full of references, why it is still okay to like the piece in spite of its fantasy-loaded content. Modern dance (Cunningham, De Keersmaeker) has decoupled or emancipated movement from music. In classical ballet, at least, you still know what comes next and this is aesthetically appealing for most people. Besides Wilfried, no he is not part of the “Wilis” (could be an interesting variant), but in the ballet there figures “Hilarion”. He is not hilarious at all. Splendid entries are from Myrtha (close to Martha, but not quite the same) and, of course, Giselle, when she leaves her tomb and turned into a “Wili”. Then there is Albrecht in a pas de deux with Giselle, swirling between earth and space. Aldi dances like mad on impulse from Myrtha, but Giselle vanishes nevertheless. End of story, or is it? Giselle is a Wili and Aldi is the wally. Maybe the story could be retold like in the film “Billy Elliot – I will dance”, which is an emancipatory tale where dance is the liberation rather than part of the dooming fate.
Francois Gremaud with the astonishing performer and choreographer Samantha van Wissen have created a version of Giselle that is musical, aesthetic, funny and critic. For those who enjoy an epic theatre version of Giselle including its “alienation effects”, referring back to Berthold Brecht, will want to read the script as well, kindly distributed as a gift after the show. 
Employment
Employment is back on top of the agenda. Not as we used to think, though. Previously unemployment had dominated societal concerns. Now it is the lack of persons seeking or available for employment. What has happened? The Covid-19 crisis has demonstrated the need of persons qualified to work in the health sector. From health care and urgency care, we are short of personnel in all these fields, everywhere.  Then we discovered the role of essential services and the need to equip crucial infrastructures like ports, transport, shops, schools and ambulances with service persons resisting despite work overload. Larger cohorts leave employment to retire, some even early due to illness or burn-out. Additionally, war is back in Europe. Military personnel is in high demand again, drawing largely from younger cohorts. The need for conventional weapons. long thought to be oblivious, is forcefully back on the agenda.
Then we discovered the role of essential services and the need to equip crucial infrastructures like ports, transport, shops, schools and ambulances with service persons resisting despite work overload. Larger cohorts leave employment to retire, some even early due to illness or burn-out. Additionally, war is back in Europe. Military personnel is in high demand again, drawing largely from younger cohorts. The need for conventional weapons. long thought to be oblivious, is forcefully back on the agenda.
Growth potentials are everywhere. However, these pre-modern facts encounter a population in the western democracies that insists on new approaches to employment. Beyond hard and soft skills, recruiters seek atypical skills, competences and trajectories. A parachute jump from an airplane, cooking and dining experiences, caring spells, periods in self-employment, all are directly or indirectly relevant for employment and teamwork. So, what is your specialty? Collecting stamps? Surely you are able to spot tiny differences in images with specific content. Fake news and fake image detection or video surveillance is in high demand, just try an application and discover the employment potential of your MAD skills. Sounds crazy? No joke. Skill needs are everywhere, just give it a start again and again. Read a serious newspaper regularly (here LeMonde 19.1.2023) for inspiration.
Invent
The nice thing about mathematics is that it asks you to invent new ways of thinking. Numbers, percentages, Venn-Diagramms, infinite series etc. have accompanied us at school. The story is far from finished. Under www.spektrum.de there is a nice introduction to the new theory of numbers, called “condensed mathematics“. Their lecture notes (pdf-file) are a tough read. My take home message simply is, the invention of new approaches to old problems, providing more general answers and/or unifying different fields are particularly rewarding. Maths is a fascinating discipline. You study abstract problems, hardly anybody else has had so far, but you are not considered strange as for example some artists at times. Imagine your new world in music, painting or the arts in more general terms or try to become a mathematician. Finding ways to communicate about your predilection and invention is the next challenge. Many scientist, inventors or artists found very few people to talk to about their new stuff. The internet and social media have changed this. Persons with interests or findings beyond the mainstream find colleagues in other parts of the world. Lighthouses from far away become visible through this. Navigation of other possible worlds turns into reality. These specialisations might turn out to be generalisations. The stretch between indepth knowledge and the polymath approach shall accompany us for a long time. Unified theories in several fields are indeed a step to be able to have an oversight about several, but not all fields. Polymaths probably start with condensed maths to move on to other fields of imagination. There is always a risk to get stuck somewhere on the road in a topological space. 
Action Verbs
Action words are in other words called action verbs. Each complete sentence has one. Hence, they are part and parcel of the basic construction of sentences.
“The purpose of an active verb is to create a clear, concise sentence. By using an active verb, you can eliminate unnecessary words and make your writing more direct. In addition to making your writing more concise, active verbs also add punch and clarity. They can make your writing more interesting and persuasive. Additionally, active verbs can create a sense of immediacy which is often useful in persuasive writing. When it comes to writing, there is nothing more important than using strong, active verbs. Not only do they make your writing more interesting and engaging, but they also convey a sense of confidence and authority. In addition to being more descriptive, active verbs also add a sense of movement and action to your writing. Rather than simply stating that something exists, you can use active verbs to show how it exists. For example, rather than saying “there is a chair in the room,” you could say “the chair sits in the corner of the room.” This may seem like a small change, but it can make a big difference in how your writing comes across. Finally, active verbs can also help to set the tone of your writing. If you want to convey a sense of wit and humour, then using playful, lighthearted verbs is a great way to do so. On the other hand, if you’re aiming for a more serious tone, then using powerful, authoritative verbs will help you achieve that.”
After the 3rd sentence this blog entry (Link) has been written by the artificial intelligence app “Neuroflash”. They promise that it is not just copy and paste, but rather written following some instructions I gave like title, table of content, style and then selected among several choices. It makes sense to me, although it is just like many other textbook entries I have found on the web. It may well serve as an introduction. Lazy journalists, priests or lawyers in case they do little research will be replaced soon by AI, who else, who is next? Big brother drafts the brave new world for us already. 
B for Balance
To reach a balance, to keep the balance or one’s balance, this highlights the process nature of balancing. Even the old tool of a balance (scale for weights) very much reflects the evening-out of the balancing process. It seems like a temporary balance most of the time. We might evolve from one level to another one. Especially imagining ourselves on a (body weight) balance in the morning and then throughout the year or years, this appears like a dynamic trajectory. The nature and/or nurture connection is evident. Beware to search for synonyms of “balance” on the internet. You get more than 3000 synonym (Link) meanings and 30 suggestions for definitions (Link) to contemplate on. I like the nice physical experience of balance and the simple (a bit nerdy) explanation of it. Economist get very excited about balance of payments and the ways to achieve equilibrium or equilibria. Balancing personal accounts can be a bit painful at times, but balancing in the arts gets our imagination going. Dancing is about balance most of the time. Playing with your own balance, the balance when 2 or more persons are in action, how not to be absorbed by such experiences. In music, the balance is a primary issue since Bach’s “wohltemperiertes Klavier” and balance and tension are the origin of much jazz. An image or photo might be balanced, certainly architecture is playing with or restricted by balancing acts. Herta Müller’s “Atemschaukel” has thrown us off balance for a while. History we study often with a concern for a balance of power. In peace and war times, the balance of power within and between countries or superpowers are a long-lasting research issue. At times when this balance is at risk or completely out-of-balance we are deeply concerned about the return of a balanced situation. Babies and children draw comfort from being balanced. Adults as well. Let’s try again (chanson). (balance22-venice -video). 
Y for YinYang
Y in maths stands for the phenomenon that is to be explained. If you are lucky, it is just one single Y. To explain this phenomenon, we usually have a multitude of different X-es and some random chance element. To complicate things a bit, we have X running over time. Example: Happiness at retirement age (66) might be explained by your earnings over years and marital unions/separations over time plus health over time and other random, not specified elements.
In my understanding of the YinYang philosophy of balancing the complementary of Yin and Yang, I probably should have thrived for a balance of earnings and health throughout my working life, to arrive at a happy retirement. Balancing not only among the X-es, but also between X and Y might even out the excitement about retirement. Additionally, this reasoning leads us to the more complicated case of multiple Y-s and multiple X-es. We can image the optimisation issue of y for 2 persons rather than just 1. Now, the maths starts to get more complicated without being complex in the mathematical sense. If you can solve such equations in statistics using different forms of random and not- so-random error terms, yr doomed for a Nobel medal in economics. What the heck, man this has to do with Yin and Yang? Beware of your work-life balance, be selective, I suppose. Breathe carefully, repair (YoYi) and read up on Chinese philosophy and maybe TCM, short for Traditional Chinese Medicine. Let’s try to re-balance in a lot of life-domains. We know our Western way of life (CO2) is not sustainable. Imagine 1 billion Europeans driving a diesel car on this planet and you have an idea about what hell might be like. An open mind to the Yin and Yang philosophy could be helpful for us, just as much as it would be for the leading Chinese politicians and their policies. Yes, Y in French is much more common than in other languages “Y avait …” is the beginning of chansons (ex 1 Aufray, ex 2 Kaas, portrait). Drawing YinYang using formulas is a bit like drawing or painting mandalas. It helps your inner balance. I am not quite there yet. 
X for Xeno
Xeno is the root of the much more commonly used words of xenophobia or xenophilia. Xenos, in its Greek original, just means guest, strangeness or coming from another place. With the awareness of coming from another place or dreaming of another place we create the link Xeno-link to migration. Everybody knows about migration experiences, be they just from one village to the neighbouring one, rural- urban migration or beyond language or legal boundaries. Interesting new perspectives on the issue are rare. To view migration from an optimism or pessimism angle is a bit like a Picasso-like view on the century-old topic. Beyond out-migration and in-migration there is the population left behind in the villages, regions, countries or nations. Optimism seems to guide the outmigrants. Realizing to become viewed and stigmatised as an immigrant might reduce optimism considerably. Pessimism might spread among the persons who do not succeed locally or to migrate in those sending regions or countries. Migration is a selection process of multiple forms. The western view of in-migration has for most parts focused on labour market related preferences. Skill shortages urge us to accept the “being somehow different” more easily. Learning to cope with this is called “intercultural competence”. In Berlin this is accessible through learning-by-doing or going to cultural events. Even there, 2 further steps are needed:
First step ahead, have more diversity everywhere, including so-called high art or centers of excellence (video xeno video22). Second step, consider it strange, if diversity is not the standard or part of day-to-day or normal life.
The performance of Mozart’s opera “Mitridate” at the Deutsche Staatsoper with performers and creators (booklet!) from all continents might be a good start to nourish xenophilia instead of xenophobia.
W for War
In Europe many people were lucky to live without the existential threat of war for a long time now. Putin has stopped this with his land-grabbing in Ukraine. We wonder why, what, when and where? War is back in our minds again. Members of the birth cohorts of the 1920s, 30s or early 40s have direct experience our traumatic memories related to war times. Some later born cohorts suffered from various forms of deprivation . Economic reconstruction or even so-called miracles may follow and can soften the traumatic experience, often by way of focusing attention on repair and new investments.
The work by James Hillman “A terrible love of war” has been a difficult read. To acknowledge that “war is normal” and our mindsets should take this into account, is hard to accept. Hillman cites Susan Sontag to state that “we cannot imagine how terrible war is – and how normal war can become”. We need a leap of imagination (p. 9) to grasp the mythical element about war which seems to be beyond the rational understanding of it. Greek tragedies told us, all along for more than 2000 years. The Romans exceled in it and German perfectionism and cold-bloodedness added the most horrible recent experience of war for millions of people. Memory and historical knowledge are important to activate recall for older and learning for younger generations. (short Video clip on war and UKR)

V for Value
Value in its singular form refers for most people to the value of things. Since Karl Marx we have been fighting about the surplus value of a worker’s work. Nowadays, we have to deal with speculation bubbles on the value of property or even basic elements of nutrition (Water, wheat, energy). Max Weber introduced us to the rigorous analysis of value judgements. In political science the plural “values” refers to basic human rights as fundamental values of humanity. Many other associations with the letter V pop up and arouse emotions: victory, video, view(s), vision, visit, voice, vote, vulnerability.
Creating lasting value seems to transform itself into part of our system of values later on. The longitudinal dimension of value is often neglected, particularly in the short-term focus of much of economic reasoning. Value over time, in addition to the distribution question, or as part of distribution over time, excites researchers of inequality and policy design for generations. Approaching the end of the alphabet increases the stakes of the “endgame”, it seems. Value for me, might not be of value for others. I hope you have found a person that values much of the same as you do yourself.
Interpersonal value, value exchange and intertemporal value are own fields of research. Since the Scottish enlightenment and Adam Smith’s work on “The theory of moral sentiments (TMS)”, reciprocity in value exchange has been an issue, well before the utilitarian turn in his own writings on “The wealth of nations”. Even Adam Smith refers to happiness and interest as a kind of value and “very laudable principles of actions” (part VII.ii.3.15 in TMS).
Children learn and experience value as natural part of growing up. Material things which you valued highly as toddler, you are ready to trash or exchange a couple of years later at much lower prices. Above which monetary value are you ready to trade in your humanitarian values? Never? History and bargaining theory is full of experiments and experiences that teach us otherwise. Corruption is the prominent example of exchanging or trading material value against immaterial values. Reading Kwame Anthony Appiah on “Experiments in ethics” is highly instructive. This bring me back to the economist joke I used to tell in lectures: You know that you’re an economist, if you ask your child, whether s/he prefers 20 Euros in cash, a trip to an adventure park later, a basket ball set or a pizza party for the next birthday. Economists do all this to find out about the value of each item, the preferences, the time frame of delayed reward or discounting of value also called the net-present value. Reading up to here is equal to the value of, maybe, an online bachelor in economics or social science. In your very own life review of learnings you then can estimate the value of your readings to you, your community or humanity. Alternatively, enjoy the joy of just living in peace with optimism. 
U for Union
Union, understanding, undo, unknown, uncertainty, universe, urbanization, use, u-turn. All those u-words spark imagination. Additionally, the short forms of u as abbreviation for you, ur = your, youth and smartphone typing are creating for us abbreviations to communicate even faster and shorter via social media. Union is my favourite of this list for several reasons: (1) Marital union, passionate topic not only for family sociologists, (2) trade unions, as collective form to organize solidarity in and across societies, (3) European Union, the formidable tool to create, conserve and ensure peaceful developments in Europe. We have to prolong this list with the union jack, the united states, the united nations and …, please continue the list.
For me, in union I see a whole film running, a process proceeding, or persons uniting. Unionization, just like two persons deciding to pass more time together, has some magic in it. Match making is the modern term for it. No Union without reunion, dissolving a union might be part of the process as well, as painful it can turn out to be. Most of the times we grow throughout the process. Forming a union, in all senses of the word and of all sorts of forms, is a kind of teleological urge of us as a species. We share this with many animals but have also developed strategies and weapons to force others into union. Unfortunately, no u-word without its potential to be used in the sense of abuse. Unite to defend the union of fans of unions. (Evolution of Union of Tweets own Video 12-2022). IMG_4611
T for Time
“The times they are a changing“, end of blog entry T.
We live time forward, but we seem to understand it only backwards or in retrospect. Towards the end of each year, it is common practice to look back and review the last 12 months. Then we imagine what will the future be like. Our concept of time is past, present or future oriented. In classical physics we reflect this with a depiction of time on a linear axis. However, modern concepts of time include Einstein’s relativity theory, whereby in 2 different places time may run with different speed. Similarly, quantum physics allows that the causal relationship between 2 physical states is no longer observable in a logic that follows linear time. A particle may exit in 2 states in parallel. Hard to imagine, maybe, but demonstrations of these effects are found in textbooks for pupils already. Our grasping of the world around us is enhanced through scientific rigour.
Story-telling also plays with time frames. Analepsis and prolepsis are common techniques constructing a story, a film or any form or narrative. We tend to perceive chronological time even as boring. Our memory is also playing tricks with us on time scales. When was …? Additionally, we have multiple clocks ticking away. Time to submit a report, pay taxes, until the next medication or the psychological concept of “time until death”. Strangely enough, depending on which ticking clock we focus most, our behaviour is likely to change. Mobile time management tools have been created for centuries for us to handle all this jazz (call them a watch). They all have not changed our concept of time, only the precision to measure and cramp more activities or the same one faster into our daily life. Happier since? Test your self-efficacy, more general than time management! Try meditation to slow down the pace, use an app!? I started to clone myself with a virtual presence to experience the quantum effect of my life. Podcasts are played with 1,5x the normal speed now. Rhythm and music are the remaining traditional metrics of time. Even there, John Cage’s piece “silence” managed to abandon the time reference, partly at least. Okay, time is up, next letter, please.
S for Society
At least since the “Greek Polis” became a subject of science, the study of society has filled libraries around the world. To catch up with the social sciences view on society, we may start with foundations based on Max Weber, Niklas Luhmann, Jürgen Habermas, Ulrich Beck to then move on to my predilection with micro-level foundation of social theory based on work from James Coleman. The history of sociological ideas runs from the protestant work ethic, autopoiesis in systems theory, ethics of discourse and communicative action, risk management to “1 to 1 relationships” as pillars of theorising about society. 10.000 pages later on, you might still ask yourself the question: what practical knowledge have I gained from this. Well let’s see. Imagine you want to learn about a friend and whether s/he is really a friend. Nowadays we would start with an online-search to find profiles of a person (facebook, Instagram, linked-in, twitter, twitch, mastodon). When the first entries pop-up, we start to learn about interests, looks, friends and preferences of the person. In which social media the person is (or not) participating tells a lot. We start to build an image of the person and her/his networks and communities. Soon we start comparing the person’s world reference framework with our set of values and characteristics. Welcome to thinking about society in small, and interactions within society or between groups of society. Adding some solid knowledge about statistics and you’re ready to start the science of society.
Yet, so many still open questions. When talking about society, we have to think about the trend of individualisation and ways to keep society together despite increasing plurality of life courses. “Solitude versus loneliness” is as much a social as it is an individual based issue. Community-building with inclusion, staying-on and exclusion processes have to be studied in detail. The whole process of civilisation or the study of suicide has been a sociological topic since its inception by Emile Durkheim. Imagineering is an additional tool to speculate in a systematic way about the past and future of society. That’s where all the arts come into the picture as well. The history of art is full of perspectives on society, its splendour, the misery of individuals, communities and societies. An emotional starting point is a very valid starting point, the science of society then moves on to abstraction and generalisations as well. The challenge is, to capture audiences emotionally, with short reflections on society. 
Q for Question
Quality and quantity or queer and query could have made valuable entries here as well. Common to all is the underlying process of questions. Questions put to oneself, to others, society or supra natural or supra national instances. Can quantity turn into quality? Is a queer perspective a new one? Is a query in a programming language the beginning of each algorithm? Questioning is a child’s “natural” approach to understanding the world. This does not stop soon after childhood, but it is occupying, if not haunting, us until the end of our life. When is this exactly happening – the end thing? Are we free to chose this? Just try to answer one of these questions and you’ll find out how one question leads to the next. We are all the same in this behaviour. However, we all find different stopping rules to the query algorithm. Religion is a fast shortcut to stop further questions. Sciences are the never, ever, ending type of questioning. Mathematics solved part of the problem. For a lot of series we are able to calculated the limit value towards which the series evolves circumventing the lack of a stopping rule. Fundamental human rights are such a far-reaching stopping rule. Just like after the French revolution, the question was, how to quickly spread the message of human rights. Didactic and paedagogics evolved in parallel. From “cogito ergo sum” to “rogatio ergo sum”. 
P for Policy
Politics and policy are key elements of democracy. Agreeing that we might strongly disagree, is a virtue of democracy, particularly in order to avoid a confrontation using force. Dialectic thinking builds on the confrontation of opposite opinions originating even of the same factual knowledge. Based on different theories the same evidence will be interpreted differently. Hence, in the field of politics, where disagreement is part and parcel of the game to build majorities, policies will change. This then leads to the belief that we need a policy in each and every subject of the alphabetical list we are about to create. There is a high risk, if you are not having a digital security policy, you will be at high risks that crucial infrastructure might not work in case of a major internal or external conflict. Candide in his small garden might run out of water to water the plants or climate change is threatening the species growing until recently. Young startups, just like ageing enterprises, persons or societies need a policy to take care of survival, not only of the fittest. As the challenges and stakes of humanity rise fast, a revival of the policy sciences is dearly needed before the pervasive skill shortages creap into the fields of social sciences as well. 
O for Optimism
Looking back at the end of every year to what happened in the last 12 months gives mixed feelings in annual repetition. Developments of nature and biodiversity are sometimes troublesome (variants of viruses like omicron). Despite wars and man-made disasters most people have a capacity to bolster with optimism. To view a glass as half-full rather than half-empty is a common description of two different perspectives on the same fact. Additionally from a longitudinal perspective it matters, whether you started from a full glass beforehand or from the empty glass. In experiments we would need to clarify the role of the starting point and evolution before the statement on the 50-50 state of affairs.
In the French enlightenment, represented by Voltaire‘s “Candide ou l’optimisme“, a critical view on the optimism of Leibniz is expressed. The optimistic claim of Leibniz, “we live in the best of possible worlds” is questioned by Candide who believes taking care of his own little garden is probably the best he can do to preserve nature and the world. These two apparently opposite perspectives and conclusions on the potential of human action we find reflected still nowadays in politics and world affairs. Do we stand up to defend human rights or do we believe the fight is futile? The optimism embedded in Ukranian culture, for example, demonstrates the power that might come out of optimism. It would even go as far as stating that optimism is a precondition for democracy, always striving for the improvement and spread of democratic procedures. Creating opportunities to more freedom to do something is the driving force besides ensuring to curb infringements on one’s freedom. Optimism is a close ally of imagination, imagination of all people living in peace. A nice sunset gives hope for a nice sunrise as well.
M for Memory
Besides the English term memory, which refers to a huge scientific literature starting with cognitive psychology, I like the French version of “mémoire”, because it is more comprehensive with additional meanings, nicely represented by Wikipedia.org. On the German Wikipedia-page you find first the reference to the children’s game memory, turning around images and memorising where the counterpart is/was (play pairs). This diversity hints towards a cultural element in memory. There is a person’s memory or mental capacity to recall and ways to remember. The latter term refers a lot more to collective memories and becomes a more debated issue. Danny Trom uses the term “split memory” in a chapter on France and the “myths of nations” (p.129-151). In David Brook’s reader on “the social animal” he states that grandmasters in chess (p.88) were long believed to have superior memory. This is actually not true as memory experiments showed, but they rather saw formations and “internal connections forming networked chunks of information”.
“Mémoire”, on the contrary, refers also to the writing of a person’s own biography. Nowadays, book shops contain whole sections of autobiographies, the most sold appears to be the one by Michele Obama recently, if I recall correctly. Among the most scandalous is the publication of the “Journal pour Anne (Pingeot) 1964-1970” by Francois Mitterand. All the autobiographical documents make explicit major parts of what might form collective memory later on.
Memory has found its way into engineering and computing. The memory effect in batteries or being “out of memory” frightens users in computing or programming. In short, I wish you the best of memories reading this page and stimulation by visiting memorials (image: Jewish Museum in Berlin 2022, Ullmann exhibition). 
L for Law
Contrary to a popular misunderstanding. Law is not boring. The history of ideas is full of exiting projects based on laws. Starting with the foundation of empiricism, i.e. the comparison of laws governing the different Greek city states pioneered by Aristotle. Considering law from the perspective of legislation gives it an actionable touch and makes it more exciting to many persons. Contrary to a static perception of law, laws can be changed and are subject to interpretation continuously by courts and judges. The fascination with law might start with the philosophers of the French enlightenment like Montesquieu. “De l’esprit des lois” – explains already the need to look behind the literal text of law. What is the spirit of law, becomes the driving question. Not only the categories of countries like republic, monarchy and despotism were argued by him, but also the separation of powers into an executive, legislative and judicial power is his original contribution. These principles govern the German “Grundgesetz” and are a common understanding of the founding states of the European Union as well as a potential breaking point.
A sociological perspective on law is formulated by Niklas Luhmann (short intro in D) and highlights the danger of laws as a self-referential system. This dominated by experts who develop the system further independent of the concerns and understandings of wider society. In order to understand this concern, it is probably useful to think of climate change as an urgent problem. Bio-diversity has for much too long not been of much relevance for legal founding principles of our constitutions. In the same vein, women judges or diversity in the legal profession is a point of concern. Majorities versus minority rights create intrinsic tensions in law, legislation, execution and interpretation. Analysing the half-life of laws is interesting, i.e. how fast do they really change or get abandoned altogether. Equality in front of the law remains a thorny issue. It is a huge issue when moving from law to justice as primary concern. The most interesting point is the view of law as a changing matter, hopefully for the better, but this is another question altogether. Reveillons-nous l’esprit des lois ! (pas seulement au Reveillon). 
K for Knowledge
Readers of the sociology and/or the philosophy of science or knowledge have a hard time. Each discipline is evolving at such a high speed that is terribly hard for humans to follow more than 1 or 2 fields. Perhaps the choice of Karma instead of knowledge would have made it easier here. Alternatively, in German it is easy to find many nouns starting with a capital K. Kapital, Krieg, Kritik or Käsekuchen would have been popular, I guess. Soon I shall open the comments for suggestions for additional nouns, as part of the empirical “swarm knowledge strategy” rather than the theory-driven deductive method applied in knowledge generation on my side so far.
But wait, we are already in the middle of the unsatiable quest for knowledge. On a meta-level we would deal with the multiple ways to acquire knowledge and create new knowledge. Artifical intelligence is certainly one of the hypes at the moment. New data and new combinations of data drive us forward in the expanding universe and knowledge space. We have witnessed the disappearance of the thick printed encyclopedia in most households, replaced by specilised digital dictionaries or the network society’s shared knowledge base of “wikipedia“. Knowledge is linked to the history of ideas and Peter Burke is a prominent figure to rely on as a reference in this field. 20 years after “A social history of knowledge: From Gutenberg to Diderot” he published the much acclaimed: “The Polymath. A cultural history from Leonardo da Vinci to Susan Sontag” in 2020. To synthesise across the many “monsters of knowledge” over centuries is a daunting task. I like quotes like the one from Leibniz (p.77) “the horrible heap of books that is constantly increasing” and then his own continuation: “Printing, once viewed as a solution to the problem, had become a problem itself”. The whole section is devoted to information overload. Fragmentation of knowledge into disciplines and, much worse, the manufacturing of false knowledge create new challenges to knowledge. Maybe transforming the term to “knowledges” rather than knowledge is likely to capture better the differences between artificial knowledge, created by artificial intelligence and specialised algorithms, and human based knowledge. In knowledge storage we have lost the race with computers, but in deciding what are promising combinations between different fields of knowledge, we are still a wee bit ahead of the machines. Klara tell me, where is the exit, or your synthesis of the whole lot. Meanwhile I continue to read – what? books and the like. 
H for Health
Health is not just a personal issue. Of course, in modern times most people are primarily concerned with their very own health. Particularly, if pain is involved, we tend to put ourselves first. Only various religions and ideologies put God or some other bigger thing, for example identity, in front of personal pain. This bigger thing is believed to decide wars, like Russia trying to anihilate Ukraine. Russia’s military agression stands against the fight for freedom, democracy and perpetuates corruption.
At the beginning of the Corona-Crisis most persons and societies still believed health and infections are only a very personal issue. Researchers with knowledge about “public health” knew already, viruses have accompanied humanity since its beginnings and maybe continue to do so even beyond our disappearance. Hence, addressing the topic of society and health from a public health perspective has become much more popular as prevention is key to fight pandemics as early as possible. However, for prevention to work you have to involve and rely on individual behaviour. As soon as we leave the personal issue of health, we have to address a whole set of other topics like patient – carer relationships, cooperation, interdisciplinarity, public expenditure, public-private partnerships, corruption or behaviour of large crowds. We have developed antidotes against most difficulties, probably the strongest one is solidarity. Social systems that address inequality of provision (e.g. between regions) or inequality in access to and quality of medical services (e.g. doctors, care or pharmaceuticals) have a strong role to play. Structural, financial and political issues play a powerful role in health. As we think more about prevention and costs we start to understand that we have to start with nutrition, mobility, mortality and our western style of life in more general terms, particularly if we think about health on a global scale. There is no planet B where we could travel to, once it has become impossible to lead a healthy life on our planet. Topics of health over the life course or ageing will need a lot more attention. Findings on the risk of suicide after onset of physical health problems (Link to study) asks for fast responses. Access to digital tools might be part of the solution like “Sympatient” as well as being part of the problem like data leakage. 
G for God
God is dead, wrote Nietzsche about 140 years ago. So, is he, is she, are they? The discussion is ongoing. As science has debunked the myths surrounding birth, the jury is out as humanity is claiming freedom of choice also towards the end of life. Our cathedrals of Modernity, i.e. libraries , or Tempel of knowledge, i.e. universities, offer lots of instruction and Musea artefacts or Anschauungsmaterial to answer these existential questions. Perhaps this is just a lot of noise about “rien”, “nichts” or “Much ado about nothing“.
We might have to rethink society from scratch, starting with the definition of social backround and identity , but there are plenty of good sources to build upon, starting with basic human rights and the Schuman declaration for the construction of Europe, rising out of the ashes. Lots of hard thinking to do, Rodin thought so, too. The thinker above the “porte de l’enfer” ready for meditation in the Musée Rodin Paris 7eme arrondisement. 
F for Freedom
This choice is no surprise, or is it? Who is longing the most for freedom? People in the so-called Western world are reported to score highest in the rankings of achieved levels of freedom. However, the longing for freedom often seems the strongest in countries, or regions within a country, where elements of freedom are restricted. Then fighting for freedom becomes an intense struggle, sometimes leading to outright war or fighting back like in Ukraine. Beyond the negative freedom (free from capital punishment) there is the positive freedom to express yourself freely. Both perspectives on freedom are crucial. Being free from prosecution is often only a first step towards the goal of being free to live your way of life as you feel it. It has always been a political struggle and will remain one today as well as in future. Less consensus reigns on the topic to what extent economic freedom is a constituent part of the term freedom. Far-reaching economic inequality within societies frequently limit persons at the bottom of the distribution to fully participate in society and excercise many components of freedom like decent food, housing, health and health care. All this remains the biggest challenge for humanity for years to come. We shall need a lot more heros in the name of freedom like the famous Nobel prize winners. Fighting for freedom in a peaceful way is probably the biggest challenge for humanity also in the 21 century. 
E for Enterprise
There is a new start-up scene in development in Germany. Interesting to witness the new entrepreneurial spirit. Many of the youngsters grow out of their peer community, wanting to try new ways of working and living together. The new bottom-up or grassroots form of growing a business out of a subculture seems to be an adequate response to the growing diversity of societies and easier ways of community building through online social media. Name it “reach” today, it is similar to what you previously called having a customer base. The new element refers to a blending of cultures. Learning through being online connected to the world, yes, the whole world, allows wide-spread influences from other sub-cultures, be they American, Asian or African. The young are open-minded to new stimuli like “Ikigai” from Japan and, of course, the life histories of founders and individual biographies from entrepreneurs like the legend of Steve Jobs, Apple’s legendary founder. Imagineering has become part of the movie-influenced influencers. Short clips out of a longer story build communities. The witty comment, like at school, gets more attention than the long boring story of the preacher, teacher or the mansplainer. The experience of “flow” is all around these communities and this creates the specific magic of the start-up scene. They take each other to new levels, mutually, reinforcing their preferences and life-styles. They are well aware of the risks they are taking. “Keinhorn” German short for “not an Einhorn”, the one billion value threshold for super successful enterprises taught them crucial lessons. The “ecology of organisations” which I referred to in my courses at the now renamed “Constructor University” previously “International University Bremen”, then “Jacobs University”, (let’s see what comes next?) is an important complementary research tradition to assess the “survival” of enterprises. I still recommend this University, which I quit to start new endeavors. It carries in its several  “names” the important message:
“names” the important message:
start, fail, change, (repeat). 
D for Democracy
Stand up for Democracy. Give me a D. Yes, we are passionate for democracy. Even if we are not singing Beethoven‘s “Ode an die Freude” every day, we are well aware that we have to defend democracy at numerous places. The essay in the New Yorker by Jill Lepore from January 2020 on the manifold risks to democracy and the way forward is a great inspiration. Democracy is always a “work in progress”. It improves and in most cases rises with the challenges. However, this demands to stay alert and wither the beginnings of threats to its functioning. Beyond the external threats, internal threats to democratic values are abound. The discursive element that is highlighted in the essay remains crucial. Debating in public is key. Transparency of arguments, reasoning and values are constituent parts of democracy. Clandestine ways of corruption, bribery and threatening of violence become apparent when fractions of society retreat from the public to form insider groups. Defenders of democracy need to speak out in public, publish they work, expose and perform their arts, challenge school curricula and be active in any policy field. This is a lot to do, but we have to prevail and rise to the continuous challenges to the democratic way of life. Too many dictators and autocrats around the world would like to see democracy fail. Worse, they work actively, like in “Qatargate” in November 2022 in Brussels to spread illicit practices of corruption. We have to strengthen our “antennas” and sensors to detect such practices. Prevention is key. Tough reactions with the force of the legal system to stop the spreading is also indicated. Let’s rise to the challenge, again and again with the latest technology. 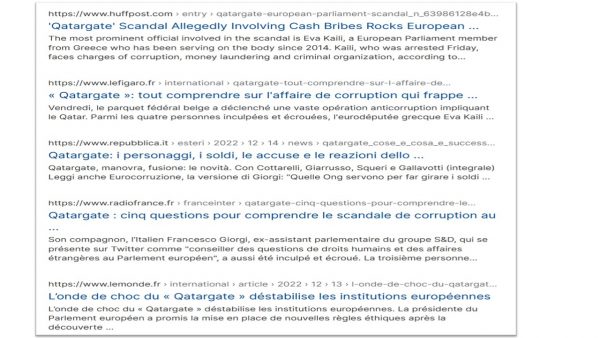
C for Corruption
After the association of C with crises of corona, climate, consumption and the church we have to come back to one of the original links: corruption. Beyond the work of describing and analysing corruption from the time of the Roman empire to the Americas of today (Link) by Thomas Strunck, the re-reading of Niccoló Machiavelli is recommended by a number of scholars (in latin here). Also, in Asia the work and writings of Niccoló have been rediscovered (Link). “non creando in veritá le cuose nove”. It needs “una ferma experienza”. As people don’t just believe in the truth of new reasons, a firm experience of them is needed. New princes cannot just pray, they have to install a new vision or belief with force (p.25) by literally forcing persons (forzare) or “fare … credere par forza” stated in Chapter 6 of THE PRINCE. If we just complement the term force by force of persuasion, or money as surrogate for both, the writing of Niccoló speaks directly to corruption in our times. History does not repeat itself. However, the history of ideas still teaches “some dogs old tricks” until they are found out by investigative journalism and an independent judiciary, which both did not exit at Niccoló’s time. (inspired by Chaudhuri, S. & Chakravarty, P. (2022) Machiavelli Then and Now: History, Politics, Literature. Cambridge University Press.) 
Human Rights
It is 10 years after the publication of a Ph.D. thesis on “Corruption: a violation of human rights and a crime under international law?” by Martine Boersma that at the top level of the European Parliament and the International Trade Union Congress the smell of corruption is investigated by police and judges. Following “Qatargate” (Radio France Link) this means that the persons accused of corruption, forming a criminal group and money laundering have changed their lobbying in return for accepting cash. Exploitation of workers and more than 100 deaths in Qatar was the result, due to the heat when building the stadiums for the Football World Cup which took place in 2022. Following the recommendations of Boersma corruption in this respect can be interpreted as these persons contributing to and being guilty of abusing their political positions to silence criticism and whistle-blowers, and the right for defendants to a fair trial for example. The advocacy to counter corruption with developing international human rights legislation and persecution in this respect is dearly needed now. “This line of reasoning transforms a corrupt act into a possible starting point for legal action, be it at the national level, …, or at the international level by submitting a complaint to a regional or global human rights monitoring body.” (Boersma, 2012 p.376) The International Criminal Court or “alternative such as the establishment of a permanent anti-corruption court, or anti-corruption commission to monitor compliance with the UN Convention Against Corruption should be kept in mind, as well as the possibility of setting up ad hoc anti-corruption tribunals” (p.380). Not much to add to this, act now, before the practice spreads.
Francesco Merloni wrote in his book (2019, p.132) on corruption with Italy in comparative perspective: “when corruption is defined in its wider meaning of maladministration, we are looking at a mass phenomenon which is “sub-criminal”, yet nonetheless with strongly negative implications for the efficiency and effectiveness of public administration and democracy in general.” The practice of excessive salaries of the Italian parliament (p.131) is mentioned in the list of case histories of corruption just like the international event of the EXPO 2015 in Milano with huge construction projects (LeMonde on Panzeri l’ex-eurodéputé). Learning from case studies is best practice in many business schools and probably beyond. Finally, attention should be drawn to prevention of corruption. Here the reading of Corruption and Anti-corruption by Larmour and Wolanin (2001, p.235) offers good advice. The micro-economics of corruption (pp. 119) states for example that “If expected penalties are sufficiently high, bribery is deterred” (p.126). Equally the real threat of a full and explicit audit of operations, promotions and financial transactions might deter corrupt activities. Most importantly the authors state, “the social networks approach to corruption allows the corruption investigator to conceptualise the operation of corrupt networks in terms of power flows and relationships rather than the attributes of actors. The question to be asked by the corruption investigator is not whether actor A is corrupt. The question should be, what is the relationship between actor A and other potentially corrupt actors in the network.” Re-reading some classics of sociology like Max Weber on bureaucracy, but also James Coleman’s foundation of social theory provide basics for understanding social interaction when things go fundamentally in the wrong direction. We might even need to use artificial intelligence to detect corruptive practices to shield and support the trade union movement. 
State of the Union
“The times they are a changing”. Currently, we witness that democracies are at multiple risks. One existential threat is, of course, war of external origin. Democracies have been perceived as often to slow to mobilize military forces sufficient to resist “Blitzkrieg”. What Nazi-Germany applied successful at the beginning took a long time and millions of dead persons to rectify. Similarly, the threat to Ukraine’s independence and liberal aspirations are threatened by Russian imperialism. The other existential threat is that of “the enemy within”. This is the conclusion by Canova (2011, p.213) when he writes on “democracy’s disappearing duties”. Whereas he has primarily in mind, that citizens need to participate more actively in the duties to democracy’s survival. These are “the duty to become informed and to vote, as well as rights and duties related to civic and/or military duties. The discussion, whether we need an army of the many or an army of specialists has shifted largely in favour of the need for specialists, simply think of cyber or drone war technology. However, the threat of the enemies from within becomes clear if we remember terrorist attacks targeted at democracies practice of free movement, free speech or art. Another centuries-old threat has come to our attention again. Corruption. The slow-motion erosion of democracies is hard to fight against as it operates not with visible tanks and weapons, but with clandestine and psychological ways of slow corrosion of organisations and institutions. Combatting corruption is even more tricky in cross-country settings like the European Union. Reference to cultural practices and exclusive or inner circles as cultural exceptionalism make it hard to introduce non-discriminatory monitoring and controlling mechanisms in democracies. Only a well-equipped security, police and judicial system can stem the risk to democracies from corruption and organized crime. It is not only a matter of state responsibility, but our democracies rely on an alert public to stand up continually for our basic values. Just singing the national and European anthem is not enough, fighting corruption is laboursome and cumbersome, particularly as corrupt circles do not refrain from using brute force and weapons (Reichsbürger, Mafia, etc.). Addressing inner and outer enemies at the same time remains high on the agenda for the surviving and thriving of democracies. The foundation ideas of the European Union were constructed by Monnet and Schuman on a sustainable democracy. Let’s not endanger this through a sluggish response on corruption.
inspired by Canova, T.A. 2011: Democracy’s disappearing duties. In: Democratic Citizenship and War. Peled, V. et al. (eds.) pp. 199-216.
Kritik der Kritik
In Berlin türmen sich als ökologisches Desaster die nicht verkauften Zeitungen auf. Darunter gerade der in neuer Aufmachung erscheinende Tagesspiegel. Mal gespannt, ob dieses teure Experiment gelingen wird. Mit sorgfältig recherchierter Kritik des kulturellen Schaffens und der etablierten Häuser rühmt sich der Tagesspiegel nicht gerade. Vielleicht ist das ein Grund, warum die beständig weniger werdenden Zeitunglesenden ebenfalls auf andere Medien umsteigen. Eine Kritik, wie die von Ulrich Amling im Tagesspiegel vom Dienstag 6.12.22 Seite B24 braucht wohl keiner. Soll er doch besser gleich Bratwurst essen auf dem benachbarten Weihnachtsmarkt. In dem neuen Format des Tagesspiegel finden sich die Kritiken eh jetzt ziemlich weit am Ende, wo der eilige Lesende meist nicht hinkommt vor dem Einschlafen. Ich würde eher davon ausgehen, dass solche Kritiken etablierte Lesende abschrecken. Für Berliner Schnauze oder Wutbürgerniveau im Kulturteil muss ich kein Geld bezahlen. Die internationale Besetzung und Ausrichtung mit Regie Satoshi Miyagi erlaubt Berlin internationale Aufmerksamkeit zu erlangen jenseits des Berliner Inner Circles von Freund- und Feindschaften. Auf der Webseite der Staatsoper lesen wir: “Ein japanisches Inszenierungsteam um den Regisseur Satoshi Miyagi taucht Mozarts »Mitridate« in ein zauberhaftes Ambiente …”. Das lese ich dann umformuliert im Tagesspiegel auch genannt Spitzel: “Unter den Linden taucht derweil ein japanisches Team um Regisseur Satoshi Miyagi “Mitridate” in Ströme von Gold”. Platter gehts nicht. Zeitung ist halt meistens 2D und nur wenigen gelingt es kulturelle Events ebenso plastisch darzustellen, wie sie eben auf der Bühne wirken. Tolle Einführung vor der Oper im Foyer übrigens. Wer Internationalität und Interkulturalität schätzt kommt hier voll auf seine Kosten.
Die Stapel Tagesspiegel als Altpapier, die zurzeit täglich entsorgt werden müssen (Foto vom 6.12.2022 18.26h am Südkreux), sind ein weiteres tägliches Ärgernis. So werden bestenfalls fake-news über eine Tageszeitung selbst produziert. Branchenkenntnis über Zeitungsmärkte beklagt das schleichende Rückbau des Mediums. “Zwar setzte sich die Erosion der Absatzzahlen fort, aber sie verstärkte sich nicht. Bei den Regionalzeitungen nahm die Zahl der Abonnements im Westen um drei Prozent auf 7,55 Millionen ab.”(BDZV Relevant 2-2021 S.25). Oft sagen Bilder mehr als Worte und dabei ist goldfarbenes Lametta in der Weihnachtszeit in der Staatsoper vielleicht doch sehr passend.
Bogenschütze
Der Bogenschütze, seine Materialien und Techniken, hat seit Jahrtausenden die Menschheit beeinflusst. Im Angriffskrieg Russlands gegen die Ukraine  sind schon mehr als 10.000 Tote auf ukrainischer Seite zu beklagen. Der stille Protest vor der russischen Botschaft in Berlin gibt davon Zeugnis. Wer hätte gedacht, dass Heckenschützen in Europa wieder wichtig im Krieg werden. Historisch ist die Bedeutung vielfach belegt und die Künste haben ihren Anteil daran. Auch im Kulturforum Berlins wird wieder aufgerüstet. Nach? der Skulptur “Bastion” vor der Stabi West, hatte die Nationalgalerie ihren dreifachen “Bogenschützen” von Henry Moore auf die Bastion gerichtet. Jetzt hat die Nationalgalerie mit dem Kauf der “Bogenschützen” von Sascha Wiederhold erneut aufgerüstet. Das farbenfrohe Werk des Malers und Bühnenbildners ist derzeit, gleich in der Eingangshalle unten zu bestaunen.
sind schon mehr als 10.000 Tote auf ukrainischer Seite zu beklagen. Der stille Protest vor der russischen Botschaft in Berlin gibt davon Zeugnis. Wer hätte gedacht, dass Heckenschützen in Europa wieder wichtig im Krieg werden. Historisch ist die Bedeutung vielfach belegt und die Künste haben ihren Anteil daran. Auch im Kulturforum Berlins wird wieder aufgerüstet. Nach? der Skulptur “Bastion” vor der Stabi West, hatte die Nationalgalerie ihren dreifachen “Bogenschützen” von Henry Moore auf die Bastion gerichtet. Jetzt hat die Nationalgalerie mit dem Kauf der “Bogenschützen” von Sascha Wiederhold erneut aufgerüstet. Das farbenfrohe Werk des Malers und Bühnenbildners ist derzeit, gleich in der Eingangshalle unten zu bestaunen.  Die “reclining figure” von Moore am UNESCO-Gebäude in Paris hat mich aufgrund des verkörperten Optimismus eher inspiriert, wenngleich das “Three Way Piece No.2 Archer” klare Stellung im Kulturforum bezieht. Die Stabi West hat mit der Renovierung der Stabi Ost und direkter Busline ihre backup Truppen deutlich verstärkt. Mit der Nachbarschaft der Scheune wird die Neue Nationalgalerie, bei erfolgter Unterstützung durch die Gemäldegalerie und der Alten Nationalgalerie auf der Museumsinsel, in einigen Jahren das Kulturforum dominieren. Das WZB hat schon mal seine Kathedrale aufgestockt und die Digitalisierung wird von der Stabi insgesamt dynamisch vorangetrieben. Schon längst ist die Kultur in einem umfassenderen Cyberwettkampf, der zunächst zwischen den Generationen ausgetragen wird. Während die Stabis von der jüngeren und mittleren Generation dominiert werden, haben die Tempel der Moderne ein Alterungsproblem. Ob es nach den Kirchen die Museen treffen wird, bleibt zu befürchten. Die hohen Studierendenzahlen verstärken die Truppen der Stabis. Letztlich hängen alle diese Institutionen am Tropf der öffentlichen Finanzen (Statistikinfo). Es wird mehr MäzenInnen brauchen und viele kleine Fördervereine, die diese wertvolle Vielfalt erhalten wollen. Retten wir, was noch zu retten ist.
Die “reclining figure” von Moore am UNESCO-Gebäude in Paris hat mich aufgrund des verkörperten Optimismus eher inspiriert, wenngleich das “Three Way Piece No.2 Archer” klare Stellung im Kulturforum bezieht. Die Stabi West hat mit der Renovierung der Stabi Ost und direkter Busline ihre backup Truppen deutlich verstärkt. Mit der Nachbarschaft der Scheune wird die Neue Nationalgalerie, bei erfolgter Unterstützung durch die Gemäldegalerie und der Alten Nationalgalerie auf der Museumsinsel, in einigen Jahren das Kulturforum dominieren. Das WZB hat schon mal seine Kathedrale aufgestockt und die Digitalisierung wird von der Stabi insgesamt dynamisch vorangetrieben. Schon längst ist die Kultur in einem umfassenderen Cyberwettkampf, der zunächst zwischen den Generationen ausgetragen wird. Während die Stabis von der jüngeren und mittleren Generation dominiert werden, haben die Tempel der Moderne ein Alterungsproblem. Ob es nach den Kirchen die Museen treffen wird, bleibt zu befürchten. Die hohen Studierendenzahlen verstärken die Truppen der Stabis. Letztlich hängen alle diese Institutionen am Tropf der öffentlichen Finanzen (Statistikinfo). Es wird mehr MäzenInnen brauchen und viele kleine Fördervereine, die diese wertvolle Vielfalt erhalten wollen. Retten wir, was noch zu retten ist.